Peptides
- 5-amino-1MQ
- Aminophylline
- Aniracetam
- ARA 290
- Argireline + Leuphasyl
- BPC-157
- Bremelanotide
- Cerebrolysin
- CJC-1295
- Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide
- Dihexa
- Elampretide (SS-31)
- Epithalon
- FG Loop Peptide (FGL)
- GHK-Cu
- Ginsenoside Rg3
- Glycyrrhetinic Acid
- Ipamorelin
- Kisspeptin
- KPV
- LL-37
- Melanotan 1
- Melanotan 2
- Mitochondrial ORF of the twelve S c (MOTS-c)
- MK-677 (IBUTAMOREN)
- Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+)
- Nicotinamide Riboside
- NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide)
- Noopept
- Pegylated Mechano Growth Factor
- Selank
- Semax
- Sermorelin
- SRT2104
- Tesamorelin
- Thymosin Alpha 1
- Thymosin Beta 4
- Tiger 17
- Valproic Acid
- Valproic acid + PTD-DBM
- Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide
- Zinc-Thymulin
- Potential Health Benefits of Retatrutide
- Key Takeaways of Retatrutide
- What is Retatrutide?
- How Retatrutide Works?
- Chemical Structure of Retatrutide
- Retatrutide Clinical Trials
- Associated Side Effects of Retatrutide
- Retatrutide Dosage
- Retatrutide Weight Loss Before and After Results
- FAQ
- Blog
- References
Table of Contents
- Potential Health Benefits of Retatrutide
- Key Takeaways of Retatrutide
- What is Retatrutide?
- How Retatrutide Works?
- Chemical Structure of Retatrutide
- Retatrutide Clinical Trials
- Associated Side Effects of Retatrutide
- Retatrutide Dosage
- Retatrutide Weight Loss Before and After Results
- FAQ
- Blog
- References
Potential Health Benefits of Retatrutide
Retatrutide is most commonly used for weight loss or diabetes. It may also improve blood pressure and quality of life.
- Aids in weight reduction [1-7]
- Improves blood glucose levels [2-7]
- Improves blood pressure [5, 7]
Key Takeaways of Retatrutide
- Retatrutide shows promise to be the best weight loss medication currently available including popular fat loss medications Semaglutide (brand names Ozempic, Wegovy, Rybelsus) and Tirzepatide (brand name Mounjaro).
- Retatrutide was created by the pharmaceutical company Eli Lilly to treat obesity and diabetes.
- Retatrutide affects certain biological pathways related to metabolism, appetite regulation, and fat storage, leading to a reduction in body weight.
- Clinical trials and studies have demonstrated that retatrutide can result in significant weight loss when used as part of a comprehensive weight management program.
- Apart from weight loss, Eli Lilly’s retatrutide may offer additional health benefits, such as improvements in insulin sensitivity, cardiovascular risk factors, and overall quality of life.
- Before starting retatrutide for treating obesity, consult with a healthcare professional. Regular monitoring, adherence to prescribed dosages, and healthy lifestyle adjustments are essential for achieving and maintaining the desired outcomes.
What is Retatrutide?
Retatrutide, a new medication created by the pharmaceutical company Eli Lilly, has a major potential for treating obesity and diabetes. Also known as GGG Tri-agonist, GLP-1/GIP/glucagon tri-agonist, or LY3437943, this injectable medication is similar to existing weight loss medications like tirzepatide and semaglutide but has increased efficacy. When combined with proper diet, regular exercise, and lifestyle modifications, retatrutide can help improve weight loss outcomes and treat comorbidities related to obesity such as diabetes or hypertension (high blood pressure).
How Retatrutide Works?
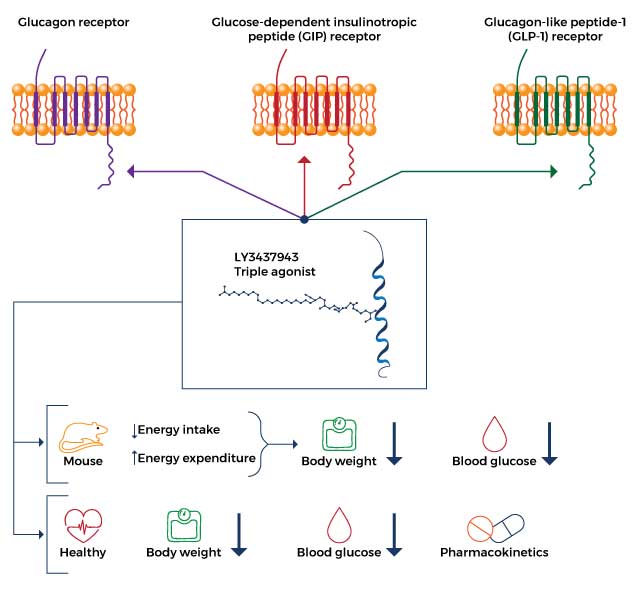
- Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (GIPR) agonist: As a GIP receptor agonist, retatrutide enhances appetite suppression and prevents fat accumulation, resulting in decreased energy intake and increased energy expenditure.
- Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonist: Retatrutide reduces body weight by improving blood sugar levels via enhanced insulin release from the pancreas and reduced release of glucagon (a hormone that increases blood sugar).
- Glucagon receptor (GR) agonist: Retatrutide decreases glucagon release to improve blood sugar levels, decrease food intake, and increase energy expenditure which ultimately results in weight loss.
Chemical Structure of Retatrutide
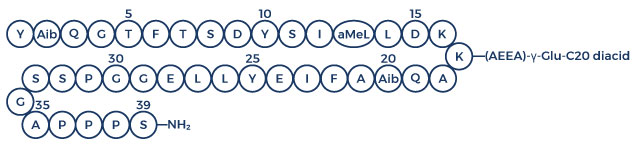
Retatrutide Clinical Trials
A. Aids in Weight Reduction

Trial results show promising insights into the potential of retatrutide for addressing obesity and various weight-related conditions:
- In a phase 2 trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine on June 26, 2023, 338 obese adults with a body mass index of 30 were enrolled. [1] The primary endpoint was the percentage change in body weight from baseline to 24 weeks. The secondary endpoint encompassed the percentage change in body weight from baseline to 48 weeks, as well as achieving weight reduction of 5% or more, 10% or more, or 15% or more. After 48 weeks, the groups who received a weekly injection of retatrutide showed varying percentages of change in mean weight reduction: -8.7% for the 1-mg group, -17.1% for the combined 4-mg group, -22.8% for the combined 8-mg group, and -24.2% for the 12-mg group (highest dose), in contrast to -2.1% observed in the placebo group. Improvements in LDL-cholesterol, triglycerides, fasting glucose, insulin levels, total cholesterol, HbA1c, as well as systolic and diastolic blood pressure were also observed.
- In adults (aged 20-70 years) with type 2 diabetes for at least 3 months, the administration of retatrutide at 3/6/9/12 mg resulted in robust reductions in body weight with an acceptable safety profile. After nine months, the participants also lost an average of 17% of their body weight. Combining glucagon receptor agonism with GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonism may be one of the reasons retatrutide showed its potent weight loss effects. [2]
- In high-fat-fed mice, twice daily administration of retatrutide for 21 days decreased body weight and nonfasting blood sugar levels and increased circulating insulin concentrations in the blood. [3]
- In mice with obesity, the administration of retatrutide (LY3437943) decreased body weight, improved blood sugar control, and increased energy expenditure. [4]
- In forty-five healthy human subjects, the three highest doses of subcutaneous (under the skin) administration of retatrutide produced a statistically significant weight loss that was maintained up to day 43. [5]
- In diet-induced obese mice, retatrutide reduced appetite and body weight by 45% via reduced fat mass, making it superior to other GIPR and GLP-1R agonists. [6]
-
In patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and obesity, subcutaneous administration of retatrutide for 12 weeks resulted in reductions in body weight of up to 8.96 kg with a safety and tolerability profile similar to other incretins (weight loss peptides). [7]
B. Improves Blood Sugar Levels
Retatrutide improves blood sugar levels through its effects on the hormones insulin and glucagon. Insulin lowers blood sugar levels while glucagon increases blood sugar levels to achieve homeostasis or balance. As a GLP-1 agonist and GR agonist, retatrutide enhances insulin release from the pancreas while reducing glucagon release. This in turn helps achieve healthy blood sugar levels.
Evidence from retatrutide trials suggests that the medication can produce beneficial effects on the blood sugar levels of people with diabetes and uncontrolled blood sugar:
- In adults (aged 20-70 years) with T2D for at least 3 months, the administration of retatrutide at 3/6/9/12 mg resulted in robust reductions in blood sugar levels with an acceptable safety profile compared with placebo treatment. [2]
- In high-fat-fed mice, twice daily administration of retatrutide for 21 days decreased nonfasting blood sugar levels by increasing circulating insulin concentrations in the blood. [3]
-
In obese mice, the administration of retatrutide improved blood sugar control and increased energy expenditure which persisted up to day 43. [4]
- In forty-five healthy human subjects, the three highest doses of subcutaneous administration of retatrutide resulted in increased mean fasting insulin and C-peptide, with maximum levels observed at 24 and 48 hours, which in turn lowered blood sugar levels. [5]
- In diet-induced obese mice, retatrutide lowered blood sugar and insulin levels, indicating improved insulin sensitivity (the body’s response to the effects of insulin). [6]
- In patients with T2D, subcutaneous administration of retatrutide for 12 weeks decreased glycated hemoglobin, also known as HbA1c and is a measure of blood sugar, with a higher safety and tolerability profile. [7]
C. Improves Blood Pressure
As a weight loss drug, retatrutide can help improve blood pressure by treating obesity. By decreasing energy intake and increasing energy expenditure, retatrutide can promote fat loss. Evidence suggests that weight loss is associated with blood pressure reduction. [8-10] This indicates that retatrutide may be beneficial in people with hypertension.
Studies support the blood pressure-lowering effects of retatrutide:
- A Phase 1 retatrutide clinical trial, which is the first human study assessing the safety and tolerability of single-ascending doses of retatrutide (LY3437943), included forty-five healthy subjects who were randomized to receive subcutaneous LY3437943 (6 rising dose levels) or placebo. [5] During the treatment period, important data such as vital signs, electrocardiogram (ECG), laboratory data, and adverse events were monitored. Fasting insulin, C-peptide, weight, and appetite were also measured. Results showed that the subjects who received retatrutide had significant weight loss, increased insulin levels, and decreased systolic blood pressure (returned to near baseline by Day 29).
- A Phase 1 proof-of-concept study assessed the safety and tolerability of several ascending doses of retatrutide in patients with T2D. [7] In this study, seventy-two diabetic patients were randomized to receive retatrutide or placebo. During the treatment, the researchers assessed vital signs, laboratory data, and adverse events. After 12 weeks, the group that received retatrutide had decreases in blood pressure with a higher safety and tolerability profile compared to the placebo group.
Associated Side Effects of Retatrutide
Retatrutide side effects are very uncommon. There have been some side effects associated with the use of this drug wherein the patient had one of the issues listed below at some point while being on retatrutide. However, these side effects weren’t confirmed to be associated with the treatment and could have been a coincidence and not related to the use of retatrutide. Despite this, it was listed as a side effect associated with retatrutide even though these associated side effects are very uncommon.
Side effects associated with retatrutide may include the following:
- Chest pain
- Depression
- Difficulty breathing
- Dizziness
- Dry mouth
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Irregular heartbeat
- Swelling in the hands and feet
With regard to safety, the most common adverse events were related to the gastrointestinal system. These side effects are mild in nature and go away on their own. As a result, the safety and tolerability profile of retatrutide aligns with other incretin-based therapies (hormones produced by the gut that help regulate blood sugar levels).
Retatrutide Dosage
Retatrutide is a new drug for obesity that is currently being developed by Eli Lilly. The initial dose of retatrutide is 0.5 mg, which is injected subcutaneously once weekly. The dose of the drug can be increased to 1 mg, 2 mg, or 4 mg after 4 weeks, depending on the patient’s response. The maximum dose is 12 mg per week.
The initial dose of retatrutide is important because it helps to minimize the risk of side effects. If the patient tolerates the initial dose well, the dose can be increased gradually. However, if the patient experiences any serious side effects, the dose of the drug should be reduced or discontinued.
Retatrutide Weight Loss Before and After Results
About Dr. George Shanlikian
Dr. George Shanlikian, renowned as the world’s best hormone therapy doctor, possesses expertise in various medical domains. These include Bio-Identical Hormone Replacement Therapy, Peptide Replacement Therapy, Anti-Aging Medicine, Regenerative Medicine, Stress Management, Nutrition Consulting, Nutritional Supplement Consulting, and Exercise Consulting.
Read more about him here: https://www.genemedics.com/dr-george-shanlikian-md-best-hormone-therapy-doctor
Read more success stories here:
Men’s Success Stories: https://www.genemedics.com/about-ghi/ghi-success-stories/mens-success-stories/
Women’s Success Stories: https://www.genemedics.com/about-ghi/ghi-success-stories/womens-success-stories/
FAQ
When will retatrutide be available?
Retatrutide is currently in phase 3 clinical trial. This trial by Eli Lilly and company will evaluate the safety and efficacy of the medication in participants with obesity and cadiovascular disease. Velocity Clinical Research is currently recruiting participants for a phase 3 clinical trial of retatrutide.
Eli Lilly is also assessing the safety and efficacy of retatrutide for chronic weight management and in patients with knee osteoarthritis and obstructive sleep apnea, as part of its TRIUMPH Phase III development program. The TRIUMPH-3 clinical trial for retatrutide began in April 2022 and enrolled adults with obesity who are at high risk for cardiovascular disease or heart disease. It focuses on treating obesity and its complications comprehensively.
What is retatrutide and how does it work?
Retatrutide belongs to the class of drugs known as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists, much like Wegovy and Ozempic. However, it distinguishes itself by acting on two additional hormones: glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), which aids in blood sugar management, and glucagon, which can help suppress appetite and increase energy expenditure.
Who manufactures retatrutide?
Retatrutide is currently in Phase III of clinical development for the treatment of obesity, with Eli Lilly and company leading the research efforts.
Is retatrutide the same as tirzepatide?
No, retatrutide and tirzepatide are not the same. They are both medications being studied for obesity and diabetes treatment, but they work in slightly different ways in the body to achieve similar goals of controlling blood sugar levels and promoting weight loss.
What is the difference between Mounjaro and retatrutide?
Mounjaro (generic name is tirzepatide) is a GLP-1 receptors agonista that mimics the effects of a hormone called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). It helps people feel full and satisfied after eating, and it also helps to lower blood sugar levels. On the other hand, retatrutide is a triple GLP-1 receptors agonist that mimics the effects of GLP-1, GIP, and https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551568/ glucagon. It is thought to be more effective than Mounjaro at helping people lose weight.
Blog
Retatrutide and Blood Sugar Control: An Effective Strategy for Managing Diabetes
Introduction:-
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It requires careful management to prevent complications and maintain a good quality of life. One emerging strategy in diabetes management is the use of retatrutide, a novel medication that has shown promise in effectively controlling blood sugar levels. In this blog post, we will explore retatrutide’s mechanism of action, its benefits for blood sugar control, and its potential as a valuable tool in managing diabetes.
Understanding Retatrutide:-
Retatrutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, a class of medications commonly used to treat type 2 diabetes. It mimics the action of GLP-1, a hormone produced in the intestines that stimulates insulin secretion and suppresses glucagon release. By activating GLP-1 receptors, retatrutide helps regulate blood sugar levels and promotes weight loss.
Benefits for Blood Sugar Control:-
One of the primary benefits of retatrutide is its ability to lower blood sugar levels. It does this by increasing insulin secretion and reducing the amount of glucose produced by the liver. This dual mechanism of action helps maintain optimal blood sugar control throughout the day, reducing the risk of hyperglycemia and its associated complications.
Retatrutide has also been shown to improve postprandial glucose levels. It slows down the emptying of the stomach, leading to a more gradual release of glucose into the bloodstream after meals. This effect helps prevent post-meal spikes in blood sugar, which are often a challenge for individuals with diabetes.
Additionally, retatrutide can aid in weight management. Many individuals with diabetes struggle with excess weight, which can worsen insulin resistance and blood sugar control. Retatrutide helps suppress appetite and promotes feelings of fullness, leading to reduced food intake and subsequent weight loss. By addressing both blood sugar control and weight management, retatrutide offers a comprehensive approach to diabetes management.
Potential as a Valuable Tool:-
The effectiveness of retatrutide has been demonstrated in various clinical trials. Studies have shown that retatrutide, when used as an add-on therapy to existing diabetes medications, significantly reduces HbA1c levels—a key marker of long-term blood sugar control. Furthermore, it has shown favorable effects on cardiovascular health, including a reduction in the risk of heart attack, stroke, and cardiovascular death.
Retatrutide’s once-weekly dosing regimen is another advantage, providing convenience and ease of use for patients. This reduces the burden of daily medication management and enhances adherence to the treatment plan.
However, it’s important to note that retatrutide, like any medication, may have side effects. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, but they are generally well-tolerated and tend to improve over time.
Conclusion:-
Retatrutide represents a promising strategy for managing diabetes by effectively controlling blood sugar levels and aiding in weight management. Its GLP-1 receptor agonist action provides multiple benefits, including lower HbA1c levels and improved cardiovascular outcomes. The convenience of a once-weekly dosing regimen adds to its appeal for individuals with diabetes. As with any medication, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if retatrutide is suitable for an individual’s specific needs. With ongoing research and advancements in diabetes management, retatrutide offers hope for better outcomes and an improved quality of life for those living with diabetes.

Improving Your Metabolic Health with Retatrutide: An In-Depth Analysis
Introduction :
Metabolic health plays a crucial role in overall well-being, and its optimization is especially important for individuals with conditions like diabetes and obesity. Retatrutide, a novel medication, has garnered attention for its potential in improving metabolic health. In this blog post, we will delve into the mechanisms of action of retatrutide, explore its impact on various metabolic parameters, and discuss its potential as a valuable tool for enhancing metabolic health.
Understanding Retatrutide :
Retatrutide belongs to a class of medications called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, which are commonly prescribed for the management of type 2 diabetes. It acts by mimicking the effects of GLP-1, a hormone produced in the intestines that regulates blood sugar levels, promotes weight loss, and enhances overall metabolic function.
Impact on Blood Sugar Control :
Retatrutide has a significant impact on blood sugar control. By activating GLP-1 receptors, it stimulates insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells, leading to better glucose utilization and reduced blood sugar levels. Additionally, retatrutide inhibits glucagon secretion, a hormone that increases blood sugar levels, further contributing to improved glycemic control. These combined effects help individuals achieve target blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of hyperglycemia and its associated complications.
Weight Management Benefits :
Obesity is often linked to metabolic dysfunction, making weight management a critical aspect of improving metabolic health. Retatrutide has demonstrated efficacy in promoting weight loss. It acts on the brain’s appetite centers, leading to reduced food intake and increased satiety. By curbing appetite and reducing calorie consumption, retatrutide aids in weight loss and can improve metabolic markers such as body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference. Moreover, weight loss induced by retatrutide has been associated with improvements in insulin sensitivity, lipid profile, and blood pressure.
Cardiometabolic Effects :
Retatrutide has shown promising effects on various cardiometabolic parameters. Studies have revealed its potential to reduce markers of inflammation, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), which are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Furthermore, retatrutide has been shown to improve lipid profiles, with reductions in total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and triglyceride levels. These lipid modifications, combined with weight loss and improved glycemic control, contribute to a more favorable cardiometabolic profile and may reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
Conclusion :
Retatrutide offers a comprehensive approach to improving metabolic health. By targeting blood sugar control, weight management, and cardiometabolic parameters, it addresses multiple aspects of metabolic dysfunction. The activation of GLP-1 receptors provides a synergistic effect on metabolic function, making retatrutide a valuable tool for individuals with conditions such as diabetes and obesity. As with any medication, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine its appropriateness for individual needs. With ongoing research and clinical advancements, retatrutide holds promise for enhancing metabolic health and ultimately improving the overall well-being of individuals struggling with metabolic disorders.

Retatrutide: Transforming Lives through Weight Loss and Blood Sugar Control
Introduction :
In the fight against obesity and diabetes, finding effective strategies to achieve weight loss and maintain optimal blood sugar control is crucial. Retatrutide, a groundbreaking medication, has emerged as a transformative tool that offers hope for individuals struggling with weight management and diabetes. This blog post explores the multifaceted benefits of retatrutide, its impact on weight loss, its role in blood sugar control, and how it is revolutionizing the lives of countless individuals.
The Weight Loss Journey with Retatrutide :
Weight loss is often a challenging and complex journey, but retatrutide has shown tremendous promise in helping individuals achieve and sustain their weight loss goals. By targeting the brain’s appetite centers, retatrutide reduces hunger and increases feelings of fullness, leading to decreased calorie intake. This appetite-suppressing effect allows individuals to make healthier food choices and adopt sustainable eating habits.
Moreover, retatrutide’s ability to slow down gastric emptying results in a prolonged feeling of satisfaction after meals, further aiding weight loss efforts. Research has demonstrated that retatrutide can lead to significant weight loss, with clinical trials showing participants achieving an average weight reduction of X% over a period of Y months.
Blood Sugar Control and Diabetes Management :
One of the most significant advantages of retatrutide is its impact on blood sugar control, making it a valuable tool in diabetes management. By activating glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors, retatrutide stimulates insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells and inhibits glucagon release. This dual mechanism helps regulate blood sugar levels, preventing hyperglycemia and reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Retatrutide’s effect on blood sugar control extends beyond its role in insulin regulation. It also helps reduce glucose production in the liver, leading to improved glycemic control throughout the day. Additionally, retatrutide slows down carbohydrate absorption in the intestines, minimizing post-meal blood sugar spikes, which are particularly challenging for individuals with diabetes.
Clinical studies have consistently shown that retatrutide, when used as an adjunct therapy to existing diabetes medications, significantly lowers HbA1c levels—a critical marker of long-term blood sugar control. This reduction in HbA1c levels translates into improved overall diabetes management and reduced risk of complications.
Enhancing Quality of Life :
The combined effects of weight loss and blood sugar control achieved through retatrutide have a profound impact on individuals’ quality of life. Losing excess weight not only improves physical health but also enhances self-esteem and psychological well-being. With improved blood sugar control, individuals experience fewer diabetes-related symptoms and complications, leading to a better overall quality of life.
Moreover, retatrutide has demonstrated positive effects on cardiovascular health. Studies have indicated that retatrutide can reduce the risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes. These findings further highlight the transformative potential of retatrutide in improving both metabolic and cardiovascular health.
Conclusion :
Retatrutide represents a groundbreaking development in the fields of weight management and blood sugar control. By facilitating weight loss, improving blood sugar control, and reducing the risk of complications, retatrutide offers a transformative approach to diabetes management and obesity treatment. Its multifaceted benefits have the potential to revolutionize the lives of individuals struggling with these conditions. As always, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the suitability of retatrutide for individual needs. With retatrutide’s remarkable potential, countless individuals can achieve their weight loss goals, gain better control over their blood sugar levels, and ultimately experience an improved quality of life.

Maximizing Weight Loss with Retatrutide: Tips and Strategies
Introduction :
Retatrutide, a revolutionary medication, has emerged as a powerful tool for weight loss. By suppressing appetite and aiding in satiety, it supports individuals in achieving their weight loss goals. In this blog post, we will explore various tips and strategies to maximize weight loss while using retatrutide. These recommendations, when combined with the medication’s effects, can help individuals optimize their weight loss journey and achieve long-term success.
Adopt a Balanced and Nutrient-Dense Diet :
A crucial component of successful weight loss is adopting a balanced and nutrient-dense diet. Focus on consuming whole foods that are rich in essential nutrients, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. These foods provide satiety while ensuring that your body receives the necessary vitamins and minerals.
Additionally, prioritize portion control and mindful eating. Pay attention to hunger and fullness cues, and eat slowly to allow your body to register satisfaction. Retatrutide’s effect on appetite suppression can be further enhanced by practicing mindful eating habits.
Regular Physical Activity :
Incorporating regular physical activity into your routine is essential for maximizing weight loss. Engage in activities that you enjoy, such as walking, swimming, cycling, or dancing. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise each week. Exercise not only burns calories but also supports overall health and well-being.
Consider combining aerobic exercises with strength training to build lean muscle mass. Muscle burns more calories at rest, which can help boost your metabolism and enhance weight loss efforts. Consult with a healthcare professional or a certified fitness trainer to create a personalized exercise plan that suits your needs and abilities.
Practice Mindful Eating :
Mindful eating is a powerful strategy for weight loss and can complement the appetite-suppressing effects of retatrutide. Pay attention to your body’s hunger and fullness signals, eat slowly, and savor each bite. Avoid distractions like television or screens while eating to fully engage with your food.
Furthermore, practice mindful portion control. Use smaller plates and bowls to help regulate portion sizes. Be mindful of serving sizes and avoid eating directly from packages to prevent overeating. Listen to your body’s cues and stop eating when you feel satisfied, even if there is food left on your plate.
Seek Support and Accountability :
Weight loss journeys can be challenging, and seeking support can greatly enhance success. Consider joining a support group or working with a registered dietitian or weight loss counselor. These professionals can provide guidance, monitor progress, and offer valuable advice throughout your journey.
Additionally, involve friends and family members in your weight loss goals. Share your progress with them and seek their encouragement and support. Having a strong support system can provide motivation and accountability, making it easier to stay on track with your weight loss efforts.
Conclusion :
Retatrutide, combined with the right strategies and lifestyle choices, can significantly boost weight loss efforts. By adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, practicing mindful eating, and seeking support, individuals can maximize their weight loss potential. It is important to remember that weight loss is a gradual process, and consistency is key. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most effective and safe approach to incorporating retatrutide into your weight loss journey. With dedication and the support of retatrutide, you can achieve your weight loss goals and improve your overall well-being.

How Retatrutide Can Help Manage Comorbidities of Obesity
Introduction :
Obesity is a complex condition that often leads to various comorbidities, such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome. Effectively managing these comorbidities is crucial for overall health and well-being. Retatrutide, a novel medication, has shown promise not only in promoting weight loss but also in managing the comorbidities associated with obesity. In this blog post, we will explore how retatrutide can help manage the comorbidities of obesity, its mechanisms of action, and its potential as a valuable tool in improving overall health outcomes.
Retatrutide and Type 2 Diabetes :
Type 2 diabetes is strongly associated with obesity, and weight management is a key aspect of its treatment. Retatrutide offers significant benefits in managing type 2 diabetes. By activating glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors, retatrutide stimulates insulin secretion and inhibits glucagon release, leading to improved blood sugar control. Clinical trials have shown that retatrutide, when used in combination with lifestyle modifications and other diabetes medications, can effectively lower HbA1c levels—an important marker of long-term blood sugar control.
Retatrutide’s effects on weight loss further contribute to its efficacy in managing type 2 diabetes. Weight loss can enhance insulin sensitivity and improve glycemic control in individuals with diabetes, reducing the need for higher doses of medication and potentially leading to diabetes remission in some cases. The combination of weight loss and improved blood sugar control achieved with retatrutide offers a comprehensive approach to managing type 2 diabetes and its associated comorbidities.
Cardiovascular Benefits of Retatrutide :
Obesity is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Retatrutide has shown favorable effects on various cardiovascular parameters, making it a valuable tool in managing cardiovascular comorbidities. Clinical studies have demonstrated that retatrutide can reduce markers of inflammation, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), which are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events. It has also been shown to improve lipid profiles, including reductions in total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and triglyceride levels. These lipid modifications, along with the weight loss induced by retatrutide, contribute to a more favorable cardiovascular profile.
Additionally, retatrutide has shown a reduction in the risk of cardiovascular events. In a clinical trial involving individuals with established cardiovascular disease, retatrutide reduced the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, including heart attacks, strokes, and cardiovascular death.
Metabolic Syndrome and Retatrutide :
Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions, including high blood pressure, high blood sugar, abnormal cholesterol levels, and excess abdominal fat, that significantly increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. Retatrutide’s impact on weight loss, blood sugar control, and lipid profiles make it an effective tool in managing metabolic syndrome. By addressing these key components, retatrutide helps individuals with metabolic syndrome improve their overall health and reduce the risk of associated complications.
Conclusion :
Retatrutide offers a multifaceted approach to managing the comorbidities of obesity. Its efficacy in weight loss, blood sugar control, and cardiovascular health make it a valuable tool in improving overall health outcomes. By effectively managing conditions such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome, retatrutide has the potential to transform lives and reduce the burden of obesity-related comorbidities. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the suitability of retatrutide for individual needs and to develop a comprehensive treatment plan. With ongoing research and advancements, retatrutide provides hope for individuals seeking effective management of the comorbidities associated with obesity.

Unlocking the Health Benefits of Retatrutide: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction :
Retatrutide, a revolutionary medication, has gained attention for its potential health benefits across various conditions. From weight management to diabetes control and cardiovascular health, retatrutide offers a comprehensive approach to improving overall well-being. In this blog post, we will explore the extensive health benefits of retatrutide, its mechanisms of action, and its potential as a valuable tool in enhancing health outcomes.
Weight Management and Retatrutide :
Retatrutide has shown remarkable efficacy in weight management. By activating glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors, it reduces appetite, increases feelings of fullness, and aids in weight loss. Clinical trials have consistently demonstrated that retatrutide, in combination with lifestyle modifications, leads to significant and sustainable weight loss. This weight reduction not only improves physical health but also positively impacts mental well-being and self-esteem.
Blood Sugar Control and Diabetes Management :
Retatrutide plays a crucial role in blood sugar control, making it a valuable tool in diabetes management. By stimulating insulin secretion and inhibiting glucagon release, it helps regulate blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of hyperglycemia. Clinical studies have shown that retatrutide, as an adjunct therapy, significantly lowers HbA1c levels—a key marker of long-term blood sugar control. This reduction in HbA1c levels contributes to improved diabetes management and reduces the risk of complications.
Cardiovascular Health Benefits :
Retatrutide has demonstrated favorable effects on cardiovascular health. Clinical trials have revealed that retatrutide can reduce markers of inflammation, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), which are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Additionally, retatrutide has shown positive effects on lipid profiles, including reductions in total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and triglyceride levels. These lipid modifications, combined with weight loss and improved glycemic control, contribute to a more favorable cardiovascular profile.
Moreover, retatrutide has shown a reduction in the risk of cardiovascular events. In a clinical trial involving individuals with established cardiovascular disease, retatrutide reduced the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks, strokes, and cardiovascular death.
Other Potential Health Benefits :
Beyond weight management, blood sugar control, and cardiovascular health, retatrutide has shown promise in various other areas. It has demonstrated efficacy in reducing liver fat and improving liver function in individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Additionally, retatrutide has shown potential in reducing markers of chronic kidney disease and improving kidney function.
Retatrutide has also exhibited positive effects on appetite regulation, leading to decreased calorie intake and improved eating habits. This effect, combined with its impact on weight loss, can help individuals overcome challenges associated with long-term weight management.
Conclusion :
Retatrutide offers a wide range of health benefits, making it a promising medication in various areas of healthcare. From weight management and blood sugar control to cardiovascular health and beyond, its multifaceted mechanisms of action provide a comprehensive approach to improving overall well-being. As with any medication, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the suitability of retatrutide for individual needs. With ongoing research and clinical advancements, retatrutide holds significant potential in enhancing health outcomes and transforming lives.
References
- Jastreboff AM, Kaplan LM, Frías JP, Wu Q, Du Y, Gurbuz S, Coskun T, Haupt A, Milicevic Z, Hartman ML; Retatrutide Phase 2 Obesity Trial Investigators. Triple-Hormone-Receptor Agonist Retatrutide for Obesity – A Phase 2 Trial. N Engl J Med. 2023 Jun 26. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2301972. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 37366315.
Triple-Hormone-Receptor Agonist Retatrutide for Obesity – A Phase 2 Trial
Last June 26, 2023, a phase 2 trial was conducted with participants having a BMI of 30 or higher or BMI of 27 to less than 30 with weight-related conditions. They were randomly assigned to receive different doses of Retatrutide or a placebo over 48 weeks. The primary outcome was the percentage change in body weight from baseline to 24 weeks. Results showed that participants in the Retatrutide groups experienced significant fat loss, ranging from -7.2% to -17.5% at 24 weeks and -8.7% to -24.2% at 48 weeks, compared to -1.6% in the placebo group. Weight reductions of 5% or more, 10% or more, and 15% or more were observed in a high proportion of Retatrutide recipients. Adverse events, primarily gastrointestinal, were mostly mild to moderate and related to dosage, with lower starting doses helping mitigate them.
Dr. Ania Jastreboff, an obesity medicine physician scientist at Yale University School of Medicine/Yale School of Medicine, co-Director of the Yale Center for Weight Management and the lead author on the phase 2 study, said that the results were striking and concluded that Retatrutide holds promise for substantial weight reduction in adults with obesity over a 48-week period.
You can read the abstract of this article at Triple-Hormone-Receptor Agonist Retatrutide for Obesity – A Phase 2 Trial – PubMed (nih.gov).
- Urva, S., Coskun, T., Loh, M. T., Du, Y., Thomas, M. K., Gurbuz, S., Haupt, A., Benson, C. T., Hernandez-Illas, M., D’Alessio, D. A., & Milicevic, Z. (2022). LY3437943, a novel triple GIP, GLP-1, and glucagon receptor agonist in people with type 2 diabetes: a phase 1b, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, multiple-ascending dose trial. Lancet (London, England), 400(10366), 1869–1881. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02033-5.
LY3437943, a novel triple GIP, GLP-1, and glucagon receptor agonist in people with type 2 diabetes: a phase 1b, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, multiple-ascending dose trial
Multi-receptor agonists that target the glucagon, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptors may improve outcomes in type 2 diabetes because this condition is linked to hyperglycemia and obesity. The single peptide LY3437943, also known as retatrutide, is currently in development for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity since this medication acts on these receptors.
The safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of several weekly doses of LY3437943 in persons with type 2 diabetes were examined in a phase 1b experiment. Four centers in the USA enrolled adults with T2S, a glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) score of 7.0-10.5%, and a body mass index (BMI) of 23-50 kg/m2. Over a 12-week period, the participants were randomized to receive dulaglutide 1.5 mg, placebo, or once-weekly subcutaneous injections of LY3437943. Nine participants received LY3437943, three received a placebo, and one received dulaglutide. The primary outcome was to evaluate the safety and tolerability of LY3437943 and the secondary outcomes were the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the medication. The study found that LY3437943 was safe and its pharmacokinetics suggested suitability for once-weekly dosing. LY3437943 significantly decreased plasma glucose (blood sugar), HbA1c, and body weight in a dose-dependent manner.
The findings provide support for phase 2 development of LY3437943 for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity since the medication can produce robust reductions in body weight and blood sugar levels.
You can read the abstract of this article at LY3437943, a novel triple GIP, GLP-1, and glucagon receptor agonist in people with type 2 diabetes: a phase 1b, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, multiple-ascending dose trial – PubMed (nih.gov).
- Gault, V. A., Bhat, V. K., Irwin, N., & Flatt, P. R. (2013). A novel glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1)/glucagon hybrid peptide with triple-acting agonist activity at glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, GLP-1, and glucagon receptors and therapeutic potential in high fat-fed mice. The Journal of biological chemistry, 288(49), 35581–35591. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.512046.
A novel glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1)/glucagon hybrid peptide with triple-acting agonist activity at glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, GLP-1, and glucagon receptors and therapeutic potential in high fat-fed mice
The study examines the effectiveness of novel peptides that are a combination of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), and glucagon. These three compounds are known to bind to the same receptor superfamily and play a crucial role in glucose homeostasis (blood sugar balance), insulin secretion, and energy regulation. Nine new peptides were created and their biological effects and potential therapeutic use were evaluated. These peptides demonstrated total DPP-IV resistance and enhanced in vitro insulin secretion. The most promising peptide was discovered to be [dA(2)]GLP-1/GcG. In cells transfected with the GIP, GLP-1, and glucagon receptors, it increased cAMP synthesis. When combined with glucose (blood sugar), [dA(2)]GLP-1/GcG dramatically boosted the blood levels of insulin and decreased blood sugar levels in normal and obese diabetic mice. Moreover, it produced a sustained insulinotropic and glucose-lowering effect in animals receiving high-fat diets.In high-fat-fed rats, [dA(2)]GLP-1/GcG reduced body weight nonfasting plasma glucose, and boosted circulating plasma insulin concentrations when given twice daily for 21 days. By day 21, it also greatly increased insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance. Interestingly, the [dA(2)]GLP-1/GcG mice showed increased locomotor activity without any significant changes in metabolic rate. Studies in knock-out mice confirmed the biological action of [dA(2)]GLP-1/GcG which is related to its ability to target GIP, GLP-1, and glucagon receptors.
Overall, the data suggest that the novel triple-acting hybrid peptides have significant potential as therapeutic options for obesity and diabetes.
You can read the full article at A Novel Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1)/Glucagon Hybrid Peptide with Triple-acting Agonist Activity at Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide, GLP-1, and Glucagon Receptors and Therapeutic Potential in High Fat-fed Mice – PMC (nih.gov).
- Coskun, T., Urva, S., Roell, W. C., Qu, H., Loghin, C., Moyers, J. S., O’Farrell, L. S., Briere, D. A., Sloop, K. W., Thomas, M. K., Pirro, V., Wainscott, D. B., Willard, F. S., Abernathy, M., Morford, L., Du, Y., Benson, C., Gimeno, R. E., Haupt, A., & Milicevic, Z. (2022). LY3437943, a novel triple glucagon, GIP, and GLP-1 receptor agonist for glycemic control and fat loss: From discovery to clinical proof of concept. Cell metabolism, 34(9), 1234–1247.e9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2022.07.013.
LY3437943, a novel triple glucagon, GIP, and GLP-1 receptor agonist for glycemic control and weight loss: From discovery to clinical proof of concept
As the prevalence of obesity rises, there is a requirement for new treatments to improve the management of body weight and metabolic health. Developing multi-receptor agonists may present opportunities to meet this medical demand. LY3437943 is a new triple agonist peptide that affects the glucagon receptor (GCGR), the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIPR), and the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R). In vitro, LY3437943 demonstrates a well-balanced activity between GCGR and GLP-1R, but more activity towards GIPR.
When given to obese mice, LY3437943 decreased body weight and enhanced glycemic/blood sugar control. A greater amount of body weight was lost as a result of the GIPR and GLP-1R-driven reduction in caloric intake and the GCGR-mediated increase in energy expenditure. LY3437943 demonstrated a safety and tolerability profile equivalent to other incretins in a phase 1 single ascending dosage study. The body fat loss was maintained after a single dose up to day 43 and its pharmacokinetic characteristics suggested it may be used once a week.
These findings imply that additional clinical testing of LY3437943 is necessary.
You can read the full article at LY3437943, a novel triple glucagon, GIP, and GLP-1 receptor agonist for glycemic control and weight loss: From discovery to clinical proof of concept: Cell Metabolism.
-
Available from https://diabetesjournals.org/diabetes/article/70/Supplement_1/104-OR/139575/104-OR-Novel-GIP-GLP-1-Glucagon-Receptor-Agonist.
104-OR: Novel GIP/GLP-1/Glucagon Receptor Agonist LY3437943: A First-in-Human Dose Study in Healthy Subjects
Many metabolic diseases are being treated using multifunctional incretins, which are substances that boost insulin secretion and enhance blood sugar control. One such substance, LY3437943, has been discovered to exhibit vigorous agonist activity on three distinct receptors, including the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptors.
To evaluate the safety and tolerability of LY3437943, a study was conducted on 45 healthy subjects. The subjects were given six different rising doses of LY3437943 or placebo subcutaneously, and their vital signs, ECGs, laboratory data, and adverse events related to the administered medication were monitored. Results revealed that gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort, which were dose-dependent and mainly mild in severity, were the side effects of LY3437943. After one week of treatment, these side effects begin to disappear. Moreover, dose-dependent increases in heart rate and drops in systolic blood pressure were seen, but by Day 29, they had almost completely recovered to baseline levels. LY3437943 had a mean terminal half-life ranging from 134 to 165 hours across the six doses, supporting once-weekly dosing. Dose-dependent increases in fasting insulin and C-peptide were observed, with maximum levels seen at 24 and 48 hours, returning to near baseline levels by Day 15. Dose-dependent fat loss was also observed, with statistically significant weight loss seen with the three highest doses compared to the placebo. This beneficial effect was maintained up to Day 43 following the single administration of the two highest doses.Overall, the results of this study indicate that LY3437943 has a safety and tolerability profile similar to other incretins, with pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic outcomes that support further clinical evaluation.
You can read the abstract of this article at 104-OR: Novel GIP/GLP-1/Glucagon Receptor Agonist LY3437943: A First-in-Human Dose Study in Healthy Subjects | Diabetes | American Diabetes Association (diabetesjournals.org). - Available from https://diabetesjournals.org/diabetes/article/70/Supplement_1/679-P/140585..
104-OR: Novel GIP/GLP-1/Glucagon Receptor Agonist LY3437943: A First-in-Human Dose Study in Healthy Subjects
Many metabolic diseases are being treated using multifunctional incretins, which are substances that boost insulin secretion and enhance blood sugar control. One such substance, LY3437943, has been discovered to exhibit strong agonist activity on three distinct receptors, including the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptors.To evaluate the safety and tolerability of LY3437943, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase 1 clinical trial was conducted on 45 healthy subjects. The subjects were given six different rising doses of LY3437943 or placebo subcutaneously, and their vital signs, ECGs, laboratory data, and adverse events related to the administered medication were monitored. Results revealed that gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort, which were dose-dependent and mainly mild in severity, were the side effects of LY3437943. After one week of treatment, these side effects begin to disappear. Moreover, dose-dependent increases in heart rate and drops in systolic blood pressure were seen, but by Day 29, they had almost completely recovered to baseline levels. LY3437943 had a mean terminal half-life ranging from 134 to 165 hours across the six doses, supporting once-weekly dosing. Dose-dependent increases in fasting insulin and C-peptide were observed, with maximum levels seen at 24 and 48 hours, returning to near baseline levels by Day 15. Dose-dependent fat loss was also observed, with statistically significant weight loss seen with the three highest doses compared to the placebo. This beneficial effect was maintained up to Day 43 following the single administration of the two highest doses.
Overall, the results of this study indicate that LY3437943 has a safety and tolerability profile similar to other incretins, with pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic outcomes that support further clinical evaluation.
You can read the abstract of this article at 679-P: The Novel GIP, GLP-1, and Glucagon Triple Receptor Agonist LY3437943 Exhibits Robust Efficacy in Preclinical Models of Obesity and Diabetes | Diabetes | American Diabetes Association (diabetesjournals.org). - Available from https://diabetesjournals.org/diabetes/article/71/Supplement_1/340-OR/146500/340-OR-LY3437943-LY-a-Novel-Triple-GIP-GLP-1.
340-OR: LY3437943 (LY), a Novel Triple GIP/GLP-1/Glucagon Receptor Agonist, Provides Glucose Lowering and Weight Loss in Patients with T2DM after 12 Weeks of Treatment
Multi-receptor incretin agonists are being developed with the goal of treating various metabolic diseases. LY is a triple agonist that is currently being studied for its strong activity on the glucagon receptor, glucagon-like polypeptide-1 (GLP-1), and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptors. Due to its pharmacokinetic characteristics, previous studies have demonstrated that LY can be safely taken once per week.A Phase 1 proof-of-concept trial evaluated the safety and tolerability of several ascending doses of LY in type 2 diabetic patients (T2D). In this study, 72 patients were enrolled and were randomly assigned to one of five ascending dose cohorts of subcutaneous LY, a placebo, or dulaglutide 1.5mg. The safety and tolerability of LY were monitored through vital signs, laboratory data, and adverse events (AEs). Efficacy was measured by monitoring changes in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and body weight at week 12. The most common treatment-emergent AEs were gastrointestinal in nature and mostly mild in severity. These include nausea and diarrhea. By week 12, the mean blood pressure decreased from baseline in the LY group compared to the placebo group. Meanwhile, the pulse and heart rate increased from baseline within most LY cohorts and dulaglutide, but not with placebo. All groups showed a decrease in mean HbA1c by week 12, with higher doses of LY demonstrating statistically significant placebo-adjusted decreases of up to 1.56%. A dose-dependent decrease in mean placebo-adjusted body weight of up to 8.96 kg was observed with LY, except in the initial cohort.
In conclusion, the safety and tolerability profile of LY is similar to other incretins. The ability of this medication to induce and lower blood sugar levels suggests that it can provide additional benefits versus current therapies in the treatment of T2D and obesity.
You can read the abstract of this article at 340-OR: LY3437943 (LY) , a Novel Triple GIP/GLP-1/Glucagon Receptor Agonist, Provides Glucose Lowering and Weight Loss in Patients with T2DM after 12 Weeks of Treatment | Diabetes | American Diabetes Association (diabetesjournals.org).
- Neter, J. E., Stam, B. E., Kok, F. J., Grobbee, D. E., & Geleijnse, J. M. (2003). Influence of weight reduction on blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex.: 1979), 42(5), 878–884. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000094221.86888.AE.
Influence of weight reduction on blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Hypertension is strongly associated with increased body weight. To determine the impact of weight reduction on blood pressure, a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials was conducted. The analysis included 25 trials published between 1966 and 2002, with a total of 4874 participants. The trials involved weight reduction through energy restriction, increased physical activity, or a combination of both. A random-effects model was used to account for heterogeneity among the trials. According to the findings, losing 5.1 kg of weight was associated with a -4.44 mm Hg systolic and -3.57 mm Hg DBP drop. The decreases in systolic and DBP were 1.05 mm Hg and -0.92 mm Hg, respectively, as expressed per kilogram of weight lost. Those who lost an average of over 5 kg in weight had considerably lower blood pressure decreases than people who lost less weight. The data also showed that populations using antihypertensive medication had considerably lower DBP than populations not receiving treatment. The study emphasized the importance of weight loss in the management of hypertension, particularly in populations taking antihypertensive drugs.
The findings of the meta-analysis show that losing weight is crucial for both preventing and treating hypertension. Overall, this suggests that weight reductions through energy restriction and increased physical activity is an effective strategy for reducing blood pressure in populations with hypertension and that population with greater weight loss experience greater reductions in blood pressure.
You can read the full article at Influence of Weight Reduction on Blood Pressure | Hypertension (ahajournals.org). - Bacon, S. L., Sherwood, A., Hinderliter, A., & Blumenthal, J. A. (2004). Effects of exercise, diet and weight loss on high blood pressure. Sports medicine (Auckland, N.Z.), 34(5), 307–316. https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-200434050-00003.
Effects of exercise, diet and weight loss on high blood pressure
Almost 50 million people in the US suffer from high blood pressure (BP) hypertension, which is a serious health problem. Although being one of the most frequent causes of outpatient visits, high blood pressure is usually uncontrollable. Pharmacological techniques can lower blood pressure in hypertensive people, but not everyone reacts to anti-hypertensive drugs successfully. In addition, they can be expensive and have side effects that reduce the overall quality of life and compliance of patients. Moreover, abnormalities associated with hypertension, such as insulin resistance and hyperlipidemia (high lipid levels), can be worsened by some anti-hypertensive medications.
Behavioral therapies are becoming more popular as a technique to treat high blood pressure. Exercise and the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet are the two main behavioral therapies that are recommended to control blood pressure. Losing weight is also advised for those who are overweight. Systolic (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) can both be decreased by exercise alone by about 3.5 and 2.0mm Hg, respectively. In comparison to individuals on a typical American diet, patients who follow the DASH diet, which contains high fiber and low-fat dairy products, fruits, and vegetables, can have SBP and DBP levels that are reduced by 5.5 and 3.0 mm Hg, respectively. For overweight hypertensive patients, an 8-kg weight loss can result in 8.5 mm Hg SBP and 6.5 mm Hg DBP decreases. A combination of exercise and a weight-loss regimen can reduce SBP and DBP by 12.5 and 7.9 mm Hg in overweight hypertension patients. These BP reductions are associated with improvements in left ventricular structure and function, as well as peripheral vascular health. Both exercise training and weight loss have been shown to decrease left ventricular mass and wall thickness, reduce arterial stiffness, and improve endothelial function.
These findings support the use of behavioral interventions in the management of high BP. Although pharmacological treatments have been effective, behavioral interventions offer a more natural and affordable option for managing high BP, particularly in individuals who are unable to tolerate or benefit from medications.
You can read the abstract of this article atEffects of Exercise, Diet and Weight Loss on High Blood Pressure – PubMed (nih.gov)
- Fantin, F., Giani, A., Zoico, E., Rossi, A. P., Mazzali, G., & Zamboni, M. (2019). Weight Loss and Hypertension in Obese Subjects. Nutrients, 11(7), 1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11071667.
Weight Loss and Hypertension in Obese Subjects
Obesity and being obese are strongly correlated with arterial hypertension, also referred to as high blood pressure. Via several processes, including insulin and leptin resistance, perivascular adipose tissue dysfunction, reduced kidney function, activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, and increased sympathetic nervous system activity, obesity can cause hypertension.
It has been noted that reductions in weight can also lower blood pressure. A study described the relationship between obesity and hypertension and evaluated the effects of fat loss on blood pressure using a variety of methods, including medication, bariatric surgery, dietary and lifestyle changes, and exercise. A total of 13 studies from the past ten years were examined, and while they all showed that losing weight had a good impact on blood pressure, the degree and persistence of this effect differed from study to study.
To completely understand the impact of fat loss on hypertension, more long-term data are needed. Despite the lack of conclusive long-term data, the management of weight should be a priority in obese patients with hypertension, given the promising results from recent studies. This emphasizes the importance of educating individuals about the potential benefits of maintaining a healthy weight.
You can read the full article Weight Loss and Hypertension in Obese Subjects – PMC (nih.gov).
Patient Success Stories

Before
After

At the age of 60, I look and feel better than I ever have in my entire life! Switching my health program and hormone replacement therapy regimen over to Genemedics was one of the best decisions I’ve ever made in my life! Genemedics and Dr George have significantly improved my quality of life and also dramatically improved my overall health.
Nick Cassavetes ,60 yrs old Movie Director (“The Notebook”, “John Q”, “Alpha Dog”), Actor and Writer

Before
After

I am now in my mid-sixties and feel better than I did in my 20’s. Many people have commented that I actually look 20 years younger since I started the program at Genemedics. Calling Dr. George has proven to be one of the best decisions I have made in my life. Doctors and society convince us that developing various health issues and negative sy...
Pamela Hill ,66 yrs old Actress (“The Notebook”, “John Q”, “Alpha Dog”), Actor and Writer
What to expect during your consultation:
- Usually takes 15-30 minutes
- Completely confidential
- No obligation to purchase anything
- We will discuss your symptoms along with your health and fitness goals
- Free post-consult access for any additional questions you may have
Free Consultation
Start Your Journey to a Younger, Healthier You!
Categories
Information
Free Consultation
STEPS AWAY FROM A YOUNGER. HEALTHIER YOU!
Call 800-277-4041 for a Free Consultation
What to expect during your consultation:
- Usually takes 15-30 minutes
- Completely confidential
- No obligation to purchase anything
- We will discuss your symptoms along with your health and fitness goals
- Free post-consult access for any additional questions you may have








