GENEMEDICS APP
GENEMEDICS NUTRITION
Peptides for Wound Healing
Author: Dr. George Shanlikian, M.D. | Last Updated: January 31st, 2024
- Home
- >
- Health Library
- >
- Peptides for Wound Healing
- 5-amino-1MQ
- Aminophylline
- Aniracetam
- ARA 290
- Argireline + Leuphasyl
- BPC-157
- Bremelanotide
- Cerebrolysin
- CJC-1295
- Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide
- Dihexa
- Elampretide (SS-31)
- Epithalon
- FG Loop Peptide (FGL)
- GHK-Cu
- Ginsenoside Rg3
- Glycyrrhetinic Acid
- Ipamorelin
- Kisspeptin
- KPV
- LL-37
- Melanotan 1
- Melanotan 2
- Mitochondrial ORF of the twelve S c (MOTS-c)
- MK-677 (IBUTAMOREN)
- Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+)
- Nicotinamide Riboside
- NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide)
- Noopept
- Pegylated Mechano Growth Factor
- Selank
- Semax
- Sermorelin
- SRT2104
- Tesamorelin
- Thymosin Alpha 1
- Thymosin Beta 4
- Tiger 17
- Valproic Acid
- Valproic acid + PTD-DBM
- Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide
- Zinc-Thymulin
Book a Free Consultation
Potential Benefits of Wound Healing Peptides
Wound Healing Peptides offer several valuable benefits, including accelerating wound closure, enhancing collagen production for tissue repair, and promoting the formation of new blood vessels to support healing. Additionally, they play a role in fighting inflammation, exerting antimicrobial activity, and reducing scar formation, contributing to the overall effectiveness of wound healing processes.
- Accelerates wound closure
- Enhances collagen production
- Promotes the formation of new blood vessels
- Fights inflammation
- Exerts antimicrobial activity
- Reduces scar formation
Key Takeaways
- Wound-healing peptides are short chains of amino acids that play a crucial role in the wound healing process. Wound healing peptides can promote the migration and proliferation of various types of cells involved in wound repair, such as fibroblasts and keratinocytes. This acceleration of cellular activities leads to faster wound closure and reduced healing time.
- Wound healing peptides can stimulate the synthesis of collagen, a key component of the extracellular matrix that provides structural support and strength to the wound. This helps promote the formation of new tissue and improves the overall quality of the healed wound.
- Wound-healing peptides can stimulate angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels), facilitating the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the wound and promoting tissue regeneration.
- Wound healing peptides possess anti-inflammatory properties, helping to reduce inflammation at the wound site and creating an optimal environment for healing to occur.
- Wound healing peptides have antimicrobial properties and can effectively target and kill a broad spectrum of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and even some drug-resistant strains. By preventing or treating infections, these peptides contribute to improved wound healing outcomes.
- Wound healing peptides have been found to modulate the activity of fibroblasts and reduce the production of scar tissue, leading to less noticeable scars and improved cosmetic appearance of the healed wound.
What are Wound Healing Peptides?
Wound healing peptides are naturally occurring peptides found in the human body that plays a crucial role in the wound healing process. These peptides act as powerful immune system modulators and have been shown to regulate immune responses during tissue repair. Additionally, recent research has revealed their potential role in the central nervous system, suggesting that these peptides may influence wound healing outcomes through interactions with the nervous system.
Wound healing/repair peptides are a class of biologically active compounds that play a crucial role in promoting the body’s natural healing process. These peptides consist of short chains of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. They function by stimulating various cellular processes involved in tissue repair, regeneration, and wound healing.
These peptides work by enhancing processes such as inflammation control, cellular migration, angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels), and collagen synthesis. By modulating these processes, wound healing and repair peptides accelerate the recovery of injured tissues, reduce scar formation, and improve the overall healing outcome. These peptides are often used in medical applications to treat various types of injuries, skin conditions, and surgical wounds, as well as in cosmetic products to promote skin health and rejuvenation.
The Wound Healing Process
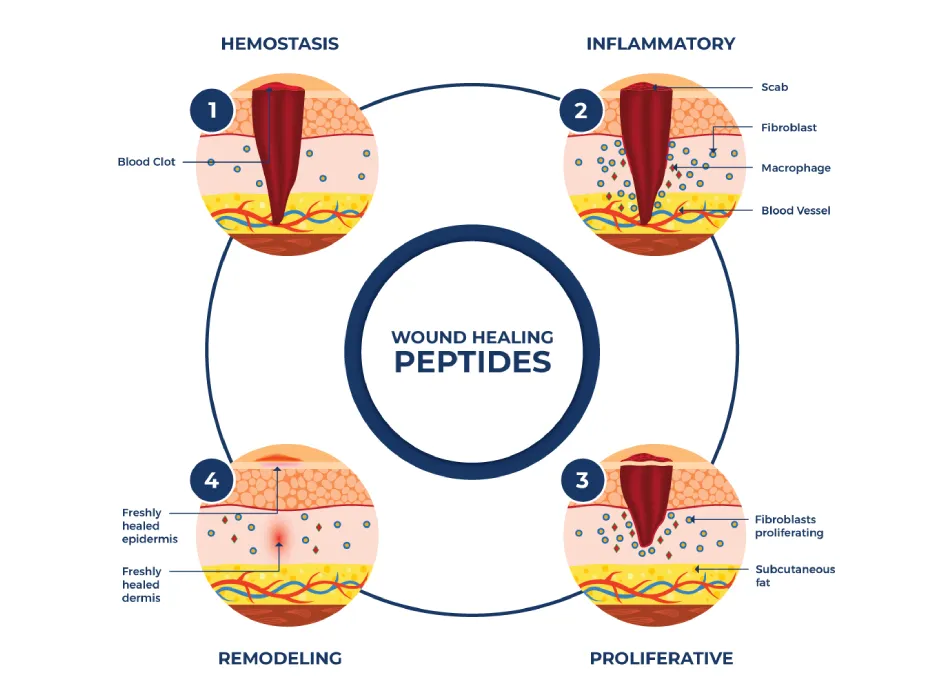
The wound-healing process is a complex and dynamic series of events that the body undergoes to repair tissue and restore its structural and functional integrity. It typically consists of four overlapping stages: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling. Here’s a detailed discussion of each stage:
Hemostasis
The wound-healing process begins with hemostasis, which is the immediate response to injury. When a wound occurs, the body initiates a series of processes to stop bleeding and form a blood clot. Platelets, tiny blood cells, aggregate at the wound site, releasing chemical signals that promote clotting. The clot serves as a temporary seal, preventing further blood loss and creating a provisional matrix for subsequent tissue repair.
Inflammation
The second stage is inflammation, which is characterized by redness, swelling, heat, and pain at the wound site. During inflammation, immune cells, such as neutrophils and macrophages, migrate to the wound to fight off any invading pathogens and clear away debris and injured tissue. These cells release cytokines and growth factors that signal other cells to begin the healing process. Inflammation sets the stage for the subsequent phases of wound repair.
Proliferation
The proliferation stage involves the formation of new tissue to fill the wound gap. Fibroblasts, specialized cells, play a critical role in this stage by synthesizing and depositing collagen, which provides strength and structure to the healing wound. New blood vessels form through angiogenesis, bringing oxygen and nutrients to support tissue growth. Epithelial cells also multiply and migrate to cover the wound surface, re-establishing the skin barrier.
Remodeling
The final stage is remodeling, where the newly formed tissue undergoes reorganization and maturation. Collagen fibers are realigned and cross-linked to enhance tissue strength. The excess collagen is broken down, and the wound contracts, reducing its size. This stage can last for months to years, depending on the wound’s size and complexity.
The wound healing process is a tightly regulated and highly orchestrated sequence of events. Several factors can influence the healing rate and outcome, including age, overall health, nutrition, and the presence of underlying medical conditions like diabetes or immunosuppression.
While the body’s natural healing abilities are usually sufficient for minor wounds, some wounds may require medical intervention, such as wound dressings, sutures, or even wound healing peptides or growth factors, to support and expedite the healing process. Proper wound care and timely medical attention can significantly improve the outcome of wound healing and minimize the risk of complications.
How Peptides for Healing Speed Up Tissue Repair
Peptides for healing can speed up the process of treating injuries through several mechanisms that promote tissue repair and regeneration. Here are some ways in which these peptides work to accelerate wound healing:
Cellular Proliferation
Peptides for healing can stimulate the proliferation (multiplication) of various cells involved in the healing process, such as fibroblasts and keratinocytes. These cells play essential roles in creating new tissue and re-epithelializing the wound.
Angiogenesis Promotion
Peptides for healing can promote angiogenesis near the wound site. Increased blood supply brings oxygen, nutrients, and immune cells, supporting tissue repair and reducing the risk of infection.
Collagen Synthesis
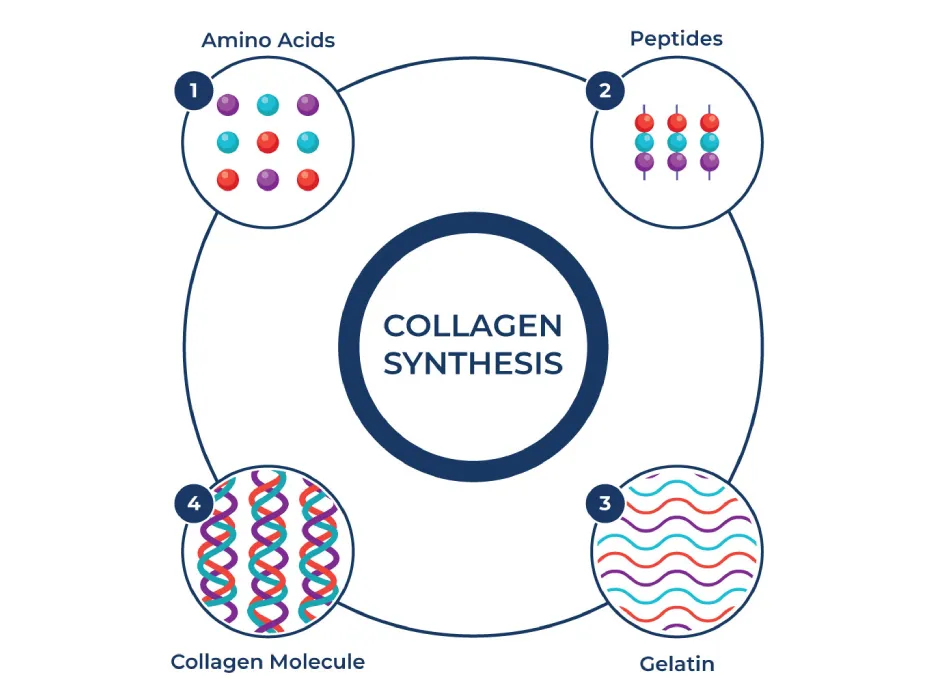
Peptides for healing can enhance the production of collagen, a key protein that provides structural support to the healing tissue. More collagen means increased tensile strength and better wound closure.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects

Some peptides for healing have anti-inflammatory properties, reducing excessive inflammation at the wound site. This controlled inflammation allows for a more efficient healing process.
Antimicrobial Activity
Certain peptides for healing have antimicrobial properties that help combat infection-causing bacteria and pathogens. By preventing or resolving infections, wound healing is facilitated without complications.
Removal of Dead Tissue
Some peptides for healing aid in the removal of dead or damaged tissue from the wound, a process known as debridement. This helps create a clean environment for healing and reduces the risk of infection.
Modulation of Growth Factors
Peptides for healing can interact with growth factors such as Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF), Mechano Growth Factor (MGF), and cytokines, which are involved in wound healing pathways.
Enhanced Immune Response

Peptides for healing can boost the immune function, leading to improved defense against infections and a more efficient healing process.
Overall, peptides for healing act as biological signals that trigger and support various processes necessary for effective tissue repair. Their ability to accelerate wound healing makes them valuable in medical applications, such as chronic wound management and post-surgical care, as well as in the development of cosmeceutical products for skin rejuvenation and scar reduction.
Best Peptides for Healing Injuries
Determining the specific wound healing/repair peptide that is suitable for an individual depends on several factors, including the type and severity of the wound, individual health conditions, and medical history. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in wound care to assess your unique circumstances and provide personalized recommendations. The following are the most effective and best healing peptides:
ARA 290 – Soft Tissue Repair
ARA 290, also known as cibinetide, is an 11–amino acid peptide that has potent tissue-protective and tissue-regenerative properties. It is called “nonhematopoietic peptide” because ARA 290 exerts its beneficial effects without stimulating erythropoiesis or red blood cell production. Preclinical and clinical studies have shown that by selectively interacting with the innate repair receptor, ARA 290 mediates tissue protection. ARA 290 is designed from the structure of erythropoietin. It mediates tissue protection by selectively interacting with the innate repair receptor. This in turn stimulates tissue repair and decreases inflammation and apoptosis (programmed cell death).
BPC-157 – Blood Vessel Growth
BPC-157, also known as Body Protecting Compound, is a 15-amino acid long peptide. A peptide is simply a compound consisting of two or more amino acids. Your body already produces BPC-157 in very small amounts, which serves to signal certain body processes to happen and protect the digestive system. BPC-157 is a naturally occurring peptide found within the body, most specifically in human gastric contents.
Researchers believe that if you get the super concentrated version of BPC-157 into your system, it has an extremely high level of regenerative effects and healing properties. BPC-157 can promote angiogenesis and enhance the growth hormone receptor expression in tendon fibroblasts. This process is important in promoting healing and faster cell regeneration, especially in physical injuries involving connective tissue and muscle tissue, making BPC-157 one of the best peptides for wound repair.
BPC-157 has also shown promising potential in improving gut health aside from being a healing peptide. BPC-157 regulates the inflammatory response and promotes tissue repair in the gastrointestinal tract. By enhancing gut health, BPC-157 may alleviate various gastrointestinal issues, such as gastritis, ulcer, and inflammatory bowel disease.
CJC-1295 – Growth Hormone Booster
CJC-1295 is also known as drug affinity complex: growth hormone-releasing factor (DAC: GRF). It’s a synthetic analogue of growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) and is primarily used to boost blood levels of growth hormone by up to ten times its normal capacity. Because CJC-1295 has a similar structure to GHRH, it has the ability to stimulate the pituitary gland to release growth hormone as well as other anabolic hormones such as insulin-like growth factor 1.
Originally, CJC-1295 and other synthetic peptides (compounds consisting of two or more amino acids linked in a chain) were commonly prescribed by medical professionals to treat patients suffering from muscle wasting, growth disorders, and burn injuries. Today, CJC-1295 is still widely prescribed in the treatment of these disorders because it can promote muscle growth via increased production of muscle cells and faster recovery with minimal side effects.
CJC-1295 peptide has been shown to increase growth hormone receptor expression, leading to an increase in growth hormone secretion. In order to ensure balance (homeostasis), the body still releases growth hormones in pulses. With increased GH levels, it lead to increased muscle mass and strength, muscle repair, fat loss, tissue regeneration, and higher levels of extracellular matrix deposition (a framework that helps heal wounds by producing important proteins like collagen and elastin).
Unlock your potential: Discover the power of Growth Hormone-Boosting Peptides today! Supercharge your vitality, enhance muscle growth, and rejuvenate your body. Experience the benefits of cutting-edge peptide therapies for optimal health and performance. Take the first step towards a better you!
GHK-Cu – Potent Antioxidant
The human copper-binding peptide GHK-Cu is a natural peptide that is currently used as a protective a regenerative ingredient in skin and hair products because of its numerous benefits on the skin and hair. For instance, GHK-Cu improves wound healing, stimulates collagen and glycosaminoglycan synthesis in the skin, boosts the immune system, and promotes the growth of blood vessels.
GHK-Cu also has significant anti-aging effects as it has potent antioxidant properties and anti-inflammatory effects. This healing peptide works by boosting collagen and elastin production in the skin. It promotes nerve regeneration by increasing the production of nerve growth factors.
Ibutamoren (MK-677) – Healing Peptide for Physical Injuries
MK-677, also known as ibutamoren or ibutamoren mesylate, belongs to a group called growth hormone secretagogues. They are substances that boost the production of growth hormone (GH). MK-677 can also increase the production of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), a hormone similar in molecular structure and function to insulin.
The ability of MK-677 to boost the levels of GH and IGF-1 is associated with a wide array of health benefits. Growth hormone secretagogues such as MK-677 have the ability to accelerate the repair of damaged tissues caused by physical trauma or sports-related injuries. Higher GH and IGF-1 levels are also associated with increased production of muscle cells which is important for muscle repair.
Ipamorelin – Regenerative Peptide with Minimal Side Effects
Ipamorelin is considered a growth hormone-releasing peptide (GHRP) or growth hormone secretagogue. As a pentapeptide (composed of five amino acids), it has the capacity to mimic the body’s natural release of growth hormone and ghrelin (the hunger hormone).
Because this peptide does not affect the release of other hormones in the body such as acetylcholine, aldosterone, cortisol, and prolactin, it has virtually no negative side effects. Therefore, it is considered one of the safest and most effective forms of growth hormone replacement therapy, widely used to fight the effects of aging, manage certain diseases, enhance sports performance, and balance growth hormone deficiency.
Most medical professionals prescribe ipamorelin more than other therapies because it can help optimize human growth hormone for a longer period of time, thus having a more potent effect. Growth hormone-releasing peptides such as ipamorelin can help repair damaged tissues caused by a sports injury or physical trauma.
KPV – Powerful Immune System Modulator
KPV is a tripeptide (Lysine-Proline-Valine) that possesses potent anti-inflammatory properties. It’s a C-terminal tripeptide of α-MSH (alpha-Melanocyte-stimulating hormone). Peptides like KPV often act as hormones and relay information from one tissue through the blood to another via biological messengers.
Whether given orally or in the form of injections, the KPV tripeptide has the potential to treat immune-mediated inflammatory conditions such as dermatitis, bowel diseases, allergic asthma, and arthritis. The ability of KPV to reduce inflammation may also play a role in speeding up the wound-healing process.
Since KPV does not cause skin pigmentation, this makes it a good candidate for improving wound healing while avoiding unpleasant skin changes. Another mechanism that is thought to contribute to faster wound healing is the immune-boosting effects of KPV, which helps lower the risk of infection during the regeneration process.
LL-37 – Antimicrobial Peptide
LL-37, also known as Human Cathelicidin Antimicrobial Peptide (CAMP), is touted as a “mammal’s core tool” to fight off various harmful microorganisms in the body. It’s produced by many cell types including natural killer (NK) cells, white blood cells, and skin cells. Different body systems such as the respiratory system, gastrointestinal tract, testes, and ocular surface also produce LL-37.
This powerful peptide has piqued the interest of the research community because its immune-modulating activities have the potential to accelerate tissue recovery and significantly improve the survival rate of patients with chronic debilitating medical conditions. The human cathelicidin LL-37 serves a critical role in the innate immune system by defending against bacterial infections. LL-37 can interact with the molecules of the cell wall and perforate cytoplasmic membranes resulting in bacterial cell death.
Just like BPC-157, LL-37 helps promote wound repair by stimulating angiogenesis. This process enhances blood supply to the wound, facilitating tissue repair and faster healing. LL-37 also exerts its healing properties by promoting skin cell migration to the site of injury and stimulating the production of growth factors and extracellular matrix components.
Semax – Cell Growth and Cell Migration
Semax is a synthetic peptide drug. It was developed based on the molecular structure of the adrenocorticotropic hormone, which is a naturally occurring peptide produced by the pituitary gland.
It was originally used in Russia for the prevention and treatment of injuries to the central nervous system caused by stroke or Alzheimer’s disease. It has the ability to enhance cognition, protect brain cells, and ward off depression. This healing peptide also has neuroprotective, nootropic, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Semax works by stimulating certain parts of the brain involved in the release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). BDNFs are chemicals involved in neurogenesis (formation of new neurons in the brain) and survival of existing neurons. Just like BPC-157, it can also enhance wound healing by promoting the formation of new blood vessels but it has the ability to boost the production of collagen.
Tesamorelin – Muscle Growth and Muscle Repair
Tesamorelin is an FDA-approved drug for lipodystrophy, a medical condition characterized by an abnormal distribution of body fat. This small molecule (known as peptides) is a synthetic analog of growth hormone–releasing factor, which means that it stimulates the pituitary gland to secrete growth hormone (GH). This mechanism is thought to play an integral role in body fat reduction since direct GH administration has fat-burning effects. Research suggests that growth hormone-based therapies such as tesamorelin treatment can speed up the rate of healing of damaged nerves.
Aside from wound healing and tissue repair, other peptides also offer benefits such as weight loss. Peptides can induce weight loss by influencing various metabolic pathways, appetite regulation, and fat-burning processes in the body.
Discover the Power of Peptides for Weight Loss! Explore our selection of cutting-edge peptides designed to support your weight loss journey and unlock the potential of these remarkable compounds to boost your health and fitness goals. Don’t miss out on this opportunity to harness the science of peptides for a leaner, healthier you!
Thymosin Alpha 1 – Powerful Immune System Modulator
Thymosin alpha 1 (T α 1) is a peptide (consists of two or more amino acids linked in a chain) that is naturally produced by the thymus gland. It plays an integral role in the maturation of immune system cells known as T-cells, which are vital in fighting harmful bacteria, fungi, or viruses. Thymosin alpha 1 also has anti-inflammatory and anti-fatigue properties and is given in patients with hepatitis B and C, malignant melanoma, liver cancer, drug-resistant tuberculosis, Lyme disease, and Di George’s syndrome (immunodeficiency disease). Thymosin alpha 1 stimulates signaling pathways in the immune system. By acting through toll-like receptors (a class of proteins that is essential in the innate immune system), antimicrobial peptides such as thymosin alpha 1 discourage the replication of viruses, bacteria, fungi, and other harmful microorganisms – this mechanism is important in wound healing.
Thymosin Beta -4 – Immune Function Booster
Thymosin is a hormone secreted by the thymus gland. This powerful hormone serves a vital role in the training and development of a special type of white blood cell known as T-lymphocytes or T cells. In addition, thymosin also assists in the development of antibodies necessary for a strong immune system. The predominant form of thymosin known as thymosin beta-4 is an actin, a multi-functional protein that helps muscles and cells move. Thymosin beta-4 also plays a crucial role in tissue regeneration and protection.
Thymosin beta-4 is a naturally occurring peptide that plays a significant role in regulating the immune system. It is found in various tissues, including the thymus, spleen, and white blood cells, where it modulates immune responses and supports immune cell functions.
Thymosin beta-4 can boost the immune system in several ways:
- Stimulating Immune Cell Activity: Thymosin beta-4 can enhance the activity of immune cells, such as T cells and natural killer (NK) cells, which play crucial roles in defending the body against infections and abnormal cells.
- Reducing Inflammation: Thymosin beta-4 has anti-inflammatory properties, helping to reduce excessive inflammation in the body. By controlling inflammation, it contributes to a more balanced and efficient immune response.
- Promoting Wound Healing: Thymosin beta-4 is involved in tissue repair and wound healing processes. Its ability to stimulate cell migration and tissue regeneration supports the body’s ability to heal injuries.
- Enhancing Tissue Protection: Thymosin beta-4 has been shown to protect cells from damage caused by oxidative stress and other harmful factors, promoting overall tissue health.
- Regulating Immune Signaling: Thymosin beta-4 can modulate various immune signaling pathways, contributing to a well-coordinated and controlled immune response.
Tiger 17 – Dermal Healing Peptide
One of the major health concerns worldwide is hard-to-treat wounds such as diabetes-induced skin ulcers and burn injuries. These wounds require long and sterile treatments as they increase the affected individual’s risk of infection and permanent tissue damage. Recently, clinical trials have been conducted to find the ideal treatment for debilitating wounds. Researchers found that small peptides such as Tiger 17 possess potent wound healing capacity via their actions on the production of wound healing agents such as transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) and positive effects on the stages of healing.
Valproic acid + PTD-DBM – Connective Tissue Repair
Valproic acid is an anticonvulsant medication that is primarily used to treat epilepsy, bipolar disorder, neuropathic pain, migraine, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and other psychological disorders. PTD-DBM is a man-made peptide that is known to fight hair loss. It exerts its benefits on hair health by affecting the production of the CXXC-type zinc finger protein 5 (CXXC5). The combination treatment of PTD-DBM and valproic acid can accelerate the healing of wounds. The mechanism behind this is by stimulating the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide (VIP) – Naturally Occurring Peptide with Anti-inflammatory Properties
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) is a peptide hormone of 28 amino acids. It is found in the intestines, pancreas, and central nervous system. It is involved in various important bodily functions such as heart contraction, blood circulation, energy production, blood pressure regulation, and smooth muscle relaxation. VIP promotes wound healing by stimulating tissue and blood vessel growth, regulating inflammation and nerve regeneration, and promoting the survival of cells.
Peptides for healing purposes should always be administered under the careful guidance and supervision of a qualified healthcare professional. While peptides offer promising potential in various therapeutic applications, their effects can be potent and specific to individual needs. A healthcare professional can determine the best healing peptides, their dosage, and their administration method by assessing a patient’s medical history, current health status, and treatment goals.
A qualified healthcare professional can monitor the patient’s response to the treatment, identify any potential side effects, and make necessary adjustments to ensure optimal efficacy and safety. By seeking the expertise of a healthcare professional, individuals can benefit from the full potential of peptides for healing while minimizing risks and ensuring a well-informed and tailored approach to their healthcare.
Peptides are versatile molecules that can aid in tissue repair and regeneration while also contributing to effective weight management. If you’re considering weight loss options, exploring the potential of peptides could offer a promising solution. Looking for effective weight loss options? Consider exploring Tesofensine as another option for achieving your weight loss goals. Take the first step towards a healthier you today!
Side Effects of Peptides for Wound Healing

Peptides used for wound healing generally have a good safety profile, but like any medical treatment, they may have potential side effects. It’s essential to use wound healing peptides under the supervision and guidance of a qualified healthcare professional. Some possible side effects of peptides for wound healing may include:
- Skin irritation
- Allergic reactions
- Infection
- Excessive inflammation
- Adverse interactions with other medications or treatments
- Undesirable tissue growth
- Systemic effects
It’s crucial to disclose any pre-existing medical conditions, allergies, or medications being taken to the healthcare professional before using wound healing peptides. This information will help assess the suitability of the treatment and minimize the risk of potential side effects.
While peptides offer valuable benefits for wound healing, the dosage and application method should be carefully determined to ensure optimal efficacy and safety. Regular monitoring and follow-up with the healthcare provider during the course of treatment can help identify and address any side effects promptly.
FAQ
Which type of peptides help with the stages of wound healing?
Various types of peptides have been studied for their potential to aid in the stages of wound healing. During the inflammatory stage, antimicrobial peptides help combat infections, and anti-inflammatory peptides reduce excessive inflammation. In the proliferation stage, growth factor peptides stimulate cell proliferation and collagen peptides enhance collagen production for tissue repair. Angiogenic peptides, such as BPC-157, promote the formation of new blood vessels to improve blood supply. Lastly, in the remodeling stage, peptides with tissue-remodeling properties help reorganize and strengthen the healing tissue. Overall, different types of peptides play critical roles in supporting and accelerating the wound-healing process by targeting specific aspects of each stage.
Do peptides help you heal faster?
Yes, numerous peptides have shown the potential to help promote faster and more efficient healing in certain contexts. Depending on the specific type of peptide and the wound’s nature, peptides can stimulate cell proliferation, collagen synthesis, angiogenesis, granulation tissue formation, and tissue repair, all of which contribute to accelerated wound healing and a shorter recovery process.
Do peptides help with wound healing?
Yes, peptides have shown promising potential in aiding wound healing. Peptides are short chains of amino acids that can influence cellular processes, and certain peptides have been specifically designed to promote tissue repair and regeneration. These wound-healing peptides can accelerate the healing process by stimulating cell proliferation, collagen synthesis, angiogenesis, and modulating the immune response. Other peptides may also help with wound healing by boosting GH and IGF-1 levels. When considering this treatment, make sure to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best peptides for your condition.
What is the therapeutic potential of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) for wound healing?
AMPs have been recognized for their immunomodulatory properties and their ability to facilitate wound healing. Specific AMPs, such as defensins and cathelicidin LL-37, are produced by various cell types, including keratinocytes. These peptides contribute to the inhibition of skin infections and provide means to a faster recovery from a skin wound.
Are healing peptides legal?
In many countries, certain healing peptides are legally available and approved for medical use, especially when prescribed and administered by qualified healthcare professionals for specific conditions. The legality of peptides may also depend on their specific intended use and the regulations set forth by health authorities in each country. Therefore, individuals interested in using healing peptides should consult with a healthcare professional to ensure that the peptides they are considering are legal, safe, and appropriate for their specific medical needs.
What is the best peptide for tissue regeneration?
Among the multitude of peptides, several have demonstrated notable potential in promoting wound healing. The best peptides for tissue regeneration are BPC-157, thymosin beta-4, Melanotan 2 (II), Sermorelin, and GHK-Cu. These peptides have garnered attention for their beneficial effects on tissue injury.
How long do peptides take to work on the skin?
The time it takes for peptides to work on the skin can vary depending on several factors, including the specific type of peptide, the concentration used, the individual’s skin type, and the targeted skin concern. Some people may notice initial improvements in their skin’s texture and appearance within a few days to a couple of weeks of using peptide-based skincare products. However, for more significant and long-term results, it is often recommended to use peptide-based skincare products consistently for at least 4 to 12 weeks.
Are peptides good for damaged skin barrier?
When the skin barrier weakens and develops cracks, it can lead to various skin problems like acne, eczema, and rosacea. However, the application of skincare products containing peptides can reinforce the skin barrier, assisting in its integrity and, as a result, promoting overall skin health. By strengthening the skin barrier, peptides contribute to maintaining healthy and problem-free skin.
Are peptides good for damaged skin?
Peptides have the ability to alleviate inflammation, facilitate the repair of damaged skin, and promote a more even skin tone. By effectively addressing inflammation, peptides contribute to the overall improvement and restoration of the skin’s health and appearance.
Why are antimicrobial peptides better than antibiotics?
AMPs are considered better than antibiotics for several reasons. First, AMPs have a broader spectrum of activity, meaning they can target a wide range of bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens, whereas antibiotics often work against specific types of bacteria. This makes AMPs more versatile in fighting infections. Second, pathogens are less likely to develop resistance to AMPs compared to antibiotics, which can become less effective over time. Third, AMPs can also stimulate the immune system, enhancing the body’s natural defense against infections. Additionally, AMPs can have lower toxicity to human cells, reducing the risk of harmful side effects. Overall, AMPs show great promise as potential alternatives or complements to traditional antibiotics in combating infections.
Can peptides heal cartilage?
Peptides have shown promise in stimulating cartilage repair and regeneration, making them a potential avenue for cartilage healing. Cartilage is a type of connective tissue found in joints and other areas of the body, and it has a limited capacity for self-repair due to its avascular nature (lack of blood vessels). In preclinical animal models and cartilage cell cultures, peptides have demonstrated the ability to enhance cartilage tissue repair.
Do peptides help scars?
Yes, peptides can help with scars. Numerous peptides have been studied for their ability to stimulate collagen production, which is essential for improving the appearance and texture of scars. By enhancing collagen synthesis, peptides can help reduce scar visibility, smooth out uneven scar tissue, and improve overall skin texture. Additionally, some peptides have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help minimize redness and swelling associated with scars. While peptides have beneficial effects on scars, individual results may vary, and it’s essential to use them under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist to ensure proper use and safety.
What is the role of antimicrobial peptides in human skin and in skin infectious diseases?
AMPs play a crucial role in human skin as natural defenders against harmful bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. They are part of the innate immune system and act as the body’s first line of defense, helping to keep the skin protected from infections. In response to microbial threats, the skin cells produce AMPs that target and neutralize these invaders. AMPs are particularly important in skin infectious diseases, as they can combat various microbes, including drug-resistant strains, and prevent infections from spreading. However, certain skin conditions or diseases can disrupt AMP production or function, making the skin more susceptible to infections.
Is antimicrobial peptides a chemical defense mechanism?
Yes, AMPs are a chemical defense mechanism used by various organisms, including humans, to protect against harmful bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. AMPs are naturally occurring short chains of amino acids that can be found in various tissues and bodily fluids. When the body detects the presence of harmful microbes, it releases AMPs to attack and destroy these invaders. AMPs work by disrupting the structure of the pathogens’ cell membranes or interfering with their essential cellular processes, effectively killing or neutralizing them. This chemical defense mechanism helps the body defend against infections and maintain a healthy balance between the host and microorganisms. AMPs play a crucial role in the innate immune system and serve as an important frontline defense against various infectious agents.
Are healing peptides steroids?
In contrast to conventional anabolic steroids that may come with undesired side effects, healing peptides provide a more precise and focused approach to aid the body’s natural healing and growth mechanisms. These peptides have the ability to selectively interact with specific receptors in the body, initiating a cascade of advantageous effects that promote overall well-being and facilitate desired healing and growth processes.
What are peptides for better health?
Peptides for better health are short chains of amino acids that can positively impact various aspects of your well-being. Some of the best healing peptides are BPC 157 and thymosin beta 4. There are various other peptides that can contribute to maintaining good overall health through their beneficial effects on muscle growth, muscle repair, bone density, cardiac function or heart function, and other body systems.
Are peptides good for injuries?
Yes, peptides have healing benefits for physical injuries. Peptides for healing stimulate cell growth, collagen production, blood vessel formation, and granulation tissue formation, all of which are essential for healing injured tissues. By supporting these processes, peptides can aid in the recovery of various injuries, including cuts, burns, and musculoskeletal injuries. However, it’s essential to use peptides for healing injuries under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional to ensure proper dosing and safety.
How long do peptides take to work on the skin?
Peptides typically start showing initial improvements on the skin within a few days to a couple of weeks of consistent use. They may help produce anti-aging effects such as better skin hydration, smoother texture, and improved tone. However, for more significant and long-term results like increased collagen production and reduced fine lines and wrinkles, it’s best to use peptide-based skincare products consistently for at least 4 to 12 weeks. If you have a skin wound, you will need to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best peptides for your condition.
Do peptides help dry skin?
Peptides play a vital role in the regeneration and repair of damaged cells, while also stimulating collagen production, which helps slow down the aging process. As a result, peptides are a preferred choice for moisturizers among a wide range of individuals, including those with sensitive, dry, and acne-prone skin.
Can peptides heal injuries?
Peptides for healing can potentially accelerate your recovery if you are experiencing inflammation, physical injuries, or other types of injuries. It is important to note that the process of connective tissue repair, including strains, sprains, and similar injuries, usually requires a certain amount of time.
Are peptides stable in skincare?
Certain studies indicate that natural peptides exhibit instability when dissolved in water solutions, which poses a challenge for many skincare products that incorporate water as an ingredient. As a result, synthetic peptides are often favored in the realm of skincare due to their enhanced stability and generally more affordable nature.
Do peptides help with inflammation?
Yes, peptides can help reduce inflammation. When peptides interact with cells involved in the inflammatory response, they can regulate the production of inflammatory molecules, leading to a calming effect on the inflamed area. By reducing inflammation, peptides may provide relief from discomfort and support the body’s natural healing processes.
Do peptides boost the immune system?
Yes, some peptides have been studied for their potential to boost the immune system. Peptides like BPC-157 and thymosin beta 4 have shown promise in reducing inflammation, which is essential for a healthy immune response. Clinical trials have shown that these peptides have anti-aging properties and the ability to support tissue repair and regeneration, which are crucial for overall immune health.
Can peptides thicken skin?
Peptides are fragments of amino acids that combine to create proteins. Certain types of peptides have the ability to instruct the body to increase the production of a vital protein called collagen. By stimulating collagen synthesis, peptides contribute to maintaining the firmness and thickness of the skin.
Are peptides generally safe and recommended for wound healing?
Yes, peptides are generally considered safe and can be recommended for wound healing when used appropriately. Peptides are naturally occurring or synthetic short chains of amino acids that can help promote tissue repair and regeneration. Certain peptides, like BPC-157 and thymosin beta 4, have shown promise in enhancing wound healing by stimulating cell growth, collagen production, and angiogenesis. When used under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional, peptides can be beneficial in supporting the wound healing process and improving overall outcomes. However, individual responses to peptides may vary, and it’s essential to follow the healthcare professional’s instructions and ensure the wound is appropriately assessed and treated.
What are bioactive peptides?
Bioactive peptides are short chains of amino acids derived from proteins found in various food sources, such as milk, fish, meat, and plants. These peptides have specific physiological effects on the body and can positively influence various biological processes, such as digestion, blood pressure regulation, immune response, and antioxidant activity. Bioactive peptides are known for their potential health benefits and have been studied for their role in promoting overall well-being and disease prevention. They are often used as functional ingredients in food products and nutraceuticals to harness their health-promoting properties.
Do peptides improve heart function?
Yes, some peptides have been shown to improve heart function. These peptides include:
- Natriuretic peptides: These peptides are released by the heart in response to increased pressure. They have a number of beneficial effects on the heart, including reducing blood pressure, increasing blood flow, and protecting the heart from damage.
- Myocardial growth factors: These peptides help to repair and regenerate damaged heart muscle. They have been shown to improve cardiac function in patients with heart failure.
- Peptide hormones: These peptides, such as ghrelin and insulin, have a number of effects on the heart, including improving blood sugar control, reducing inflammation, and protecting the heart from damage.
Do peptides increase bone density?
Yes, certain peptides have shown potential in increasing bone density. These peptides mimic the effects of naturally occurring hormones involved in bone metabolism, promoting the activity of bone-forming cells (osteoblasts), and increasing the rate of bone remodeling.
Success Stories
 before after
before after
At the age of 60, I look and feel better than I ever have in my entire life! Switching my health program and hormone replacement therapy regimen over to Genemedics was one of the best decisions I’ve ever made in my life! Genemedics and Dr George have significantly improved my quality of life and also dramatically improved my overall health. I hav...
Nick Cassavetes ,60 yrs old
Movie Director (“The Notebook”, “John Q”, “Alpha Dog”), Actor and Writer
 Before After
Before After
I am now in my mid-sixties and feel better than I did in my 20’s. Many people have commented that I actually look 20 years younger since I started the program at Genemedics.
Calling Dr. George has proven to be one of the best decisions I have made in my life. Doctors and society convince us that developing various health issues and negative sy...
Pamela Hill ,66 yrs old
Call 800-277-4041 for a Free Consultation
- Usually takes 15-30 minutes
- Completely confidential
- No obligation to purchase anything
- We will discuss your symptoms along with your health and fitness goals
- Free post-consult access for any additional questions you may have
About
Genemedics® Health Institute is a global premier institute dedicated to revolutionizing health and medicine through healthy lifestyle education, guidance and accountability in harmony with functional medicine. Our physician-supervised health programs are personally customized to help you reach your health and fitness goals while looking and feeling better than ever.
Quick Links
Our Services
Our Locations
© Copyright Genemedics Health Institute. All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy.

