GENEMEDICS APP
GENEMEDICS NUTRITION
Magnesium (Boosts Energy Levels)
Author: Dr. George Shanlikian, M.D. | Last Updated: November 28th, 2024
- Home
- >
- Health Library
- >
- Magnesium (Boosts Energy Levels)
- 5-amino-1MQ
- Aminophylline
- Aniracetam
- ARA 290
- Argireline + Leuphasyl
- BPC-157
- Bremelanotide
- Cerebrolysin
- CJC-1295
- Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide
- Dihexa
- Elampretide (SS-31)
- Epithalon
- FG Loop Peptide (FGL)
- GHK-Cu
- Ginsenoside Rg3
- Glycyrrhetinic Acid
- Ipamorelin
- Kisspeptin
- KPV
- LL-37
- Melanotan 1
- Melanotan 2
- Mitochondrial ORF of the twelve S c (MOTS-c)
- MK-677 (IBUTAMOREN)
- Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+)
- Nicotinamide Riboside
- NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide)
- Noopept
- Pegylated Mechano Growth Factor
- Selank
- Semax
- Sermorelin
- SRT2104
- Tesamorelin
- Thymosin Alpha 1
- Thymosin Beta 4
- Tiger 17
- Valproic Acid
- Valproic acid + PTD-DBM
- Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide
- Zinc-Thymulin
- Potential Health Benefits of Magnesium
- Key Takeaways
- What is Magnesium?
- How Magnesium Works
- Chemical Structure of Magnesium
- Research on Magnesium
- Magnesium Daily Intake
- Magnesium Supplements
- Magnesium Deficiency
- What is Magnesium used For?
- What is Magnesium Glycinate?
- Magnesium Tablets
- Magnesium Side Effects
- FAQ
- Reference
Book a Free Consultation
Table of Contents
- Potential Health Benefits of Magnesium
- Key Takeaways
- What is Magnesium?
- How Magnesium Works
- Chemical Structure of Magnesium
- Research on Magnesium
- Magnesium Daily Intake
- Magnesium Supplements
- Magnesium Deficiency
- What is Magnesium used For?
- What is Magnesium Glycinate?
- Magnesium Tablets
- Magnesium Side Effects
- FAQ
- Reference
Potential Health Benefits of Magnesium
Magnesium benefits include enhancing energy production, mood stabilization, sleep improvement, and constipation prevention, as well as relieving muscle aches and lowering the risk of cardiovascular disease. It also plays a crucial role in managing type 2 diabetes by improving symptoms and preventing its development, in addition to fighting inflammation.
- Boosts energy levels [1-4]
- Helps stabilize mood [5-13]
- Improves sleep quality [14-24]
- Prevents constipation [25-32]
- Relieves muscle aches and spasms [33-46]
- Lowers the risk of cardiovascular disease [47-58]
- Improves symptoms of type 2 diabetes and prevents its development [59-69]
- Fights inflammation [70-84]
Key Takeaways
- Magnesium serves as a crucial cofactor for over 300 enzymatic reactions in the body. These reactions are involved in various processes such as energy production, DNA and RNA synthesis, muscle function, and regulation of blood pressure.
- Magnesium plays a significant role in metabolic pathways, including those related to adenosine triphosphate (ATP) metabolism. It is essential for insulin metabolism, blood sugar regulation, and the synthesis of proteins.
- Adequate magnesium intake is associated with cardiovascular health. It helps regulate blood pressure, maintain normal heart rhythm, and has been linked to improved serum lipid profiles, potentially reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Magnesium is crucial for the regulation of muscular contraction, including the heart muscle. It is involved in oxygen uptake, electrolyte balance, and can impact exercise performance. Magnesium deficiency may lead to muscle cramps and weakness.
- Magnesium is vital for bone health, working in tandem with calcium and vitamin D. It contributes to bone density and helps prevent conditions like osteoporosis, playing a crucial role in maintaining bone mineral density. A balanced intake of magnesium is essential for overall skeletal development and maintenance, ensuring that bone mineral density is optimized to support a strong and healthy framework.
What is Magnesium?
Magnesium is a versatile mineral serving as a cofactor in over 300 enzymatic reactions crucial for energy production, DNA and RNA synthesis, muscle function, and blood pressure regulation. Playing a key role in metabolic pathways, magnesium supports ATP metabolism, insulin regulation, and protein synthesis. Adequate magnesium intake is linked to cardiovascular health, helping regulate blood pressure and improve lipid profiles. Essential for muscle function, magnesium impacts oxygen uptake, electrolyte balance, and exercise performance, preventing issues like muscle cramps. Additionally, magnesium is vital for bone health, collaborating with calcium and vitamin D to maintain bone density and prevent conditions such as osteoporosis. A balanced magnesium intake is fundamental for overall skeletal development and maintenance.
How Magnesium Works
Magnesium operates as a vital mineral in the body, participating in over 300 enzymatic reactions critical for diverse physiological functions. Serving as a cofactor, magnesium facilitates these enzymatic processes, including energy production, DNA and RNA synthesis, muscle contraction, and blood pressure regulation. It plays a key role in metabolic pathways, supporting ATP metabolism, insulin regulation, and protein synthesis. Magnesium is essential for cardiovascular health, contributing to blood pressure regulation and improved lipid profiles. Additionally, it influences muscle function, impacting oxygen uptake and electrolyte balance, which is crucial for exercise performance. Moreover, magnesium collaborates with calcium and vitamin D for bone health, contributing to bone density and overall skeletal development.
Chemical Structure of Magnesium
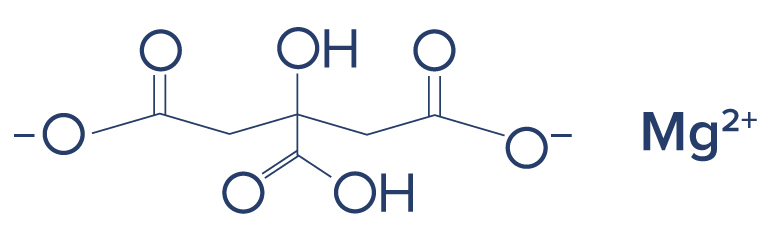
Research on Magnesium
A. Boosts Energy Levels

Magnesium boosts energy levels by playing a pivotal role in cellular energy production. It is a key component of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of the cell, involved in converting glucose into energy. By activating ATP, magnesium ensures that our cells have the fuel they need to perform bodily functions efficiently, from muscle contractions to nerve transmission. This essential mineral thus helps maintain high energy levels and supports overall vitality.
The energy-boosting properties of magnesium are backed by a number of studies:
- There is evidence that magnesium deficiency impairs exercise performance and enhances the negative consequences of vigorous physical activity. Based on dietary surveys and recent human experiments, increased intake of magnesium through diet or supplements has beneficial effects on exercise performance in magnesium-deficient individuals. [1]
- Studies show that Mg can enhance exercise performance by improving glucose availability in the brain, muscles, and blood, and reducing lactate accumulation in muscles. [2] Human studies have mainly examined physiological effects on diastolic blood pressure and systolic blood pressure, heart rate, and VO₂ max, but evidence also suggests a positive impact on muscle performance and strength. Intervention studies indicate that Mg supplementation can improve functional indices such as quadriceps torque, and in elderly women, it has been shown to enhance gait speed and chair stand time, highlighting its importance in both exercise performance and daily functional activities.
- Magnesium, the fourth most abundant mineral and a crucial intracellular divalent cation, plays a vital role in over 300 metabolic reactions in the body. It supports normal nerve and muscle function, heart rhythm, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, immune system, bone integrity, and regulates blood glucose levels while also enhancing calcium absorption. Given its significant involvement in energy production, muscle function, and glucose management, magnesium has been extensively researched as a performance enhancer for athletes. [3]
- A study investigated the effects of magnesium (Mg) on glucose and lactate dynamics in rats during and after exercise. [4] Pretreatment with magnesium sulfate significantly increased glucose levels approximately two-fold in muscle, blood, and brain during exercise compared to the control, indicating enhanced glucose availability. Furthermore, while lactate levels rose sharply in all areas during exercise in both groups, the Mg-treated rats showed a further increase in brain lactate during exercise and improved lactate clearance in muscle post-exercise, suggesting that Mg plays a crucial role in energy production and exercise performance by modulating glucose utilization and lactate clearance.
B. Helps Stabilize Mood

Magnesium improves mood by regulating neurotransmitters, which are chemicals in the brain that transmit messages between nerve cells and the brain. It plays a crucial role in the function of the nervous system and the regulation of the stress-response system. Magnesium’s ability to modulate the activity of the body’s stress-response system helps prevent the brain from becoming overstimulated, which can lead to anxiety, stress, and depression. Therefore, by maintaining adequate levels of magnesium, it can help stabilize mood, reduce stress levels, and contribute to overall emotional well-being.
Studies support the mood-enhancing effects of magnesium:
- Magnesium plays a crucial role in brain biochemistry and neuronal membrane fluidity, with deficiency linked to various neuromuscular and psychiatric symptoms, including depression. Despite mixed results regarding plasma/serum magnesium levels as indicators for depressive disorders, magnesium compounds are increasingly recognized for their therapeutic potential in treating not only depression but also migraines, alcoholism, asthma, heart diseases, and more. [5] Magnesium’s mechanisms as an antidepressant are not fully understood, but its impact on multiple systems related to depression development is acknowledged. Historical and contemporary research supports the efficacy and safety of magnesium supplementation, highlighting its significance in both conventional and homeopathic medicine as a treatment for mental health issues.
- A study investigated the impact of magnesium supplementation on depression in patients with magnesium deficiency, involving 60 individuals divided into two groups: one receiving magnesium oxide and the other a placebo for 8 weeks. [6] Results showed significant improvements in magnesium levels and depression scores, particularly in the magnesium group, where a notable reduction in the Beck Depression Inventory-II scores was observed compared to the placebo group. The findings suggest that daily intake of 500 mg magnesium oxide can effectively enhance depression status and correct magnesium deficiencies in depressed patients, indicating the importance of assessing and addressing magnesium levels in depression treatment.
- A study reviewed scientific literature from 2010 to March 2020 to assess the link between magnesium levels and various psychiatric disorders, including depression, anxiety, ADHD, autism, OCD, schizophrenia, and eating disorders, across 32 articles. [7] The findings indicate a notable association between low magnesium levels and depression, with some studies showing improvement in depressive symptoms following magnesium supplementation, either alone or in combination with antidepressants. However, the results regarding magnesium’s effectiveness and its plasma levels in other psychiatric conditions like anxiety, ADHD, and autism were mixed and less conclusive. Despite the variability in outcomes, the evidence suggests potential benefits from magnesium supplementation in managing psychiatric symptoms, underscoring the need for well-designed clinical trials to further explore magnesium’s therapeutic role and optimal use in psychiatric treatment.
- Major depression, a debilitating mood disorder, may not always respond well to antidepressants, which have been linked to increased suicide rates, especially among young people. [8] Magnesium deficiency, known to cause neuropathologies, exacerbates this issue as modern diets and water supplies often lack adequate magnesium, crucial for regulating neuronal calcium channels and nitric oxide production. Hypothesized as an effective treatment for major depression due to intraneuronal magnesium deficits caused by dietary insufficiencies, stress, and excessive dietary calcium, magnesium supplementation has shown rapid recovery in case histories. These findings suggest not only magnesium’s potential in treating depression and related mental health issues but also highlight the need for further research into magnesium deficiency as a public health concern, recommending the fortification of refined grain and water with magnesium to historical levels.
- A study investigated the link between dietary magnesium intake and depression among 8,894 US adults using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2007-2010). [9] Results revealed a statistically significant association between very low magnesium intake (less than 184 mg/day) and increased risk of depression, particularly in individuals younger than 65 years old. Conversely, in seniors, low magnesium intake appeared to have a protective effect against depression. These findings underscore the importance of magnesium in mental health and suggest age-specific impacts, highlighting the need for further research to understand the protective role of magnesium intake in older adults.
- A double-blind, randomized study on 32 women with premenstrual syndrome (PMS) assessed the impact of oral magnesium (Mg) supplementation on premenstrual symptoms. [10] Over two menstrual cycles, participants received either magnesium pyrrolidone carboxylic acid (360 mg Mg) or a placebo from the 15th day of their cycle until the start of menstruation. Results showed that magnesium significantly reduced total premenstrual distress as well as specific symptoms related to “pain” and “negative affect.” Additionally, significant increases in magnesium levels were observed in lymphocytes and polymorphonuclear cells but not in plasma and erythrocytes. These findings suggest magnesium supplementation as an effective treatment for mood-related PMS symptoms.
- An open-label, randomized, cross-over trial involving 126 adults with mild-to-moderate depression found that 6 weeks of magnesium chloride supplementation (248 mg of elemental magnesium per day) resulted in a significant improvement in depression and anxiety symptoms, with a net decrease in PHQ-9 and Generalized Anxiety Disorders-7 scores. [11] The study, conducted between June 2015 and May 2016, demonstrated high adherence rates (83%) and good tolerability, with 61% of participants expressing willingness to continue using magnesium supplements. The positive effects of magnesium on depression were observed within two weeks and were consistent across various demographic and clinical subgroups, suggesting magnesium’s potential as a fast-acting and well-tolerated treatment option for mild-to-moderate depression.
- In an 8-week randomized controlled study of individuals with low magnesium levels and severe stress, magnesium combined with vitamin B6 was found to significantly reduce stress more effectively than magnesium alone. [12] This secondary analysis focused on the impact of these supplements on depression, anxiety, and quality of life (QoL). Participants, all experiencing high stress as measured by the DASS-42 stress subscale, received either a combination of magnesium and vitamin B6 or magnesium alone. Results showed notable improvements in anxiety and depression scores for both groups, with a particularly rapid improvement within the first four weeks. Additionally, QoL enhancements were observed over the 8 weeks, with a more significant increase in perceived physical activity capacity in those taking both magnesium and vitamin B6. The study concludes that magnesium supplementation, both with and without vitamin B6, offers significant clinical benefits for individuals with stress and low magnesium levels.
- Sixty percent of clinical depression cases are considered treatment-resistant depression (TRD), with magnesium deficiency implicated as a significant factor due to its role in neuronal injury and neurological dysfunction, potentially manifesting as major depression. [13] Studies have shown that magnesium supplementation produces anti-depressant-like effects in animals, similar to strong anti-depressant drugs, and low cerebral spinal fluid and brain magnesium levels have been observed in patients with TRD and suicidal tendencies. Despite the historical and recent evidence supporting magnesium’s effectiveness in treating TRD, including a 2008 trial where magnesium was as effective as imipramine for depression in diabetics without side effects, comprehensive clinical trials are scarce. The removal of magnesium from processed foods and the addition of calcium, glutamate, and aspartate may exacerbate affective disorders. This evidence suggests that dietary magnesium inadequacy could be a primary cause of TRD, advocating for magnesium supplementation as a treatment, potentially benefiting nearly all individuals with depression.
C. Improves Sleep Quality

Magnesium improves sleep quality by regulating neurotransmitters involved in the sleep cycle, including increasing gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) levels in the brain, which promotes relaxation and stress reduction. Its role in maintaining healthy levels of GABA facilitates the transition to sleep and enhances the overall quality of sleep. Additionally, magnesium’s muscle-relaxing properties can alleviate physical discomfort, further contributing to a restful night’s sleep by reducing instances of nighttime awakenings and ensuring deeper, more restorative sleep phases.
A number of evidence supports the benefits of magnesium on sleeping problems:
- A systematic review aimed to explore the association between magnesium (Mg) intake and sleep patterns in adults by analyzing observational and interventional studies sourced from PubMed, Scopus, and ISI Web of Science up to November 2021. [14] Involving 7,582 subjects across 9 studies, it found observational evidence suggesting a positive link between magnesium status and sleep quality, such as reduced daytime sleepiness and longer sleep duration. However, randomized clinical trials (RCTs) presented mixed results, highlighting the need for more comprehensive trials to conclusively determine magnesium’s effect on sleep disorders.
- In a longitudinal study analyzing 3,964 participants from the CARDIA study, magnesium (Mg) intake was found to be marginally associated with improved sleep quality and significantly associated with reduced likelihood of short sleep duration (<7 hours), particularly among individuals without depressive disorders. [15] The study, which assessed dietary and supplementary Mg intake as well as the calcium-to-magnesium (Ca:Mg) intake ratio, found no significant association between Ca:Mg and sleep outcomes. These findings suggest a potential beneficial role of magnesium in promoting better sleep quality and longer sleep duration, highlighting the need for randomized controlled trials with objective sleep measures to further explore this relationship.
- In a double-blind randomized clinical trial involving 46 elderly subjects, magnesium supplementation was found to significantly improve various measures of insomnia compared to a placebo. [16] Over an 8-week period, subjects receiving 500 mg of magnesium daily experienced increases in sleep time, sleep efficiency, serum renin, and melatonin levels, along with decreases in the insomnia severity index (ISI) score, sleep onset latency, and serum cortisol concentration. These results suggest that magnesium supplementation could be an effective strategy to improve both subjective and objective insomnia parameters in the elderly, highlighting magnesium’s potential role in enhancing sleep quality and circadian rhythm regulation.
- A review analyzed three randomized control trials comparing oral magnesium supplementation to placebo in 151 older adults across three countries, using databases like MEDLINE and EMBASE. [17] The pooled analysis indicated a significant reduction in sleep onset latency by 17.36 minutes with magnesium supplementation, although the increase in total sleep time was not statistically significant. Despite the moderate-to-high risk of bias and the low to very low quality of evidence, the findings suggest that oral magnesium, being affordable and widely available, may offer some benefit for insomnia symptoms in older adults when taken in doses of less than 1 gram up to three times a day. The current literature’s quality, however, is insufficient for making well-informed clinical recommendations.
- In an experiment involving 100 adults with poor sleep quality, participants were assigned to receive either a 320 mg/day magnesium supplement or a placebo for seven weeks. [18] Initial assessments showed that 58% of participants consumed less than the recommended amount of magnesium, associated with higher BMI and plasma C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, indicating chronic inflammatory stress. While overall sleep quality improved for all participants, magnesium supplementation specifically increased serum magnesium levels in those with initial deficiency and decreased plasma CRP levels in participants with higher baseline inflammatory markers. These results suggest a link between low magnesium status and increased chronic inflammatory stress, potentially alleviated by magnesium intake. However, the improvement in sleep quality, regardless of supplementation, points to the need for further research to clarify the relationship between magnesium status and sleep quality.
- Using data from the Jiangsu Nutrition Study, which included 1487 adults, research indicated that higher dietary magnesium intake is associated with a reduced likelihood of experiencing daytime falling asleep among women, with an intake mean of 332.5 mg/day. [19] Despite these findings, no significant associations were observed between dietary magnesium consumption and other sleep disorder symptoms such as daytime sleepiness or snoring at night for either gender. The study highlights the potential gender-specific benefits of dietary magnesium in mitigating certain sleep disorder symptoms, underscoring the need for further investigation into the role of magnesium in sleep health at the population level.
- In a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial conducted in a long-term care facility in Pavia, Italy, involving 43 elderly participants with primary insomnia, it was found that a nightly regimen of melatonin (5 mg), magnesium (225 mg), and zinc (11.25 mg) mixed with pear pulp significantly improved sleep quality over an 8-week period compared to a placebo. [20] The supplemented group showed notable improvements in sleep quality scores, ease of falling asleep, quality and restorative value of sleep, morning alertness, and quality of life, as measured by the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index, Leeds Sleep Evaluation Questionnaire, Short Insomnia Questionnaire, and SF-36, respectively. Total sleep time, assessed by a wearable sensor, also increased significantly, indicating that the combination of melatonin, magnesium, and zinc effectively enhances sleep and life quality in elderly individuals with primary insomnia.
- A study conducted a systematic review of clinical studies to investigate the relationship between serum magnesium (Mg) levels and obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA), revealing that OSA patients often have lower serum Mg levels compared to healthy controls, with a meta-analysis indicating a significant deficiency. [21] Although the mean serum Mg level in OSA patients falls within the normal range, the severity of OSA negatively impacts these levels, which tend to improve with OSA treatment. Additionally, low serum Mg levels in OSA patients are associated with increased systemic inflammation and cardiovascular risk, as evidenced by correlations with biomarkers like C-reactive protein and carotid intima-media thickness. These findings suggest that sleep deprivation linked to OSA may lead to Mg depletion, heightening the risk of cardiovascular and metabolic disorders.
- In a clinical trial involving 60 open-heart surgery candidates, magnesium supplementation significantly improved anxiety, depression levels, and sleep quality post-surgery. [22] Participants receiving 500 mg of magnesium oxide daily for five days showed higher magnesium levels, reduced anxiety and depression according to the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), and better sleep quality based on the Petersburg Sleep Quality Inventory (PSQI), compared to the control group receiving routine care. These findings support the inclusion of magnesium supplements in post-operative care plans to enhance recovery outcomes related to psychological well-being and sleep in heart surgery patients.
- In an open clinical study involving 10 patients suffering from insomnia related to periodic limb movements during sleep (PLMS) or mild-to-moderate restless legs syndrome (RLS), oral magnesium therapy showed promising results. [23] Administered at a dose of 12.4 mmol in the evening for 4-6 weeks, magnesium significantly reduced PLMS associated with arousals and moderately reduced PLMS without arousal, while sleep efficiency improved notably. Especially in patients who reported improved sleep or RLS symptoms post-therapy, the effects of magnesium were more pronounced. This study suggests that magnesium treatment could be an effective alternative therapy for patients with mild or moderate RLS or PLMS-related insomnia, highlighting the need for further research on magnesium’s role in RLS pathophysiology and placebo-controlled studies.
- A study aimed at evaluating the efficacy of a magnesium-melatonin-vitamin B complex supplement in treating insomnia, 60 patients were divided into a study group and a control group. [24] The study group, treated with a daily dose of the supplement one hour before sleep for three months, showed a significant reduction in insomnia symptoms as measured by the Athens insomnia scale (AIS), with mean AIS scores decreasing from moderate to mild insomnia levels. In contrast, the control group remained at moderate insomnia levels. The findings suggest that a three-month regimen of Magnesium-melatonin-vitamin B complex supplementation can effectively reduce the severity of insomnia symptoms, demonstrating its potential as a beneficial treatment option for insomnia regardless of the cause.
D. Prevents Constipation

Magnesium prevents constipation by drawing water into the intestines, which softens the stool and makes it easier to pass. This process, known as osmosis, increases stool bulk and encourages bowel movements. Additionally, magnesium helps relax the muscles in the intestinal wall, improving gut motility and further aiding in the elimination process. As a result, adequate magnesium intake is essential for maintaining regular bowel movements and preventing constipation.
Studies show that magnesium is beneficial for gut health:
- Magnesium oxide has long been utilized as a laxative in East Asia based on empirical knowledge, with recent years seeing a revival in interest due to its convenience, low cost, and safety. [25] However, emerging clinical evidence suggests the need for careful consideration of dosage, serum concentration, potential drug-drug interactions, and side effects, particularly in the elderly and those with renal impairment. This review aims to assess the evidence for magnesium oxide’s use in treating constipation, offering a balanced guide to its benefits and limitations.
- In a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study conducted in Japan, magnesium oxide (MgO) was evaluated for its effectiveness in treating chronic constipation (CC) among 34 female patients. [26] The study found that MgO significantly improved overall improvement, spontaneous bowel movements, stool form, and colonic transit time over a 28-day period compared to a placebo. Although MgO did not significantly enhance complete spontaneous bowel movement response rates, it notably improved quality of life related to constipation. This demonstrates MgO’s efficacy as a treatment for CC in patients with mild to moderate symptoms.
- A study explored the relationship between dietary magnesium intake and chronic constipation using data from the 2007-2010 NHANES, including 9,519 participants aged ≥20 years. [27] It found that higher dietary magnesium intake was inversely associated with chronic constipation when defined by stool frequency, particularly among men, indicating a potential beneficial effect of magnesium on bowel health. However, no significant link was observed when constipation was defined by stool consistency. The findings suggest that increasing dietary magnesium might reduce the prevalence of chronic constipation, emphasizing the need for further longitudinal studies to confirm these results.
- A prospective, double-blinded randomized control trial involving 100 children with spastic cerebral palsy (sCP) and chronic constipation demonstrated that oral magnesium sulfate significantly improved constipation symptoms, stool frequency, and consistency compared to a placebo. [28] After a month of treatment, 68% of children in the magnesium sulfate group showed effective, safe relief from constipation versus 9.5% in the placebo group. This intervention also resulted in a noticeable reduction in the time mothers spent assisting with bowel evacuations, highlighting oral magnesium sulfate’s potential to not only alleviate constipation in children with sCP but also to reduce the caregiving burden.
- Functional constipation (FC), a chronic condition without identifiable physiological or anatomical causes, significantly affects quality of life and healthcare costs. [29] Traditionally managed through increased physical activity and dietary adjustments in fiber and water intake, FC often requires medication when these measures fail. Magnesium sulfate, known for its laxative properties and used in magnesium sulfate-rich mineral waters for centuries, has been widely recognized for its effectiveness. Despite its historical use, clinical studies on its efficacy in FC were scarce until the 21st century. Recent reviews of clinical data on magnesium sulfate-rich natural mineral waters have highlighted their potential as a safe, natural treatment option for FC, underscoring their efficacy and safety.
- In a trial involving 64 geriatric long-stay patients aged 65 years or older, all of whom were previously using laxatives, magnesium hydroxide was found to be more effective than bulk-laxative in treating constipation. [30] Patients taking magnesium hydroxide experienced more frequent bowel movements and required less additional laxative support compared to those on bulk-laxative, with more normal stool consistency observed during magnesium hydroxide treatment. Although two patients showed elevated serum magnesium levels, no clinical signs of hypermagnesemia were reported, suggesting magnesium hydroxide’s efficacy and relative safety for constipation relief in elderly patients.
- In the first prospective, double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial comparing a stimulant laxative (senna) and an osmotic agent (magnesium oxide [MgO]) in treating chronic idiopathic constipation, both senna and MgO demonstrated significant efficacy over placebo. [31] Enrolled participants, predominantly women with a long history of constipation, showed marked improvements in overall symptom relief, spontaneous bowel movements, complete spontaneous bowel movements, and quality of life related to constipation, with no severe treatment-related adverse events reported. This study highlights the effectiveness of both senna and MgO as treatment options for chronic constipation, indicating their potential to improve bowel function and patient well-being significantly.
- In an open-label study comparing magnesium (Mg)-enriched formula with a control formula for treating functional constipation in infants ≤6 months old, the Mg-enriched formula significantly improved stool consistency and frequency. [32] Within just 7 days, a greater proportion of infants fed with the Mg-rich formula experienced normal stool consistency and an increased daily stool frequency compared to those on the control formula. By the end of the study, parents reported high satisfaction with the Mg-enriched formula, with the majority expressing willingness to continue its use, demonstrating its effectiveness and parental approval in managing infant constipation.
E. Relieves Muscle Aches and Spasms

Magnesium helps relieve muscle aches and spasms by acting as a natural calcium blocker, which helps muscles relax. When magnesium levels are adequate, muscles can contract and relax properly, preventing cramping and spasms. Additionally, it aids in the transportation of calcium and potassium ions across cell membranes, a process essential for normal muscle function, nerve impulse conduction, and maintaining normal heart rhythm. This mechanism is why sufficient magnesium intake is crucial for preventing and alleviating muscle discomfort.
The benefits of magnesium on muscle aches and spasms are supported by several studies:
- Magnesium supplementation does not significantly reduce the frequency or intensity of skeletal muscle cramps in older adults, suggesting it may not be an effective preventative treatment for this group. [33] However, the effectiveness of magnesium for pregnancy-associated leg cramps remains uncertain due to conflicting research findings, indicating a need for further studies in this specific population.
- Muscle cramps, characterized by sudden, painful contractions of skeletal muscle fibers, can occur idiopathically or be associated with neuromuscular diseases, systemic disorders, and electrolyte imbalances, notably hypomagnesemia. [34] Magnesium plays a critical role in nerve transmission and muscle contraction, suggesting potential benefits for preventing or treating cramps. Despite its marketing as a prophylactic measure and experimental evidence suggesting improved exercise performance through enhanced glucose uptake and reduced lactate accumulation, the effectiveness of magnesium supplementation in cramp management remains uncertain.
- In a double-blind study, magnesium supplementation (350 mg daily for 10 days) significantly reduced muscle soreness among college-aged male and female subjects and showed a positive impact on performance, including total repetitions to failure at varying intensities. [35] Subjects reported lower levels of soreness on a 6-point scale post-supplementation, with improved perceptual responses regarding exertion and recovery compared to the placebo group. While performance improvements approached significance, the study indicates magnesium’s potential to enhance recovery and reduce muscle soreness.
- A study found that magnesium supplementation (350 mg daily for 10 days) significantly reduced muscle soreness and enhanced perceptual recovery in college-aged participants, compared to a placebo group. [36] These findings were accompanied by notable, though not statistically significant, improvements in performance metrics such as repetitions to failure at various percentages of the participants’ one-repetition maximum. Overall, magnesium showed potential benefits for both reducing muscle soreness and improving exercise performance, highlighting its value in sports nutrition and recovery strategies.
- A crossover randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial conducted in Buenos Aires, Argentina, aimed to assess the efficacy of magnesium for treating nocturnal leg cramps but found no significant difference between magnesium and placebo treatments in reducing the number, duration, severity, or sleep disturbances caused by leg cramps. [37] Despite a total of 42 patients completing the study, which involved administering 900 mg of magnesium citrate twice daily for one month, all patients showed improvement over time, suggesting the observed benefits were likely due to natural progression, regression to the mean, or placebo effects rather than the magnesium treatment itself.
- A case report from a pediatric intensive care unit at a tertiary care, university-based children’s hospital detailed the successful use of intravenous magnesium sulfate to control muscle spasms and severe generalized rigidity in a 12-year-old child with moderate to severe tetanus. [38] This approach allowed for the avoidance of prolonged deep sedation, mechanical ventilation, or neuromuscular blockade. The treatment with magnesium sulfate showed significant improvement in the patient’s condition without any adverse effects, suggesting magnesium sulfate as a viable option for managing tetanus-induced muscle spasms and rigidity, with the caveat of close monitoring of the patient’s neurologic, cardiovascular, and respiratory status.
- A randomized, double-blind, cross-over placebo-controlled trial investigated the effectiveness of magnesium citrate in treating nocturnal leg cramps in non-pregnant individuals. [39] Participants received magnesium citrate equivalent to 300 mg of magnesium and a matching placebo for 6 weeks each. The study found a trend towards fewer cramps during magnesium treatment compared to placebo, with a significant number of subjects perceiving magnesium as helpful. Although there was no significant difference in the severity and duration of cramps between the treatments, the findings suggest that magnesium may be an effective treatment option for nocturnal leg cramps, warranting further evaluation. Diarrhea was noted as a side effect of magnesium citrate.
- A study explored the association between chronic musculoskeletal pain (CMP) and cardiovascular disease (CVD), identifying older age, female sex, hypertension, and calcium supplement use as factors linked to increased CMP intensity among CVD patients. [40] Additionally, the efficacy of Ice Power Magnesium In Strong Cream in alleviating muscle cramp pain in the lower extremities was evaluated. Results from 396 outpatients showed significant associations between the aforementioned factors and CMP intensity, while a separate analysis of 73 patients with muscle cramps demonstrated that the cream significantly reduced pain scores over 4 weeks. This indicates that specific demographic and health-related factors can influence CMP severity in CVD patients, and that topical magnesium cream is effective in treating muscle cramps.
- A review of four randomized controlled trials involving 332 pregnant women investigated the efficacy of magnesium supplementation for leg cramps during pregnancy, a symptom affecting 30%-50% of pregnant women. [41] The analysis, which included data up until July 2, 2020, found that magnesium supplementation did not significantly reduce the frequency of leg cramps, improve recovery from leg cramps, or produce significant side effects compared to a control group. The weighted mean difference for the frequency of post-treatment leg cramps and the odds ratios for recovery and side effects indicated that oral magnesium supplementation is ineffective in treating pregnancy-related leg cramps.
- A double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial on 46 older adults suffering from rest (nocturnal) cramps assessed the efficacy of a 5-day intravenous magnesium sulfate infusion in reducing leg cramp frequency. [42] Despite overcoming the oral bioavailability limitations of magnesium, the treatment did not significantly decrease the number of weekly cramps compared to the placebo, with no correlation found between magnesium retention and treatment response. This suggests that magnesium therapy, despite its popular marketing, may not be an effective treatment for rest cramps in the geriatric population.
- A 25-year-old paraplegic man, suffering from a severe and painful spasm in the left hamstring muscle group that resulted in extreme knee flexion, experienced immediate relief after receiving an intravenous injection of 2 g magnesium sulphate. [43] This case, following a T3/T4 vertebral compression fracture sustained three years earlier, highlights magnesium’s potential therapeutic effects on muscle spasms, inviting further discussion on the mechanisms through which magnesium operates to alleviate such conditions.
- A double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial involving 86 pregnant women with frequent leg cramps assessed the efficacy of oral magnesium bisglycinate chelate (300 mg per day) over a 4-week period. [44] The study found that magnesium supplementation significantly reduced both the frequency (86% vs. 60.5%, P=0.007) and intensity (69.8% vs. 48.8%, P=0.048) of pregnancy-induced leg cramps compared to placebo, without notable side effects like nausea and diarrhea. These findings suggest that oral magnesium could be a viable treatment option for managing leg cramps in pregnant women.
- A systematic review of seven randomized controlled trials (RCTs), including 361 participants, assessed the effectiveness of magnesium in treating nocturnal leg cramps (NLC) compared to placebo. [45] While magnesium therapy showed a slight effect in reducing leg cramps per week among pregnant women, it did not significantly affect the general population. Gastrointestinal side effects were slightly more common with magnesium than with placebo, but the overall evidence strength was considered weak due to small study sizes and short follow-up periods. The findings suggest that magnesium may have a modest benefit for pregnant women with NLC, though further, better-designed RCTs are needed.
- In a counterbalanced, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over study involving nine male recreational runners, magnesium supplementation (500 mg/day for 7 days) prior to a 10 km downhill running time trial showed beneficial effects on inflammation and recovery post-exercise. [46] Magnesium intake significantly reduced interleukin-6 levels, indicating less inflammation, and improved recovery of blood glucose and muscle soreness, compared to the placebo. However, there were no significant differences in exercise performance, glucose and lactate levels during the time trial, or in creatine kinase levels and maximal muscle force post-exercise, suggesting that while magnesium may aid in recovery aspects, it does not enhance performance or functional recovery measures directly.
F. Lowers the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
Magnesium plays a pivotal role in cardiovascular health by supporting the normal function of the heart, regulating blood pressure, and maintaining the balance of electrolytes. It helps to prevent the buildup of plaque in the arteries, reducing the risk of atherosclerosis and subsequently lowering the likelihood of heart attacks and strokes. Additionally, magnesium’s ability to improve blood flow and oxygen delivery throughout the body contributes to overall heart health and reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Magnesium, a vital intracellular cation, is crucial for cellular function, enzyme activity, and energy production, especially in the heart where it influences cardiac conduction and contraction by regulating ion channels. [47] It also plays a significant role in vascular health by affecting vascular tone and the process of atherogenesis, thus impacting the development of cardiovascular disease. Kidney disorders can affect magnesium levels, influencing cardiovascular risk. While observational studies link low magnesium with higher cardiovascular disease risks, supplementation trials have shown mixed results, leading to no general recommendation for magnesium supplementation in the absence of proven or suspected hypomagnesemia related to cardiac arrhythmias.
- Magnesium, a key cation in the human body, is integral to many processes crucial for cardiovascular health, including the regulation of vascular smooth muscle tone, endothelial function, and myocardial excitability. [48] It plays a pivotal role in the development and management of various cardiovascular disorders, such as hypertension, atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease, heart failure, and arrhythmias. The review highlights magnesium’s vasodilatory, anti-inflammatory, anti-ischemic, and antiarrhythmic effects, underscoring its importance in both preventing and treating cardiovascular diseases.
- Magnesium (Mg) is crucial for human health, with studies showing that higher Mg intake is linked to a reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases (CVD), including metabolic syndrome, diabetes, hypertension, stroke, and coronary heart diseases. [49] This review synthesizes evidence from epidemiological studies, randomized controlled trials (RCTs), and meta-analyses, highlighting the protective role of dietary and circulating magnesium against major cardiovascular risk factors and CVDs. The findings suggest that magnesium plays a significant role in cardiovascular health, with further research needed to explore its potential benefits in preventing CVD deaths and other cardiovascular conditions.
- A systematic review and meta-analysis examining the relationship between magnesium levels and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk found that higher circulating magnesium levels are linked to a significantly lower risk of CVD and showed a trend towards reduced risks of ischemic heart disease (IHD) and fatal IHD. [50] While dietary magnesium did not show a significant overall association with CVD risk, it was associated with a lower risk of IHD, particularly up to a dietary intake threshold of approximately 250 mg/day. These findings underscore the potential protective effects of magnesium against heart disease and highlight the importance of further clinical trials to explore magnesium’s role in CVD prevention.
- Magnesium is a vital mineral involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions, crucial for blood pressure regulation, glycemic control, and lipid peroxidation, making it essential for cardiovascular health. [51] Despite its abundance in many foods and availability as a supplement, low magnesium intake in industrialized Western countries often leads to a high prevalence of magnesium deficiency, thereby increasing the risk of cardiovascular events and death. This article reviews the impact of magnesium deficiency on the cardiovascular system, highlighting the importance of maintaining adequate magnesium levels for heart health.
- Magnesium intake ranging from 500 mg/d to 1000 mg/d may lower blood pressure by up to 5.6/2.8 mm Hg, though clinical studies show varying results, with some indicating no change in blood pressure. [52] A combined dietary approach that increases magnesium and potassium while decreasing sodium intake proves more effective for blood pressure reduction, often matching the efficacy of antihypertensive medications. Magnesium enhances the effectiveness of all classes of antihypertensive drugs and may improve conditions like insulin sensitivity, hyperglycemia, diabetes, left ventricular hypertrophy, and dyslipidemia. While it’s yet to be definitively shown that magnesium intake can prevent or treat cardiovascular diseases, preliminary evidence and its roles as a natural calcium channel blocker and vasodilator suggest potential benefits in managing hypertension and improving cardiovascular health.
- A review highlights the significant role of increased dietary magnesium in protecting against diabetes, metabolic syndrome, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases by improving insulin resistance, lipid profiles, and reducing inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and platelet aggregability. [53] Magnesium’s benefits are attributed to its actions as a calcium antagonist on vascular smooth muscle and its involvement in energy metabolism and various cellular functions. Despite the strong biological rationale for magnesium’s impact on health, prospective studies show only modest effects on preventing pathologies, and supplementation studies yield inconsistent results. The modest in-vivo role of magnesium deficiency, potential confounding by reverse causality, and the association with other beneficial nutrients suggest that the observed health benefits might be influenced by broader dietary patterns and health-conscious behaviors.
- A wealth of experimental, epidemiological, and clinical studies suggests a critical role for magnesium (Mg2+) in cardiovascular diseases, linking hypomagnesemia with electrolyte imbalances and various heart conditions, including ischemic heart disease and congestive heart failure. [54] Magnesium deficiency contributes to cardiovascular pathology through mechanisms like vasoconstriction of coronary vessels, increased intracellular calcium levels, oxidative stress, and alterations in cardiac cell membrane permeability. Additionally, magnesium’s interaction with calcium plays a pivotal role in myocardial contractility, influencing the heart’s response to stimulants and ischemic stress, particularly in the aged myocardium. Despite the ongoing debate over some mechanisms and the need for further research, the evidence supporting magnesium’s protective role in reducing cardiovascular disease morbidity and mortality is compelling, highlighting the potential benefits of magnesium supplementation in cardiac health management.
- An article provided an overview of magnesium research, detailing its historical development, the effects of magnesium on cardiovascular disease through basic and clinical studies, and the current magnesium intake levels in Japan as of 2002. [55] Basic research has shown that magnesium deficiency can reduce ATPase activity, leading to increased intracellular calcium in blood vessels and subsequent cardiovascular system vasoconstriction. Clinical studies have found significantly lower serum magnesium levels in patients with ischemic heart disease. Furthermore, the National Nutrition Survey in Japan indicated that the magnesium intake among males and females aged 15-49 years falls below the country’s recommended dietary allowances, highlighting a potential area of concern for public health.
- A dose-response meta-analysis of over 1 million participants across 40 prospective cohort studies investigated the impact of dietary magnesium intake on cardiovascular disease (CVD), type 2 diabetes (T2D), and all-cause mortality, revealing mixed results. [56] While no significant link was found between magnesium intake and total CVD or coronary heart disease (CHD), increased magnesium intake was associated with a lower risk of heart failure (22% reduction), stroke (7% reduction), T2D (19% reduction), and all-cause mortality (10% reduction). These findings suggest that enhancing dietary magnesium could potentially offer protective benefits against certain health conditions, underscoring the importance of magnesium in dietary recommendations.
- Magnesium, a crucial yet often neglected electrolyte, participates in over 300 enzymatic reactions including energy metabolism, glucose utilization, and cellular ionic balance. Its deficiency is increasingly common due to factors like poor diet and diuretic use, particularly among the elderly. [57] Associated with various conditions such as hypertension, heart failure, diabetes, and preeclampsia, clinical studies suggest magnesium supplementation can offer significant benefits. Addressing magnesium deficiency involves not only supplementation for those at risk or exhibiting symptoms but also identifying and correcting underlying causes, highlighting the importance of magnesium in maintaining overall health and preventing disease progression.
- In a comprehensive study involving 86,323 women from the Nurses’ Health Study, the relationship between dietary and plasma magnesium levels and the risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) was examined. [58] Despite finding no significant association between magnesium intake and total or nonfatal CHD, an inverse relationship was observed between dietary magnesium intake and fatal CHD, suggesting that higher magnesium consumption could reduce the risk of fatal CHD, potentially through mechanisms related to hypertension management. However, plasma magnesium levels, while lower in CHD cases, did not show an independent association with CHD risk when considering other cardiovascular biomarkers. This indicates that while dietary magnesium may not influence overall CHD incidence, it could play a role in decreasing the risk of fatal outcomes in CHD, possibly mediated by its effects on blood pressure.
G. Improves Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes and Prevents its Development

Magnesium improves symptoms of Type 2 diabetes by enhancing insulin sensitivity and glucose control, contributing significantly to blood sugar control. It participates in the metabolism of sugar, helping to regulate blood glucose levels. Adequate magnesium levels facilitate the action of insulin, making it easier for the body to manage its blood sugar levels effectively. This can lead to improved glycemic control and a reduced risk of diabetes-related complications, making magnesium supplementation beneficial for individuals with Type 2 diabetes or those at risk for developing the condition.
- Magnesium deficiency is common in individuals with diabetes mellitus, influenced by factors such as glucosuria-induced loss, dietary inadequacies, and hyperinsulinemia. [59] While magnesium supplementation has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and secretion in Type 2 diabetes patients, it has not demonstrated a significant impact on glycemic control in either Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes. However, in animal models, magnesium supplementation has been effective in reducing the onset of Type 2 diabetes. Moreover, lower plasma magnesium levels have been associated with severe retinopathy and higher blood pressure, although evidence on blood pressure reduction is inconclusive. These findings highlight the potential role of magnesium in preventing Type 2 diabetes, retinopathy progression, and managing hypertension, warranting further research.
- Oral magnesium supplementation has been shown to positively affect glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity in individuals with diabetes or those at high risk of developing the condition. [60] Research comparing magnesium supplementation to placebo found that magnesium effectively reduces fasting plasma glucose in diabetic patients and improves glucose levels and insulin sensitivity in individuals at high risk for diabetes. These findings suggest that magnesium supplementation could be a beneficial strategy for managing glucose parameters and enhancing insulin sensitivity, indicating its potential role in diabetes prevention and management.
- Type 2 diabetes is often linked to magnesium (Mg) deficits, both extracellularly and intracellularly, with such deficiencies particularly noted in individuals with poor glycemic control. [61] Insulin and glucose levels significantly influence Mg metabolism, with intracellular Mg critical for insulin action and glucose uptake. Lowered Mg levels can impair insulin signaling pathways, exacerbating insulin resistance. The primary causes of Mg depletion in type 2 diabetes are believed to be low dietary intake and increased urinary loss. While some clinical studies suggest that Mg supplementation can improve metabolic profiles in diabetic patients, the evidence is not uniformly conclusive, indicating a need for more extensive research to establish dietary Mg supplementation as a viable public health strategy for diabetes prevention and management.
- Experimental studies and growing evidence have highlighted magnesium’s crucial role in glucose metabolism, suggesting its potential in reducing type 2 diabetes (T2D) risk. [62] Epidemiological research consistently indicates that low dietary magnesium intake correlates with a higher risk of T2D, yet results from randomized controlled trials on magnesium supplementation’s effects on glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity remain mixed and controversial. This divergence points to a clear inverse relationship between dietary magnesium intake and T2D risk from observational studies, while clinical trial outcomes are less definitive and require further investigation to establish magnesium’s role in diabetes prevention and management.
- An article reviewed the relationship between magnesium intake and the incidence of type 2 diabetes (T2D), as well as the impact of magnesium supplementation on glucose metabolism, using data up to May 15, 2019. [63] Analysis of 26 publications involving 35 cohorts showed that higher magnesium intake correlates with a 22% reduced risk of T2D, with each 100 mg daily increase in magnesium intake lowering the risk by 6%. Further examination of 26 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with 1168 participants demonstrated significant benefits of magnesium supplementation in reducing fasting plasma glucose, improving 2-hour oral glucose tolerance test results, fasting insulin levels, and insulin resistance scores, along with reductions in triglyceride levels and blood pressure. Trial sequential analysis confirmed the stability of these benefits, suggesting a dose-response relationship between magnesium intake and reduced T2D risk, and supporting magnesium supplementation to improve glucose parameters in individuals with T2D or at high risk.
- A study systematically reviewed and meta-analyzed randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to assess the impact of magnesium supplementation on cardiovascular risk factors associated with type 2 diabetes (T2D) in both diabetic and nondiabetic individuals. [64] The analysis, which included data up to June 30, 2016, found that magnesium supplementation significantly improved fasting plasma glucose, high-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein, plasma triglycerides, and systolic blood pressure. Subgroup analysis revealed that diabetic subjects with low magnesium levels benefited the most. These results suggest that magnesium supplementation could reduce the risk of T2D-associated cardiovascular diseases, highlighting the need for future large-scale RCTs to develop comprehensive clinical guidelines.
- A case-control study conducted at Hassan II University Hospital of Fez from January 2015 to 2018 investigated the association between serum magnesium (Mg) levels and common complications, comorbidities of diabetes mellitus, and other biochemical indices in 170 patients. [65] Dividing participants into low Mg (n = 85) and normal Mg (n = 85) groups, findings revealed a strong correlation between serum Mg levels and factors such as age, sex, duration of diabetes, body mass index, hypertension, and glycosylated hemoglobin. Specifically, a negative correlation was observed between Mg levels and the presence of nephropathy, while no significant correlations were found with retinopathy, neuropathy, and macroangiopathy. The results suggest low Mg levels are associated with poor glycemic control, hypertension, and nephropathy in Type 2 diabetes patients, indicating the need for further research to solidify these findings.
- A cross-sectional study conducted over six months at the Department of Medicine, S.P. Medical College & Associated Group of Hospitals, Bikaner, aimed to investigate the association between serum magnesium levels, Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM), and its complications among 50.4% male and 49.6% female patients with an average age of 48±18 years. [66] It was found that patients with hypomagnesemia (Mg < 1.7mg/dl) exhibited significant associations with diabetic microvascular complications, specifically nephropathy, neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular disease, but not with hypertension and cerebrovascular events. The study concludes that serum magnesium measurement is crucial for patients with uncontrolled blood sugar despite medication or insulin use, as low magnesium levels may contribute to microvascular complications of diabetes. Magnesium supplementation, being cost-effective, is recommended for patients with hypomagnesemia, particularly due to its correlation with nephropathy.
- A comprehensive review of eighteen randomized controlled trials (RCTs) investigated the impact of oral magnesium (Mg) supplementation on glucose and insulin-sensitivity parameters in individuals with diabetes or at high risk for it, revealing a beneficial effect compared to placebo. [67] For those already diagnosed with diabetes, Mg supplementation significantly reduced fasting plasma glucose. Among those at high risk of diabetes, Mg notably improved glucose levels after a glucose tolerance test and showed a trend towards reducing insulin resistance. These findings underscore magnesium’s potential in improving glucose control and insulin sensitivity, suggesting its supplementation could be a valuable addition to diabetes management and prevention strategies.
- In a study examining the effects of oral magnesium (Mg) supplementation in insulin-requiring Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) patients, fifty participants were randomized to receive either 15 mmol Mg or a placebo daily for three months. [68] Results showed an increase in plasma Mg concentration and Mg excretion in those receiving magnesium compared to placebo, without significant changes in erythrocyte Mg concentrations, glycaemic control (glucose and HbA1c levels), lipid profiles, or blood pressure. An analysis of patients who completed the treatment suggested a potential decrease in diastolic pressure associated with increased plasma Mg levels. However, the study concluded that three months of oral Mg supplementation increased plasma Mg concentration and urinary Mg excretion but did not significantly impact glycemic control or plasma lipid concentrations in insulin-requiring Type 2 DM patients.
- In a prospective study of 1999 Japanese adults aged 40-79 years without diabetes, followed for an average of 15.6 years, it was found that higher magnesium intake was associated with a significantly lower incidence of Type 2 diabetes. [69] The risk of developing Type 2 diabetes decreased with increasing quartiles of magnesium intake, with those in the highest quartiles showing a 33-37% lower risk compared to the lowest quartile. This protective effect was even more pronounced among individuals with insulin resistance, low-grade inflammation, or those who consumed alcohol, indicating that increased magnesium intake could significantly reduce the risk of Type 2 diabetes in the general population, particularly in individuals with specific health profiles.
H. Fights Inflammation
Magnesium fights inflammation by inhibiting the activation of inflammatory markers in the body. It plays a crucial role in the immune response by acting as a natural calcium antagonist, which helps to regulate cellular events involved in inflammation. Studies have shown that higher magnesium intake is associated with reduced levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) and other markers of inflammation in the body. This mineral’s anti-inflammatory properties are particularly beneficial in reducing the risk of chronic diseases associated with high levels of inflammation, such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
A growing body of evidence supports the anti-inflammatory effects of magnesium:
- Magnesium deficiency in animal studies has been linked to an inflammatory response characterized by the activation of leukocytes and macrophages, the release of inflammatory cytokines, and an increase in free radicals, primarily due to elevated cellular calcium levels that prime cells for inflammation. [70] This deficiency is associated with chronic low-grade inflammation, marked by elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and acute-phase reactants, contributing to the risk of diseases like cardiovascular disease, hypertension, and diabetes. Adequate magnesium intake, on the other hand, does not significantly affect these inflammation markers. These findings underscore magnesium’s critical role in preventing chronic low-grade inflammation, highlighting the importance of magnesium-rich foods in the diet, especially in countries where magnesium deficiency is common due to inadequate dietary intake.
- Magnesium plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, maintaining tissue homeostasis, and supporting immune functions by influencing both innate and adaptive immune cells. [71] Deficiency in magnesium can lead to heightened inflammatory responses, including increased phagocyte priming, granulocyte oxidative bursts, endothelial cell activation, and elevated cytokine levels, thereby exacerbating the body’s reaction to immune challenges. This underdiagnosed condition is linked to the development of numerous chronic diseases, with recent research emphasizing the connection between magnesium deficiency, inflammation, and the mechanisms driving these health issues.
- A systematic review and meta-analysis reviewed randomized control trials (RCTs) up to 23 November 2021 to assess the effects of magnesium (Mg) supplementation versus placebo on serum inflammatory markers. [72] After screening 2,484 papers, 17 RCTs involving 889 participants (average age: 46 years; 62.5% females) with generally low risk of bias were included. The findings showed that magnesium supplementation significantly reduced serum C-reactive protein (CRP) levels and increased nitric oxide (NO) levels, along with notable decreases in plasma fibrinogen, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase type 5, tumor necrosis factor-ligand superfamily member 13B, ST2 protein, and IL-1. Therefore, magnesium supplementation is potentially effective in reducing various human inflammatory markers, highlighting its beneficial impact on health outcomes.
- Magnesium deficiency (MgD) is linked to various inflammatory mechanisms in the human body, including the activation of phagocytic cells, calcium channels, the NMDA receptor, and NF-κB, leading to a systemic stress response and inflammation. [73] This inflammation can further cause pro-atherogenic changes, endothelial dysfunction, and elevated blood pressure, implicating magnesium’s crucial role in the pathophysiology of several inflammatory diseases such as diabetes, asthma, preeclampsia, atherosclerosis, heart damage, and rheumatoid arthritis. The review of clinical trials and laboratory studies underscores magnesium’s potential impact on these conditions, highlighting the importance of magnesium in managing and understanding inflammatory diseases.
- A review highlights that subclinical magnesium deficiency, often resulting from low dietary intake, is a key factor predisposing individuals to chronic inflammatory stress, thereby increasing the risk of chronic diseases like cardiovascular disease and diabetes. [74] Recent findings associate deficient magnesium intakes and low serum magnesium levels with elevated serum C-reactive protein concentrations, a marker of inflammation. Correcting magnesium deficiency by achieving adequate dietary intake or serum levels can reduce inflammation indicators to normal levels. This deficiency is particularly prevalent among obese individuals and those with chronic diseases where low-grade inflammation is a known risk factor, underscoring the importance of magnesium as a critical nutrient for health and disease prevention.
- A review consolidates experimental evidence demonstrating magnesium’s role in modulating cellular processes related to inflammation. [75] In rats, magnesium deficiency quickly leads to an inflammatory syndrome marked by the activation of leukocytes and macrophages, the release of inflammatory cytokines, and an overproduction of free radicals. Altering extracellular magnesium levels impacts the inflammatory response, with increased levels reducing and decreased levels enhancing cell activation, largely due to magnesium’s function as a natural calcium antagonist affecting intracellular calcium concentrations. Potential mechanisms include phagocytic cell priming, calcium channel opening, NMDA receptor activation, and NF-kappa B activation, alongside a systemic stress response triggered by neuroendocrinological pathway activation. Magnesium deficiency’s role in exacerbating immune and oxidative stress responses links it to pro-atherogenic changes, endothelial dysfunction, and metabolic syndrome, suggesting inflammation as a key mediator in the connection between magnesium deficiency and various diseases. While further human studies are needed, these findings highlight the importance of magnesium in managing inflammation and its related disorders.
- A literature review explores the crucial role of magnesium (Mg) in immune regulation across inflammation, infection, and cancer settings, highlighting its involvement in various immune responses and its significant anti-cancer effects. [76] Mg deficiency is linked to increased baseline inflammation, oxidative stress, and various immune system complications, underscoring the importance of Mg in immune cell function, antibody synthesis, and as a cofactor in immune reactions. The review points out that while a balanced diet typically ensures adequate Mg levels, supplementation may be necessary in certain cases, though excessive amounts could impair immune function. The findings emphasize Mg’s essential role in enhancing immune responses, regulating inflammation, and its potential therapeutic efficacy, yet call for further research to elucidate its mechanisms and clinical implications fully.
- A comprehensive literature review across major databases assessed magnesium’s (Mg) role in immune regulation within contexts of inflammation, infection, and cancer. [77] It highlights Mg’s involvement in various immunological functions, such as facilitating substance P binding, promoting cell responses to lymphokines, and supporting antibody-dependent cytolysis, alongside its cofactor role in immune processes and notable anti-cancer properties. Chronic Mg deficiency is linked to increased inflammation, oxidative stress, and various immune-related complications, including lymphoma and thymus atrophy, underscoring the necessity of Mg for immune system integrity and its potential therapeutic efficacy. The review concludes that while Mg is crucial for immune function and inflammation regulation, its mechanisms and clinical implications, especially in malignancies and inflammatory conditions, warrant further investigation. Adequate dietary Mg intake is essential, with supplementation advised in certain scenarios, albeit cautiously to avoid negative immune effects.
- Despite about 60% of adults in the United States not meeting the estimated average requirement for magnesium, overt pathological conditions directly linked to magnesium deficiency are uncommon. [78] However, low magnesium status is frequently associated with various pathological conditions that involve chronic inflammatory stress. While human deficiencies are typically marginal to moderate, animal studies have shown that such deficiencies can either be mitigated or worsened by factors affecting inflammatory and oxidative stress, a notion that recent research suggests applies to humans as well. This is particularly relevant in the context of obesity, which involves chronic low-grade inflammation and is often accompanied by low magnesium status. Thus, marginal-to-moderate magnesium deficiency might significantly contribute to chronic diseases like atherosclerosis, hypertension, osteoporosis, diabetes mellitus, and cancer by exacerbating chronic inflammatory stress.
- A review highlights how magnesium (Mg) plays a crucial role in modulating cellular events linked to inflammation, with experiments showing that severe Mg deficiency in rats triggers a clinical inflammatory syndrome, including activation of immune cells, release of inflammatory cytokines, and excessive free radical production. [79] Increasing Mg levels can reduce this inflammatory response, while its reduction leads to cell activation, due to Mg’s role as a natural calcium antagonist affecting intracellular calcium levels. Mg deficiency is implicated in exacerbating responses to immune stress and contributing to a range of conditions such as hyperlipemia, atherosclerosis, endothelial dysfunction, thrombosis, hypertension, and damage from free radicals, while also facilitating the adhesion and migration of cancer cells. These findings indicate inflammation as a key factor linking Mg deficiency to various pathological states.
- A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis, which sifted through major databases until December 14, 2020, evaluated the impact of oral magnesium supplementation on inflammatory biomarkers such as C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) in adults. [80] After assessing the quality of 18 studies involving 927 participants using the Cochrane Collaboration tool and conducting subgroup analysis to pinpoint heterogeneity sources, the analysis found that magnesium supplementation did not significantly affect serum levels of CRP, IL-6, and TNF-α when compared to controls. Furthermore, dose-response assessments revealed no significant associations between the dosage or duration of magnesium supplementation and serum CRP and IL-6 concentrations. These findings do not support the hypothesis that oral magnesium supplementation beneficially impacts these specific inflammatory biomarkers in adults.
- A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) investigated the effects of oral magnesium supplementation on plasma C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, searching databases up to August 9, 2016. [81] Analyzing data from 11 studies, the meta-analysis found that magnesium supplementation did not significantly change plasma CRP concentrations overall. However, in subgroup analyses, individuals with baseline CRP levels above 3 mg/L experienced a significant reduction in CRP following magnesium treatment, suggesting a potential beneficial effect of magnesium supplementation in managing low-grade chronic systemic inflammation, particularly among those with higher levels of inflammation. This highlights magnesium’s role as a possible adjunctive therapy in inflammatory conditions.
- A study explores the link between magnesium (Mg2+) deficiency, induced by low dietary intake and the use of certain medications like diuretics, and the development of hypertension. [82] It demonstrates that higher serum Mg2+ levels and Mg2+ supplementation are associated with lower blood pressure, implicating Mg2+ deficiency in hypertension’s pathogenesis. Specifically, the research found that a Mg2+-depleted diet in mice led to increased blood pressure, without a rise in total body fluid, and elevated levels of NLRP3, IL-1β, and IsoLGs in antigen-presenting cells, indicating a direct effect of low Mg2+ on inflammation and oxidative stress pathways. These findings highlight the potential of Mg2+ supplementation and increased dietary intake as strategies to mitigate hypertension and cardiovascular disease by targeting underlying inflammatory and oxidative mechanisms.
- In a study utilizing a 5/6 nephrectomized rat model to simulate chronic kidney disease (CKD) and in vitro experiments on vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), magnesium (Mg) supplementation was found to significantly mitigate systemic inflammation and oxidative stress. [83] Uraemic rats on a standard Mg diet exhibited increased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress markers, which were notably reduced with dietary Mg supplementation. Similarly, VSMCs exposed to high phosphate conditions showed decreased production of reactive oxygen species and inflammatory cytokines when incubated with increased Mg levels, highlighting Mg’s direct anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects on vascular cells. These results suggest that Mg supplementation could be a beneficial adjunct in the clinical management of CKD patients, reducing inflammation and oxidative stress.
- A study explored the anti-inflammatory properties of magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate (MgIG), a derivative of Glycyrrhiza glabra (licorice), particularly focusing on its effects within the phospholipase A2 (PLA2)/arachidonic acid (AA) pathway in RAW264.7 macrophages. [84] It was found that MgIG significantly suppresses the activation of PLA2 and the subsequent production of AA metabolites such as prostaglandin E2, prostacyclin, thromboxane 2, and leukotrienes, which are key inflammatory mediators. Additionally, MgIG inhibited the enzymes responsible for metabolizing AA, including COX-2, COX-1, 5-LOX, and others, indicating that its anti-inflammatory effects may be attributed to the modulation of cyclooxygenase (COXs) and 5-lipoxygenase (LOX) pathways in AA metabolism. This reveals a potential novel mechanism for MgIG’s clinical use in treating inflammatory liver diseases.
Magnesium Daily Intake: How much mg of Magnesium is Enough?
The recommended daily intake of magnesium varies by age, gender, and life stage, reflecting the importance of this mineral in numerous bodily functions and aligning with the dietary reference intakes designed to prevent deficiency. Understanding the correct magnesium dosage, as outlined in the dietary reference intakes, is crucial for maintaining health. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the general guidelines for magnesium dosage, which follow the dietary reference intakes, are as follows:
- Infants:
- 0-6 months: 30 mg (Adequate Intake)
- 7-12 months: 75 mg (Adequate Intake)
- Children:
- 1-3 years: 80 mg
- 4-8 years: 130 mg
- 9-13 years: 240 mg
- Teens and Adults:
- Males 14-18 years: 410 mg
- Females 14-18 years: 360 mg
- Males 19-30 years: 400 mg
- Females 19-30 years: 310 mg
- Males 31 years and older: 420 mg
- Females 31 years and older: 320 mg
- Pregnancy and Lactation:
- Pregnant teens: 400 mg
- Pregnant women: 350-360 mg (depending on age)
- Lactating teens: 360 mg
- Lactating women: 310-320 mg (depending on age)
It’s important to note that these values represent total daily intake from food, water, and, if necessary, supplements. Consuming magnesium within these recommended ranges is crucial for maintaining health and preventing magnesium deficiency. Research has shown that higher magnesium intakes, within safe limits, can offer additional health benefits, such as improved bone health and reduced risk of chronic diseases. Therefore, aiming for the higher end of the recommended intake, through a balanced diet and supplements if needed, can be beneficial.
Magnesium Supplements: Differences between Magnesium Chloride, Magnesium Hydroxide, Magnesium Oxide, Magnesium Citrate, and Other Forms
Magnesium supplements come in various forms, each with different absorption rates and specific uses. Here are some common examples:
- Magnesium Citrate: This form is magnesium combined with citric acid. It is one of the most bioavailable forms of magnesium and is often used for its laxative effect to treat constipation.
- Magnesium Oxide: Widely used for relieving digestive issues like heartburn and indigestion, magnesium oxide is also used to prevent magnesium deficiency. However, it has a lower absorption rate compared to other forms.
- Magnesium Chloride: Available in both pill form and as a topical solution, magnesium chloride is easily absorbed by the body. It can be used to raise magnesium levels and for kidney function improvement.
- Magnesium Glycinate: Known for its calming effects, magnesium glycinate is often recommended for those looking to improve sleep quality or manage stress and anxiety. It’s highly bioavailable and gentle on the stomach.
- Magnesium Sulfate: Also known as Epsom salt, it is typically dissolved in bath water to relieve muscle soreness and improve relaxation through skin absorption.
- Magnesium Lactate: This form is used by people with sensitive digestive systems because it is less likely to cause diarrhea. It’s effective for supplementing magnesium levels and is well-absorbed.
- Magnesium Malate: Magnesium malate contains malic acid, which is involved in the Krebs cycle (a series of chemical reactions used to release stored energy). It’s often recommended for managing fatigue and muscle pain.
- Magnesium Taurate: This form is a combination of magnesium and taurine, an amino acid. It is often chosen for its potential cardiovascular benefits.
- Magnesium L-threonate: Known for its ability to penetrate the brain barrier, it is suggested for improving cognitive function, memory, and for managing symptoms of anxiety.
- Magnesium Hydroxide: Magnesium hydroxide is a compound used primarily as an antacid to neutralize stomach acid and as a laxative to relieve constipation. This dietary supplement is recognized for its effectiveness in treating symptoms of indigestion, heartburn, and sour stomach. Additionally, magnesium hydroxide is used in some antiperspirant products due to its ability to interact with sweat to prevent body odor. It is available over the counter in various forms, including liquids and tablets, making it accessible for those seeking relief from gastrointestinal discomfort.
Each form of magnesium has unique benefits, and the choice of supplement may depend on individual health needs and goals. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure it is appropriate for your specific health situation.
Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium deficiency, medically known as hypomagnesemia, occurs when the body does not have enough magnesium, a vital mineral crucial for over 300 enzymatic reactions and various physiological functions. This deficiency can lead to a wide array of health issues since magnesium plays a key role in muscle and nerve function, maintaining a healthy immune system, keeping the heartbeat steady, and supporting bone health. It also aids in regulating blood sugar levels and blood pressure. Common causes of magnesium deficiency include inadequate dietary intake, chronic health conditions such as gastrointestinal diseases, diabetes, and excessive alcohol consumption, which can impair the body’s ability to absorb magnesium or increase its excretion.
Symptoms of magnesium deficiency are often subtle unless the levels become severely low. Initial signs can include general fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting. As the deficiency worsens, individuals may experience more severe symptoms such as numbness and tingling, muscle cramps and contractions, seizures, personality changes, abnormal heart rhythms, and coronary spasms. Diagnosing magnesium deficiency involves a clinical evaluation of symptoms and a confirmation through blood tests. Treatment typically involves dietary adjustments to include more magnesium-rich foods or magnesium supplements under medical supervision. Given the essential roles of magnesium in the body, preventing deficiency is key to maintaining overall health and well-being.
What is Magnesium used For?
Magnesium is an essential mineral used by the body for a wide range of functions and health benefits, including:
- Energy Production: Magnesium plays a pivotal role in converting food into energy, activating ATP, the energy molecule in the body.
- Protein Formation: It helps create new proteins from amino acids.
- Gene Maintenance: Magnesium is involved in the creation and repair of DNA and RNA.
- Muscle Movements: It is part of the contraction and relaxation of muscles.
- Nervous System Regulation: Magnesium regulates neurotransmitters, which send messages throughout the brain and nervous system.
- Electrolyte Balance: It helps regulate electrolyte balance, which is crucial for nerve and muscle function, blood pressure regulation, and hydration.
- Bone Health: Magnesium is vital for bone formation and influences the activities of osteoblasts and osteoclasts that build healthy bone density.
- Cardiovascular Health: It contributes to heart health by managing the transport of calcium and potassium across cell membranes, critical for normal heart rhythm and blood pressure control.
- Blood Sugar Control: Magnesium plays a key role in glucose and insulin metabolism, with higher magnesium intakes associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Mental Health: It has been studied for its role in brain function and mood regulation, including potential benefits for anxiety and depression.
- Digestion and Relieving Constipation: Magnesium draws water into the intestines, making stool easier to pass, and is often used as a natural remedy for constipation.
- Migraine Prevention: Some studies suggest that magnesium deficiency is more common in people who suffer from migraines, and supplementation may help prevent or reduce symptoms.
- Anti-inflammatory Benefits: Lower magnesium intake is linked to chronic inflammation, which is underlying many diseases. Supplementing with magnesium can reduce inflammation in certain conditions.
Magnesium supplementation can be beneficial in treating and preventing magnesium deficiency and its associated symptoms and conditions. However, it’s important to use magnesium supplements under medical supervision, especially for individuals with certain health conditions or those taking medications that might interact with magnesium.
What is Magnesium Glycinate?
Magnesium glycinate is a form of magnesium supplement where magnesium is bonded to glycine, an amino acid. This combination creates a compound that is highly bioavailable, meaning it’s easily absorbed by the body, making it one of the most effective forms of magnesium supplements available. Magnesium glycinate is particularly noted for its ability to provide the benefits of magnesium without the common side effects of gastrointestinal distress or laxative properties that other forms of magnesium supplements might cause.
It is commonly recommended for those seeking to increase their magnesium intake for various health reasons, including improving sleep quality, supporting bone health, managing stress and anxiety, aiding in muscle recovery and function, and maintaining normal nerve function. Magnesium glycinate’s enhanced absorption rate and gentle effect on the stomach make it a preferred choice for dietary supplementation, especially for individuals with magnesium deficiencies or those in need of magnesium’s therapeutic effects without gastrointestinal discomfort.
Magnesium Tablets
Magnesium tablets are a popular dietary supplement used to increase magnesium intake, an essential mineral vital for numerous bodily functions. Magnesium is crucial for over 300 enzyme reactions in the body, including DNA synthesis, muscle and nerve function, blood glucose control, and blood pressure regulation. Despite its abundance in various foods, many individuals may not consume enough magnesium through diet alone, leading to deficiencies. This shortfall is where magnesium tablets come into play, offering a convenient way to ensure adequate magnesium levels. They are particularly beneficial for individuals at risk of magnesium deficiency, including those with gastrointestinal diseases, type 2 diabetes, alcohol dependencies, and older adults.
The choice of magnesium tablets can depend on individual health needs and tolerability, as magnesium supplements come in various forms, each with different absorption rates and effects on the gastrointestinal system. For instance, magnesium citrate is known for its bioavailability and laxative effect, making it suitable for those suffering from constipation. In contrast, magnesium glycinate is often recommended for its calming effects on the brain and muscles, making it ideal for improving sleep and reducing muscle cramps without causing diarrhea. When taking magnesium tablets, it’s important to adhere to the recommended dietary allowances unless a healthcare provider advises otherwise, as excessive magnesium intake can lead to adverse effects, including diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramping.
Magnesium Side Effects
While magnesium is essential for health and involved in more than 300 biochemical reactions in the body, taking too much, especially in supplement form, can lead to side effects. These side effects are more common when magnesium is taken in high doses and can vary depending on the individual and the form of magnesium consumed. Common side effects of excessive magnesium intake include:
- Diarrhea: This is the most common side effect, especially with magnesium forms such as magnesium carbonate, chloride, oxide, and citrate, which have a laxative effect.
- Nausea and Vomiting: High doses of magnesium can upset the stomach and lead to nausea or vomiting.
- Abdominal Cramping: Overconsumption of magnesium supplements can cause stomach cramps and discomfort.
- Electrolyte Imbalance: Extremely high levels of magnesium can lead to an imbalance of electrolytes, specifically lowering calcium (hypocalcemia) and potassium levels (hypokalemia) in the blood.
- Low Blood Pressure: Excessive magnesium intake lowers blood pressure, which can be beneficial in some cases but problematic in others, especially if it causes symptoms of lightheadedness or fainting.
- Irregular Heartbeat: Though rare, very high magnesium levels can affect heart rhythms, leading to irregular heartbeats or arrhythmias.
- Breathing Problems: In severe cases, too much magnesium can lead to difficulty breathing.
- Lethargy: High doses of magnesium can cause drowsiness, lethargy, and a lack of energy.
The tolerable upper intake level (UL) for magnesium from supplements and medication, not including dietary magnesium, is 350 mg per day for adults and teenagers. This limit is set to prevent the risk of side effects. However, dietary magnesium, found naturally in foods, does not pose a risk for side effects and is not included in the UL.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have kidney function issues or take medications that could interact with magnesium supplements.
FAQ
What does magnesium do in the body?
Magnesium plays a vital role in over 300 enzymatic reactions in the body, including the metabolism of food, synthesis of fatty acids and proteins, and the transmission of nerve impulses. To ensure they meet their daily magnesium needs, many people turn to magnesium supplements, especially if their dietary intake is insufficient. These supplements can help maintain optimal magnesium levels in the body, supporting overall health and well-being. However, it’s important to choose the right type of magnesium supplements, as different forms have varying absorption rates and benefits. Regular intake of magnesium supplements can significantly contribute to improving muscle function, bone health, and reducing the risk of chronic diseases, underscoring their importance in a balanced diet. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen to determine the appropriate dosage and to avoid potential interactions with other medications.
How much magnesium per day for a woman?
The recommended daily intake of magnesium varies depending on age and life stage for women. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the general guidelines are as follows:
- For women aged 19-30 years, the recommended daily amount is 310 mg.
- For women aged 31 years and older, the recommendation increases to 320 mg per day.
- During pregnancy, the recommended daily intake varies by age: 350 mg for women aged 19-30 and 360 mg for women aged 31-50.
- Lactating women require slightly more: 310 mg per day for those aged 19-30 and 320 mg for those aged 31-50.
These amounts are designed to cover the needs of most healthy women, ensuring proper physiological function and helping to prevent magnesium deficiency.
How much magnesium should I take per day?
The amount of magnesium you should take per day depends on several factors, including your age, sex, and specific health conditions or needs. For many individuals, achieving the recommended daily intake of magnesium through diet alone can be challenging, leading to the consideration of magnesium supplements as a practical solution. These supplements can help fill the nutritional gap, ensuring you meet your daily magnesium requirements for optimal health. It’s important to select the right form of magnesium supplements, as they come in various types, each suited to different health goals and absorption rates. Moreover, consulting a healthcare provider before starting magnesium supplements is crucial, especially for those with underlying health conditions or those taking other medications, to determine the appropriate dosage and avoid potential side effects. Regularly incorporating magnesium supplements into your health regimen, under professional guidance, can support various bodily functions, from muscle and nerve function to heart health and bone strength.
Is it OK to take magnesium every day?
Yes, it is generally safe to take magnesium daily within the recommended dietary allowances, unless advised otherwise by a healthcare provider. For individuals who may not receive sufficient magnesium through their diet, magnesium supplements offer a convenient way to ensure adequate intake. These supplements can play a crucial role in maintaining health, as magnesium is vital for numerous bodily functions, including muscle and nerve function, heart rhythm, and bone health. However, it’s important to choose high-quality magnesium supplements and to consider the different forms available, as some types are absorbed better than others and are suited to different health needs. When incorporating magnesium supplements into your daily routine, it’s advisable to start with a lower dosage and adjust as needed, based on your healthcare provider’s recommendations, to avoid any potential side effects. Regular use of magnesium supplements, when aligned with dietary intake and under medical guidance, can help achieve and maintain optimal magnesium levels for overall well-being.
What is magnesium used to treat?
Magnesium is used to treat and prevent magnesium deficiency, certain conditions related to heart health, migraines, and sometimes as a laxative for constipation or preparation for medical procedures. Monitoring urinary magnesium levels can be crucial in these treatments, as it helps assess how the body is responding to magnesium supplementation, especially in cases of deficiency or heart-related conditions. Adjusting magnesium intake based on urinary magnesium levels ensures that the body maintains an optimal magnesium balance, enhancing the effectiveness of treatment and preventing potential imbalances that could affect health outcomes.
What foods have high magnesium?
Incorporating sources of magnesium into your diet is essential for maintaining optimal health. Foods high in magnesium, key sources of magnesium, include nuts and seeds, whole grains, leafy green vegetables, milk, yogurt, and fortified foods. Consuming a variety of these sources of magnesium helps meet your daily magnesium requirements and supports overall wellness, contributing to heart health, strong bones, and muscle function. Ensuring a diverse intake from these sources of magnesium can significantly impact your health by providing the magnesium necessary for hundreds of biochemical reactions in the body.
What is the magnesium good for?
Magnesium, including forms like magnesium sulphate, is good for supporting muscle and nerve function, maintaining a healthy immune system, keeping the heartbeat steady, and helping bones remain strong. Magnesium sulphate, specifically, is often used in medical settings and supplements to provide these benefits. It also helps adjust blood glucose levels, showcasing the versatility of magnesium sulphate in supporting overall health. Utilizing magnesium sulphate as part of a health regimen can contribute significantly to maintaining essential bodily functions and promoting well-being.
Which is the best form of magnesium to take?
The best form of magnesium to take can depend on your health goals; magnesium citrate is good for constipation, magnesium glycinate for relaxation and sleep, and magnesium oxide for heartburn and indigestion relief. When considering magnesium supplements, it’s important to match the specific form of magnesium to your individual health needs. For example, magnesium citrate is often recommended for its laxative effect, making it a popular choice for those seeking relief from constipation. On the other hand, magnesium glycinate is known for its calming effects on the brain and muscles, making it an excellent option for those looking to improve sleep quality or manage stress. Magnesium oxide, while less absorbable, can effectively treat symptoms of heartburn and indigestion. Incorporating magnesium supplements into your daily regimen can significantly contribute to meeting your magnesium intake requirements and supporting overall health. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any magnesium supplements to ensure they complement your health regimen without interfering with other conditions or medications.
Who should not take magnesium?
People with kidney failure, bowel obstruction, myasthenia gravis, or those who are on certain medications like bisphosphonates and antibiotics should not take magnesium supplements without consulting a healthcare provider. The use of magnesium supplements in individuals with these conditions can lead to serious health complications, including magnesium toxicity, especially in those with kidney failure due to the body’s reduced ability to excrete excess magnesium. Additionally, magnesium supplements can interact with certain medications, altering their effectiveness or leading to adverse effects. Therefore, it’s crucial for individuals with underlying health conditions or those taking prescription drugs to seek medical advice before incorporating magnesium supplements into their health regimen. This precaution ensures that magnesium supplements do not interfere with medical conditions or the action of other medications, safeguarding against potential health risks.
What foods are highest in magnesium?
While foods highest in magnesium include pumpkin seeds, almonds, spinach, cashews, and black beans, magnesium sulphate offers an alternative source of this essential mineral through supplements and topical applications. Unlike dietary sources, magnesium sulphate can be absorbed through the skin in baths or applied in lotions, providing additional routes to increase magnesium intake. Incorporating magnesium sulphate into your wellness routine, alongside consuming magnesium-rich foods, can ensure a comprehensive approach to meeting your magnesium needs and supporting overall health. This balanced strategy maximizes the benefits of both dietary and supplementary forms of magnesium, including magnesium sulphate, to maintain optimal health.
Is it OK to take magnesium daily?
Yes, taking magnesium daily is typically safe for most people within recommended guidelines, especially when using dietary supplements to address or prevent magnesium deficiencies. Magnesium is an essential mineral crucial for many bodily functions, and dietary supplements can help individuals meet their daily magnesium needs, particularly when dietary intake is insufficient. Incorporating magnesium dietary supplements into one’s daily routine can support various health aspects, including muscle and nerve function, bone health, and cardiovascular health.
However, it’s important to choose the right form of magnesium dietary supplements, as absorption rates can vary between different types of magnesium. Consulting with a healthcare provider before starting any dietary supplements is advisable to ensure they are appropriate for your health status and do not interact with any medications you may be taking. Additionally, adhering to the recommended dosage of magnesium dietary supplements is crucial to avoid potential side effects, such as gastrointestinal discomfort, which can occur with excessive intake.
Is 500mg of magnesium a day too much?
Taking 500 mg of magnesium daily may exceed the recommended dietary allowance for some individuals, potentially leading to side effects such as diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramps. This dosage, while beneficial for certain health conditions under medical supervision, could result in an intake of mg of magnesium that surpasses the body’s requirements for others. Excessive magnesium intake, particularly from supplements, can also interfere with the absorption of other minerals and affect renal function in susceptible individuals. Therefore, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any regimen that includes high doses of magnesium, to ensure that the amount of mg of magnesium taken aligns with your health needs and does not pose risks to your well-being.
Is it OK to take 400 mg of magnesium a day?
Taking 400 mg of magnesium a day is within the upper limit for adults and is generally considered safe, but individual needs may vary. For many, incorporating a magnesium supplement of 400 mg into their daily routine can help address dietary shortfalls and support various bodily functions, including muscle and nerve function, as well as bone health. However, it’s important to consider the form of the magnesium supplement, as some forms may be absorbed better than others or may be more suitable for specific health concerns. Before starting any magnesium supplement regimen, especially at doses like 400 mg, it’s wise to consult with a healthcare provider. This ensures the dosage aligns with your individual health needs and does not interact adversely with any existing conditions or medications.
How much magnesium do I need daily?
According to the National Institutes of Health, adult men require 400-420 mg per day, while adult women need 310-320 mg per day of magnesium. For some individuals, achieving this daily requirement may be challenging through diet alone, making a magnesium supplement a practical option to ensure adequate intake. Including a magnesium supplement in your daily regimen can help fill any nutritional gaps and support overall health, including muscle function, nerve function, and bone health. However, it’s essential to choose the right type and dosage of a magnesium supplement to meet your specific needs without exceeding the recommended daily intake. Consulting with a healthcare provider before starting any magnesium supplement is advisable to determine the appropriate amount for your health status and to avoid potential interactions with other medications or health conditions.
What are the side effects of too much magnesium?
Side effects of too much magnesium, often resulting from excessive intake of dietary supplements, can include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, lethargy, muscle weakness, irregular heartbeat, low blood pressure, urine retention, respiratory distress, and cardiac arrest. While magnesium is crucial for many bodily functions, overconsumption through dietary supplements without medical supervision can lead to these adverse effects. It’s important for individuals considering magnesium dietary supplements to consult with healthcare professionals to determine the appropriate dosage based on their specific health needs and to avoid surpassing the recommended dietary allowance. Additionally, monitoring magnesium intake from all sources, including dietary supplements, food, and water, is essential to prevent the potential side effects associated with excessive magnesium consumption.
What happens to your body when you take magnesium?
When you take magnesium, it helps to regulate muscle and nerve function, blood sugar levels, and blood pressure, supporting bone health, DNA synthesis, and protein synthesis. Magnesium is particularly noted for its role in managing high blood pressure, as sufficient levels can contribute to cardiovascular health by promoting relaxation of the blood vessels. Oral magnesium supplementation can be an effective way to ensure you’re getting enough of this essential mineral, especially if dietary sources are insufficient to meet your daily needs, and can be especially beneficial for individuals with high blood pressure.
Incorporating oral magnesium supplementation into your health routine can enhance magnesium’s benefits for the body, supporting overall well-being and helping to prevent conditions such as high blood pressure. This approach can be crucial for those at risk of or currently managing high blood pressure, as magnesium plays a key role in cardiovascular health. However, it’s important to discuss any supplementation plan with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and to ensure it doesn’t conflict with existing health conditions or medications, particularly for those managing high blood pressure. Adequate magnesium intake, through diet or supplementation, can thus be a valuable part of a comprehensive strategy to maintain healthy blood pressure levels and overall cardiovascular health.
What symptoms does magnesium help with?
Magnesium can help with symptoms of magnesium deficiency, including muscle cramps, fatigue, migraine headaches, and constipation, ensuring individuals receive enough magnesium is crucial for overall health and well-being. Ensuring you have enough magnesium in your diet or through supplementation can significantly reduce the risk of these uncomfortable symptoms and support vital bodily functions. For those who struggle to get adequate magnesium from their diet alone, considering a magnesium supplement may be beneficial to meet their daily needs and alleviate symptoms associated with low magnesium levels.
Furthermore, maintaining enough magnesium in the body is essential not only for alleviating symptoms of deficiency but also for supporting broader health benefits such as improved bone health, better blood sugar control, and enhanced heart health. Adequate magnesium intake helps in the prevention of chronic health issues and supports the body’s natural processes, highlighting the importance of ensuring you have enough magnesium through a balanced diet or, if necessary, through supplementation under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
What happens if you take magnesium glycinate everyday?
Taking magnesium glycinate every day can help improve sleep, reduce anxiety, and support bone health, provided it’s within recommended dosages. This specific form of magnesium is known for its high bioavailability and minimal gastrointestinal side effects, making it an excellent choice for maintaining optimal levels of magnesium. Regular intake ensures that the body’s levels of magnesium are replenished, supporting vital physiological functions such as muscle and nerve operation, protein synthesis, and blood glucose control.
Furthermore, maintaining adequate levels of magnesium through daily supplementation with magnesium glycinate can contribute to cardiovascular health and the prevention of hypertension, given magnesium’s role in blood pressure regulation. It’s important, however, to monitor your levels of magnesium if taking supplements daily to avoid excessive intake, which could lead to adverse effects. Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide guidance on the appropriate daily dosage to ensure that the levels of magnesium in your body are balanced, supporting overall health without exceeding safe intake levels.
Does magnesium glycinate make you sleepy?
Magnesium glycinate can have a calming effect and may promote better sleep by helping to relax the muscles and nervous system. This effect has been supported by various studies, including a systematic review and meta-analysis, which evaluated the impact of magnesium supplementation on sleep quality. The findings from this systematic review and meta-analysis suggest that magnesium, particularly in the form of magnesium glycinate, can significantly improve sleep efficiency and duration by enhancing the relaxation state of the body and mind. By facilitating a deeper and more restful sleep, magnesium glycinate becomes an attractive supplement for those struggling with sleep disturbances. Furthermore, the use of magnesium glycinate is often recommended in the literature on sleep health, reinforcing its role as a beneficial supplement in promoting better sleep patterns.
What is magnesium good for?
Magnesium is good for maintaining various physiological functions, including nerve transmission, muscle contraction, blood pressure regulation, and bone mineralization. Incorporating green leafy vegetables into your diet is an effective way to ensure adequate magnesium intake, as these foods are among the richest natural sources of this essential mineral. Consuming a variety of green leafy vegetables, such as spinach, kale, and Swiss chard, can significantly contribute to meeting daily magnesium requirements and supporting overall health.
Furthermore, green leafy vegetables not only provide magnesium but also a host of other nutrients vital for health, including vitamins A, C, K, and dietary fiber. Regular consumption of green leafy vegetables as part of a balanced diet can enhance the body’s ability to perform critical functions, such as maintaining strong bones and regulating heart rhythm. By prioritizing green leafy vegetables in your meals, you’re not only boosting your magnesium intake but also supporting a healthy, nutrient-rich diet that benefits your entire body.
Which fruit is high in magnesium?
Bananas, avocados, and dried figs are fruits high in magnesium, offering a delicious way to boost intake of this essential mineral. Including these fruits in your diet can help address low levels of magnesium, which are associated with various health issues such as muscle cramps, fatigue, and irregular heart rhythms. Consuming magnesium-rich fruits is especially beneficial for individuals looking to naturally increase their magnesium intake and prevent the complications associated with low levels of magnesium. Along with these fruits, incorporating other magnesium-rich foods and considering supplements, if necessary, can ensure adequate magnesium levels for optimal health and well-being.
What drink is high in magnesium?
Drinks high in magnesium include mineral water, fortified drinks, and certain vegetable juices, which can be especially beneficial for individuals looking to boost their magnesium intake. For those dealing with vitamin D deficiency, consuming magnesium-rich drinks can be particularly advantageous, as magnesium is essential for the metabolism and function of vitamin D within the body. The relationship between magnesium and vitamin D is synergistic, meaning adequate levels of magnesium can help improve vitamin D status and overall health. Additionally, addressing vitamin D deficiency by ensuring sufficient magnesium intake through these drinks, alongside direct vitamin D sources, can support bone health, immune function, and more. Therefore, incorporating magnesium-rich drinks into your diet not only helps to meet your magnesium needs but can also play a role in preventing and managing vitamin D deficiency.
How can I increase magnesium in my body?
You can increase magnesium in your body by consuming magnesium-rich foods, taking supplements, and using topical magnesium products like oils and lotions. While these methods are effective for boosting magnesium intake, it’s important to be aware of the potential risk of magnesium toxicity, especially if relying heavily on supplements for your magnesium intake. Including fortified foods in your diet is another effective strategy to boost your magnesium intake without significantly increasing the risk of magnesium toxicity. Fortified foods, such as certain breakfast cereals and grain products, have added magnesium, making it easier to meet your daily requirements in a safe manner.
Another effective method to safely increase magnesium levels is through the use of magnesium sulfate, commonly known as Epsom salt, which can be dissolved in bathwater for a relaxing soak. This form of magnesium is absorbed through the skin, providing a direct route to increase magnesium levels and promote relaxation, relieve muscle soreness, and improve sleep, all while minimizing the risk of magnesium toxicity. Incorporating magnesium sulfate baths into your routine, along with consuming fortified foods, can be a beneficial addition to dietary changes and supplements, offering a holistic approach to boosting your magnesium intake and enhancing overall well-being. However, it’s crucial to monitor your overall magnesium intake to prevent magnesium toxicity, characterized by symptoms such as nausea, diarrhea, lethargy, muscle weakness, and irregular heartbeat. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help ensure that your magnesium intake strategies are effective and safe, avoiding the adverse effects of magnesium toxicity.
What happens when magnesium is low?
Low magnesium can lead to symptoms such as muscle cramps, tremors, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, and personality changes. In such cases, magnesium supplements may be recommended to help alleviate these symptoms by restoring magnesium levels to normal. Adequate magnesium intake is crucial for overall health, and magnesium supplements may offer a convenient way to increase magnesium levels, especially when dietary intake is insufficient. However, it’s important to use magnesium supplements responsibly, as excessive intake may lead to adverse effects. Consulting with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen is advisable to ensure that magnesium supplements may safely and effectively address low magnesium levels without exceeding the recommended dietary allowance.
What depletes magnesium?
Factors that deplete magnesium include excessive intake of alcohol, salt, coffee, sugar, phosphoric acid (in soft drinks), and prolonged stress. These elements can significantly impact the body’s magnesium status, leading to decreased levels of this essential mineral. Maintaining a healthy magnesium status is crucial for various physiological functions, including muscle and nerve function, blood glucose control, and bone health. Therefore, understanding and mitigating the factors that can deplete magnesium levels is essential for maintaining optimal magnesium status.
To counteract these depleting factors and improve magnesium status, incorporating magnesium-rich foods into the diet and considering magnesium supplementation when necessary can be beneficial. Regular monitoring of magnesium status, especially in individuals with a high risk of deficiency due to these lifestyle factors, can help prevent the negative health outcomes associated with low magnesium levels. Healthcare professionals can provide guidance on strategies to maintain a healthy magnesium status, including dietary recommendations and the use of supplements if required.
How can I raise my magnesium level quickly?
To quickly raise magnesium levels, consider taking magnesium supplements, eating magnesium-rich foods, or using topical magnesium products. Additionally, incorporating magnesium sulfate, also known as Epsom salt, into your routine can be an effective method. Bathing in water infused with magnesium sulfate allows for the absorption of magnesium through the skin, which can rapidly increase your body’s magnesium levels. This method is not only efficient but also provides a soothing and relaxing experience, which can be particularly beneficial for muscle relaxation and stress relief. Furthermore, magnesium sulfate can be used in foot soaks, offering a convenient alternative for those short on time or who prefer not to take a full bath. By combining these approaches—supplementation, dietary adjustments, topical application, and the use of magnesium sulfate—you can effectively and quickly boost your magnesium levels.
What are the symptoms of being on magnesium?
Symptoms of adequate magnesium levels include normal muscle and nerve function, stable heart rate, strong bones, and balanced blood sugar levels. Ensuring sufficient magnesium intake is crucial for maintaining bone mineral density, as magnesium plays a significant role in bone health alongside calcium and vitamin D. A healthy bone mineral density is vital for preventing osteoporosis and fractures, highlighting magnesium’s importance in skeletal strength and integrity. Moreover, optimal magnesium levels can contribute to improved bone mineral density, supporting the body’s framework and enhancing overall wellbeing. It’s essential to monitor dietary intake and consider supplementation if necessary, to maintain these beneficial levels of magnesium for bone mineral density and other physiological functions.
Is it OK to have magnesium tablets every day?
Yes, it’s generally safe to have magnesium tablets every day within the recommended dietary allowances. For those seeking alternative methods to supplement their magnesium intake, magnesium sulfate, commonly known as Epsom salt, can be a useful addition. Beyond oral supplements, magnesium sulfate can be absorbed through the skin via baths or foot soaks, offering a relaxing way to increase magnesium levels. This method is particularly beneficial for individuals who may experience digestive discomfort from magnesium tablets or those looking to enhance their magnesium intake for muscle relaxation and stress relief. Furthermore, incorporating magnesium sulfate into your wellness routine, alongside daily magnesium tablets, can provide a comprehensive approach to maintaining adequate magnesium levels, supporting overall health and well-being. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate magnesium supplementation strategy for your needs, especially when considering daily magnesium tablets or adding magnesium sulfate to your regimen.
What do magnesium tablets do for the body?
Magnesium tablets can help prevent and treat magnesium deficiency, support bone health, reduce the risk of diabetes, lower blood pressure, and alleviate migraines. By providing the body with more magnesium, these tablets contribute to the necessary daily intake, ensuring that the body functions optimally. More magnesium in the diet can lead to improved health outcomes, such as stronger bones and a lower risk of chronic conditions like hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Additionally, for individuals who struggle to get enough magnesium from their diet alone, magnesium tablets offer a convenient way to increase their magnesium intake. Including more magnesium in one’s health regimen, especially through supplements, can significantly enhance well-being by supporting vital bodily processes and preventing deficiencies that could lead to health issues. It’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the right amount of magnesium supplementation, ensuring it complements your overall health strategy.
Who should not take magnesium tablets?
Individuals with kidney disease, heart disease, or those taking certain medications should consult a doctor before taking magnesium tablets. This precaution is particularly important because excessive magnesium intake can affect urinary and plasma magnesium levels, potentially leading to complications, especially in those with kidney disease who may not be able to properly excrete excess magnesium. Monitoring urinary and plasma magnesium levels can help prevent the accumulation of magnesium to harmful levels in these individuals. Additionally, magnesium can interact with certain heart medications and affect their efficacy. Therefore, understanding the balance of urinary and plasma magnesium is crucial for those with underlying health conditions or those on medication regimens, underscoring the importance of medical guidance before starting magnesium supplements.
Is 500 mg of magnesium too much for a woman?
500 mg of magnesium may exceed the recommended daily intake for a woman, potentially causing side effects, unless prescribed by a healthcare provider. In some cases, magnesium supplements may be recommended in higher doses for specific health conditions or deficiencies, but it’s crucial to use them under medical supervision. Excessive intake from magnesium supplements may lead to diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and nausea. Therefore, it’s important to assess individual needs and consult with a healthcare provider before starting any high-dose magnesium supplement regimen. Magnesium supplements may offer significant health benefits, including supporting bone health, muscle function, and cardiovascular health, but they must be taken responsibly to avoid adverse effects. Proper evaluation and monitoring by a healthcare professional can ensure that magnesium supplements may safely contribute to achieving optimal magnesium levels without exceeding safe consumption limits.
What is the safest amount of magnesium to take daily?
The safest amount of magnesium to take daily aligns with the recommended dietary allowances: 400-420 mg/day for men and 310-320 mg/day for women. It’s important to note that these recommendations include magnesium obtained from both dietary sources and supplements, such as magnesium salts. Magnesium salts, which are a common form of magnesium supplements, offer a convenient way to increase your magnesium intake, especially if dietary sources are insufficient. However, when considering the addition of magnesium salts to your regimen, it’s crucial to ensure that the total daily intake from all sources does not exceed these recommended amounts. Excessive intake of magnesium, including that from magnesium salts, can lead to adverse effects, underscoring the importance of adhering to these guidelines for safe consumption. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement to determine the appropriate dosage based on your individual health needs and to avoid potential interactions with other medications.
How much magnesium should a woman over 50 take?
A woman over 50 should take 320 mg of magnesium daily, according to the National Institutes of Health. Among the various forms of magnesium supplements available, magnesium aspartate is recognized for its high bioavailability, making it an excellent option for women over 50 seeking to meet their daily magnesium requirements. Incorporating magnesium aspartate into the diet can help ensure that the body absorbs magnesium efficiently, supporting bone health, cardiovascular function, and muscle operation, which are particularly important during this stage of life. Additionally, choosing a supplement like magnesium aspartate can aid in maintaining optimal magnesium levels, contributing to overall well-being and potentially mitigating age-related health issues.
Is it OK to take 500 mg of magnesium daily?
While some individuals may safely take 500 mg of magnesium daily under medical supervision, it exceeds the recommended daily intake for most adults. In specific medical scenarios, such as severe magnesium deficiency or certain acute conditions, doctors may prescribe intravenous magnesium sulfate to quickly correct the deficiency. This form of magnesium administration is different from oral supplements and is typically done in a hospital setting under close monitoring to avoid potential side effects, including those associated with high doses of magnesium. Intravenous magnesium sulfate is used for its immediate effect on the body, particularly in emergency situations like eclampsia in pregnant women or life-threatening arrhythmias. However, for daily supplementation, sticking to the recommended dietary allowances and consulting with a healthcare provider is advisable to determine the appropriate magnesium dosage for your needs.
What are the signs of too much magnesium
Signs of consuming high doses of elemental magnesium through supplements, include diarrhea, abdominal cramping, nausea, and, in severe cases, irregular heartbeat and cardiac arrest. It’s important to understand that the term “elemental magnesium” refers to the actual amount of magnesium in a supplement, which is the portion your body can absorb and utilize. When consuming elemental magnesium in amounts exceeding the recommended dietary allowance, the risk of experiencing these adverse effects increases significantly. To avoid symptoms associated with excessive intake of elemental magnesium, individuals should adhere to the recommended doses of magnesium supplements and consult with healthcare professionals to determine the appropriate amount of elemental magnesium for their specific health needs. Monitoring the intake of elemental magnesium is crucial for maintaining optimal magnesium levels in the body without surpassing the threshold that leads to negative side effects.
What are the benefits of taking magnesium 500mg tablets?
Taking magnesium 500mg tablets offers several health benefits, including improved bone health by helping to increase bone mineral density, which in turn reduces the risk of osteoporosis. This specific dosage can play a critical role in the body’s calcium regulation and vitamin D activation, both of which are vital for maintaining and increasing bone mineral density. Additionally, magnesium supplements at this level can contribute to better cardiovascular health by supporting heart function and blood pressure regulation, and they may also help mitigate migraines and various sleep disorders. Regular intake of magnesium 500mg tablets, under the guidance of a healthcare provider, can thus not only enhance bone health through its ability to increase bone mineral density but also provide comprehensive benefits across different aspects of physical well-being.
Can I take 500 mg of magnesium at night?
Taking 500 mg of magnesium at night may help improve sleep quality for some individuals, particularly because magnesium plays a role in relaxing the muscles and the nervous system, which can facilitate falling asleep. Additionally, this dosage of magnesium has been associated with lowering blood pressure, which can be beneficial for cardiovascular health. However, the effect of magnesium on lowering blood pressure should be considered, especially for individuals with pre-existing blood pressure conditions. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider due to the high dose, as they can provide guidance on whether this amount is suitable for your specific health needs and if it can be effectively used as part of a regimen for lowering blood pressure and improving sleep without causing adverse effects.
What is the best form of magnesium to take?
The best form of magnesium to take depends on individual health goals; magnesium citrate is recommended for constipation, magnesium glycinate for sleep and anxiety, and magnesium oxide for heartburn and indigestion relief. Another option, magnesium lactate, is known for its high bioavailability and gentleness on the digestive system, making it a suitable choice for those who may experience digestive discomfort from other forms of magnesium. Magnesium lactate can be particularly beneficial for individuals seeking to improve their overall magnesium levels without the laxative effect commonly associated with magnesium citrate. Choosing the right form of magnesium, whether it be magnesium lactate or another type, should be based on your specific health needs and any existing conditions, and it may be helpful to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most beneficial form for your situation.
Is there a downside to taking magnesium?
Potential downsides to taking magnesium, especially in supplement form, include digestive issues like diarrhea and, at very high doses, more serious side effects such as kidney problems and irregular heartbeat. Among the various types of magnesium supplements, magnesium gluconate is often recommended for those concerned about these digestive issues, as it is considered one of the most gentle forms on the stomach. Magnesium gluconate’s bioavailability is relatively high, meaning the body can absorb it efficiently, reducing the risk of diarrhea compared to other forms of magnesium. However, while magnesium gluconate may minimize digestive discomfort, it’s still important to adhere to recommended dosages to avoid the risk of accumulating excessive magnesium, which can lead to kidney problems and irregular heartbeat. Consulting with a healthcare provider before starting magnesium gluconate or any magnesium supplement can help determine the appropriate dose and mitigate potential downsides.
Is it safe to take 500mg of magnesium a day?
While it may be safe for some individuals under medical supervision, taking 500mg of magnesium a day exceeds the recommended intake and can lead to side effects for others, especially when this dosage is obtained from supplemental magnesium. High doses of supplemental magnesium can cause symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and nausea. It’s crucial for anyone considering such a high dose of supplemental magnesium to consult with a healthcare provider to assess their specific needs and potential risks. Supplemental magnesium can be beneficial for addressing deficiencies and specific health conditions, but maintaining a balance is key to avoiding adverse effects. Additionally, the body’s response to supplemental magnesium can vary based on individual health status, dietary magnesium intake, and the presence of any underlying health conditions. Therefore, while supplemental magnesium can play a significant role in achieving optimal magnesium levels, its use should be carefully managed to prevent exceeding safe consumption limits.
Is 500mg of magnesium glycinate too much?
For most people, 500mg of magnesium glycinate may exceed the recommended daily intake, potentially leading to side effects, though it may be appropriate for some under medical advice.
Is it okay to take 500 mg of magnesium every night?
Taking 500 mg of magnesium every night should be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider, as it exceeds typical recommended daily amounts. When taking magnesium supplements at such a high dosage, it’s crucial to monitor for any potential side effects, as excessive magnesium can lead to issues like diarrhea, nausea, and more serious health concerns. Therefore, individuals considering taking magnesium supplements at this level should consult with a professional to ensure it aligns with their health needs and does not interfere with existing conditions or medications. Additionally, taking magnesium supplements should be part of a balanced approach to nutrition, complementing a diet rich in magnesium-containing foods rather than replacing them. Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider can help adjust the dosage of taking magnesium supplements if necessary, ensuring safety and efficacy in meeting the body’s magnesium needs.
Reference
Nielsen FH, Lukaski HC. Update on the relationship between magnesium and exercise. Magnes Res. 2006;19(3):180-9.
Update on the relationship between magnesium and exercise
Magnesium plays a crucial role in various aspects of muscle function, influencing oxygen uptake, energy production, and electrolyte balance. Research has extensively explored the connection between magnesium status and exercise, revealing that physical activity prompts a redistribution of magnesium in the body to meet metabolic demands. Evidence suggests that even marginal magnesium deficiency can hinder exercise performance and exacerbate the adverse effects of intense physical activity, such as oxidative stress. Strenuous exercise leads to increased losses of magnesium through urine and sweat, potentially raising requirements by 10-20%. Surveys indicate that insufficient magnesium intake is common, particularly among athletes engaged in weight-controlled sports. Both supplementation and heightened dietary magnesium intake prove beneficial for exercise performance in magnesium-deficient individuals. However, physically active individuals with adequate magnesium levels do not experience enhanced performance with supplementation. Establishing activity-linked Recommended Nutrient Intake (RNI) or Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) based on long-term balance data from controlled experiments is crucial for guiding physically active individuals in managing magnesium intake to impact performance and mitigate health risks.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://www.jle.com/fr/revues/mrh/e-docs/update_on_the_relationship_between_magnesium_and_exercise_272229/article.phtml.
Zhang Y, Xun P, Wang R, Mao L, He K. Can Magnesium Enhance Exercise Performance? Nutrients. 2017 Aug 28;9(9):946. doi: 10.3390/nu9090946. PMID: 28846654; PMCID: PMC5622706.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5622706/.Can Magnesium Enhance Exercise Performance?
Magnesium (Mg) is a vital mineral crucial for energy metabolism and the maintenance of normal muscle function. Research investigating the correlation between Mg status or supplementation and exercise performance suggests an increased need for Mg with higher physical activity levels. Animal studies propose that Mg enhances exercise performance by improving glucose availability in the brain, muscle, and blood, as well as reducing or delaying lactate accumulation in the muscles. While human studies mainly focused on physiological effects like blood pressure and heart rate, some surveys indicated positive associations between Mg status and various aspects of muscle performance. Intervention studies suggested that Mg supplementation could lead to functional improvements, including enhanced gait speed and chair stand time in elderly women. This comprehensive review evaluates scientific evidence from both animal and human studies, shedding light on the role of Mg status and supplementation in exercise performance.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5622706/.
Volpe SL. Magnesium and the Athlete. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2015 Jul-Aug;14(4):279-83. doi: 10.1249/JSR.0000000000000178. PMID: 26166051.
You can read the abstract of this article at https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26166051/.Magnesium and the Athlete
Magnesium, ranking as the fourth most abundant mineral and the second most abundant intracellular divalent cation in the body, is essential for over 300 metabolic reactions. It plays a crucial role in maintaining normal nerve and muscle function, heart rhythm, vasomotor tone, blood pressure, immune system, bone integrity, and blood glucose levels, while also facilitating calcium absorption. Due to its involvement in energy production, muscle function, and glucose regulation, magnesium has garnered attention as a potential ergogenic aid for athletes. This article explores the multifaceted roles of magnesium, its dietary requirements, methods of assessing magnesium status, and the impact of magnesium intake on exercise performance, referencing research articles published from 2003 through 2014.
You can read the full article at https://journals.lww.com/acsm-
Chen HY, Cheng FC, Pan HC, Hsu JC, Wang MF. Magnesium enhances exercise performance via increasing glucose availability in the blood, muscle, and brain during exercise. PLoS One. 2014 Jan 20;9(1):e85486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085486. PMID: 24465574; PMCID: PMC3896381.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3896381/.Magnesium enhances exercise performance via increasing glucose availability in the blood, muscle, and brain during exercise
This study investigated the impact of magnesium (Mg) on glucose and lactate dynamics in muscle, blood, and the brain during exercise in rats. Rats were pretreated with either saline or magnesium sulfate before treadmill exercise. Results showed that glucose levels in the muscle, blood, and brain significantly increased during exercise and were approximately doubled in the Mg group. Lactate levels also rose significantly in both groups during exercise, with higher brain lactate levels in the Mg group. Magnesium was found to enhance glucose availability in both peripheral and central systems, along with increased lactate clearance in the muscle during exercise.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3896381/.
Serefko A, Szopa A, Wlaź P, Nowak G, Radziwoń-Zaleska M, Skalski M, Poleszak E. Magnesium in depression. Pharmacol Rep. 2013;65(3):547-54. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(13)71032-6. PMID: 23950577.
Magnesium in depression
Magnesium is a crucial mineral in the human body, intricately linked to brain biochemistry and the fluidity of neuronal membranes. Deficiency in magnesium has been associated with various neuromuscular and psychiatric symptoms, including different forms of depression. While plasma/serum magnesium levels may not consistently serve as accurate indicators of depressive disorders, recent medical practice has recognized magnesium compounds as effective agents in treating conditions such as migraine, alcoholism, asthma, heart diseases, arrhythmias, renal calcium stones, and premenstrual tension syndrome. Magnesium preparations, also utilized in homeopathy, play a significant role in addressing a range of mental health problems. Despite not fully understanding the mechanisms of magnesium’s antidepressant action, numerous studies have confirmed its beneficial safety profile, positioning magnesium as a valuable addition to the pharmacological toolkit for managing depression.
You can read the full article at http://if-pan.krakow.pl/pjp/pdf/2013/3_547.pdf.
Rajizadeh A, Mozaffari-Khosravi H, Yassini-Ardakani M, Dehghani A. Effect of magnesium supplementation on depression status in depressed patients with magnesium deficiency: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutrition. 2017 Mar;35:56-60. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2016.10.014. Epub 2016 Nov 9. PMID: 28241991.
Effect of magnesium supplementation on depression status in depressed patients with magnesium deficiency: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
The objective of this study was to assess the impact of magnesium supplementation on the depression status of individuals with depression and magnesium deficiency. Sixty participants with depression and hypomagnesemia were randomly assigned to receive either two 250-mg tablets of magnesium oxide daily or a placebo for 8 weeks. At the end of the intervention, a significantly higher percentage of the magnesium group (88.5%) achieved a normal magnesium level compared to the placebo group (48.1%). The mean changes in serum magnesium were significantly different between the two groups. The Beck Depression Inventory-II scores showed a significant reduction after the intervention, with the magnesium group experiencing a more substantial decline than the placebo group. The findings suggest that daily magnesium oxide supplementation positively influences both depression status and magnesium levels in depressed individuals with magnesium deficiency.
You can read the full article at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0899900716302441?via%3Dihub.
Botturi A, Ciappolino V, Delvecchio G, Boscutti A, Viscardi B, Brambilla P. The Role and the Effect of Magnesium in Mental Disorders: A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2020 Jun 3;12(6):1661. doi: 10.3390/nu12061661. PMID: 32503201; PMCID: PMC7352515.
The Role and the Effect of Magnesium in Mental Disorders: A Systematic Review
In this study, the relationship between magnesium levels and psychiatric disorders, particularly depression, was investigated, and the potential therapeutic effectiveness of magnesium supplementation was assessed. A systematic review of literature published from 2010 to March 2020 yielded 32 articles covering various psychiatric conditions. Positive results were observed in 12 studies focusing on depressive symptoms, with seven indicating a significant correlation between reduced plasma magnesium values and depression. Two studies reported improved depressive symptoms following magnesium intake, either alone or in combination with antidepressants. While findings were not consistently uniform across all psychiatric disorders, the evidence suggests that magnesium supplementation may hold therapeutic potential, emphasizing the need for further well-designed clinical trials to establish its efficacy, either alone or in combination with other medications, for various psychiatric conditions.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7352515/.
Eby GA, Eby KL. Rapid recovery from major depression using magnesium treatment. Med Hypotheses. 2006;67(2):362-70. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2006.01.047. Epub 2006 Mar 20. PMID: 16542786.
Rapid recovery from major depression using magnesium treatment
Major depression, characterized by feelings of inadequacy, despondency, and disrupted daily functioning, can be challenging to treat with conventional antidepressants. This study explores the potential link between magnesium deficiency and neuropathologies, suggesting that intraneuronal magnesium deficits may contribute to depression. The depletion of magnesium in modern diets, coupled with stress hormones and excess dietary calcium, might lead to neuronal damage. Case histories reveal rapid recovery from major depression with magnesium supplementation, and related mental health issues, such as anxiety and addiction, also show improvement. The study advocates for further research on the role of magnesium in treating depression and recommends considering magnesium fortification in refined grains and drinking water to address deficiencies.
You can read the full article at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0306987706001034?via%3Dihub.
Tarleton EK, Littenberg B. Magnesium intake and depression in adults. J Am Board Fam Med. 2015 Mar-Apr;28(2):249-56. doi: 10.3122/jabfm.2015.02.140176. PMID: 25748766.
Magnesium intake and depression in adults
Depression is a widespread and often debilitating condition, and while magnesium supplementation has been linked to improved depressive symptoms, a consensus on the magnesium-depression relationship remains elusive. This study aimed to investigate the association between dietary magnesium intake and depression in the adult US population using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The results revealed a statistically significant link between very low magnesium intake and depression, particularly in younger adults. Unexpectedly, low magnesium intake appeared to have a potential protective effect in older adults, suggesting a complex relationship that warrants further exploration.
You can read the full article at https://www.jabfm.org/content/28/2/249.long.
Facchinetti F, Borella P, Sances G, Fioroni L, Nappi RE, Genazzani AR. Oral magnesium successfully relieves premenstrual mood changes. Obstet Gynecol. 1991 Aug;78(2):177-81. PMID: 2067759.
Oral magnesium successfully relieves premenstrual mood changes
To assess the impact of oral magnesium (Mg) supplementation on premenstrual symptoms, a double-blind, randomized study involved 32 women with confirmed premenstrual syndrome (PMS). Following a 2-month baseline period, participants were randomly assigned to receive either a placebo or magnesium pyrrolidone carboxylic acid (360 mg Mg) three times a day during the luteal phase. After two cycles, both groups received magnesium for two additional cycles. Results showed a significant reduction in the “pain” cluster of the Menstrual Distress Questionnaire during the second month in both groups, while Mg treatment significantly affected the total Menstrual Distress Questionnaire score and the “negative affect” cluster. Mg supplementation led to increased Mg levels in lymphocytes and polymorphonuclear cells, suggesting its potential as an effective treatment for premenstrual symptoms, particularly those related to mood changes.
You can read the abstract of thel article at https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2067759/.
Tarleton EK, Littenberg B, MacLean CD, Kennedy AG, Daley C. Role of magnesium supplementation in the treatment of depression: A randomized clinical trial. PLoS One. 2017 Jun 27;12(6):e0180067. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180067. PMID: 28654669; PMCID: PMC5487054.
Role of magnesium supplementation in the treatment of depression: A randomized clinical trial
In a randomized, cross-over trial involving 126 adults with mild-to-moderate depression symptoms, the efficacy of over-the-counter magnesium chloride supplementation was investigated. The 6-week intervention with 248 mg of elemental magnesium per day demonstrated a clinically significant net improvement in Patient Health Questionnaire-9 scores, showing a decrease of -6.0 points (CI -7.9, -4.2; P<0.001). Additionally, Generalized Anxiety Disorders-7 scores exhibited a net improvement of -4.5 points (CI -6.6, -2.4; P<0.001). The magnesium supplements were well-tolerated, with an average adherence of 83%, and participants expressed a willingness to use magnesium in the future. These positive effects were observed within two weeks, suggesting that magnesium is effective for mild-to-moderate depression in adults, providing a quick and well-tolerated treatment option.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5487054/.
Noah L, Dye L, Bois De Fer B, Mazur A, Pickering G, Pouteau E. Effect of magnesium and vitamin B6 supplementation on mental health and quality of life in stressed healthy adults: Post-hoc analysis of a randomised controlled trial. Stress Health. 2021 Dec;37(5):1000-1009. doi: 10.1002/smi.3051. Epub 2021 May 6. PMID: 33864354; PMCID: PMC9292249.
Effect of magnesium and vitamin B6 supplementation on mental health and quality of life in stressed healthy adults: Post-hoc analysis of a randomised controlled trial
In a Phase IV randomized controlled study targeting individuals with low magnesemia and severe/extremely severe stress, the combined intervention of magnesium with vitamin B6 showed greater stress reduction compared to magnesium alone over 8 weeks. This previously unreported secondary analysis focused on the impact of these interventions on depression, anxiety, and quality of life (QoL). Both treatments significantly improved Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS-42) anxiety and depression scores from baseline to week 8, particularly within the first 4 weeks. Quality of life also improved steadily over the 8-week period. Moreover, the combination of magnesium and vitamin B6 showed greater enhancement in participants’ perceived capacity for physical activity in daily life by week 4. This suggests that magnesium supplementation, either alone or with vitamin B6, could offer meaningful clinical benefits for individuals experiencing stress and low magnesemia.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9292249/.
Eby GA 3rd, Eby KL. Magnesium for treatment-resistant depression: a review and hypothesis. Med Hypotheses. 2010 Apr;74(4):649-60. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2009.10.051. Epub 2009 Nov 27. PMID: 19944540.
Magnesium for treatment-resistant depression: a review and hypothesis
Sixty percent of clinical depression cases are classified as treatment-resistant depression (TRD). Magnesium deficiency can lead to biased opening of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) coupled calcium channels, causing neuronal injury and dysfunction resembling major depression in humans. Animal studies have shown that oral magnesium administration produces antidepressant-like effects comparable to strong antidepressant drugs. Cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) magnesium levels are low in treatment-resistant suicidal depression and in suicide attempters. Brain magnesium levels, measured using phosphorous nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, are also found to be low in TRD. While blood and CSF magnesium levels don’t consistently correlate with major depression, historical and modern case reports suggest the efficacy of magnesium in treating depression, supported by a 2008 clinical trial demonstrating its effectiveness comparable to tricyclic antidepressants without side effects. Intravenous and oral magnesium protocols have shown rapid and safe termination of TRD. The removal of magnesium from processed foods and the presence of additives like calcium, glutamate, and aspartate might exacerbate affective disorders. Inadequate dietary magnesium is implicated as the main cause of TRD, suggesting a potential role for magnesium supplementation in treating depression beyond TRD, given its association with serotonin levels and antidepressant mechanisms.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0306987709007300?via%3Dihub.
Arab A, Rafie N, Amani R, Shirani F. The Role of Magnesium in Sleep Health: a Systematic Review of Available Literature. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023 Jan;201(1):121-128. doi: 10.1007/s12011-022-03162-1. Epub 2022 Feb 19. PMID: 35184264.
The Role of Magnesium in Sleep Health: a Systematic Review of Available Literature
No comprehensive review has yet analyzed the existing literature on the correlation between magnesium (Mg) and sleep health. To address this gap, we conducted a systematic review encompassing observational and interventional studies investigating Mg’s impact on sleep patterns in adults. Through searches on PubMed, Scopus, and ISI Web of Science, we identified relevant studies up to November 2021, focusing on populations with high Mg intake or supplementation compared to low Mg intake or placebo groups. The review included 7,582 subjects from 9 cross-sectional, cohort, and randomized controlled trials (RCTs), revealing observational evidence linking Mg status to sleep quality but reporting conflicting findings from RCTs. Further well-designed RCTs with larger sample sizes and longer follow-up durations are warranted to clarify the association between dietary magnesium and sleep patterns.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12011-022-03162-1.
Zhang Y, Chen C, Lu L, Knutson KL, Carnethon MR, Fly AD, Luo J, Haas DM, Shikany JM, Kahe K. Association of magnesium intake with sleep duration and sleep quality: findings from the CARDIA study. Sleep. 2022 Apr 11;45(4):zsab276. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsab276. PMID: 34883514; PMCID: PMC8996025.
Association of magnesium intake with sleep duration and sleep quality: findings from the CARDIA study
The study aimed to investigate the longitudinal relationship between magnesium (Mg) intake and calcium-to-magnesium intake ratio (Ca:Mg) with sleep quality and duration. Using data from the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) study, involving 3,964 participants, Mg intake was assessed at multiple time points, and self-reported sleep outcomes were measured. Results showed a borderline association between higher Mg intake and improved sleep quality, as well as a lower likelihood of short sleep duration (<7 hours). These associations persisted among participants without depressive disorders. However, Ca:Mg intake ratio did not show any significant association with sleep outcomes, irrespective of depression status. The findings suggest a potential role of Mg intake in sleep quality and duration, warranting further investigation through randomized controlled trials with objective sleep measures.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8996025/.
Abbasi B, Kimiagar M, Sadeghniiat K, Shirazi MM, Hedayati M, Rashidkhani B. The effect of magnesium supplementation on primary insomnia in elderly: A double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Res Med Sci. 2012 Dec;17(12):1161-9. PMID: 23853635; PMCID: PMC3703169.
The effect of magnesium supplementation on primary insomnia in elderly: A double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial
In this double-blind randomized clinical trial involving 46 elderly subjects, the efficacy of magnesium supplementation in improving insomnia was investigated. Participants received either 500 mg of magnesium or a placebo daily for 8 weeks. Results showed that compared to the placebo group, those receiving magnesium experienced significant improvements in sleep time, sleep efficiency, serum renin and melatonin concentrations, and reductions in insomnia severity index score, sleep onset latency, and serum cortisol concentration. Although not statistically significant, there was also a trend towards reduced early morning awakening and serum magnesium concentration in the magnesium group. These findings suggest that magnesium supplementation may be beneficial in improving both subjective and objective measures of insomnia in elderly individuals.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3703169/.
Mah J, Pitre T. Oral magnesium supplementation for insomnia in older adults: a Systematic Review & Meta-Analysis. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021 Apr 17;21(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03297-z. PMID: 33865376; PMCID: PMC8053283.
Oral magnesium supplementation for insomnia in older adults: a Systematic Review & Meta-Analysis
Magnesium supplementation is commonly believed to enhance sleep quality, yet the evidence supporting this claim remains limited. A systematic review of three randomized controlled trials involving 151 older adults across three countries revealed that magnesium supplementation led to a significant reduction in sleep onset latency compared to placebo. However, the improvement in total sleep time was not statistically significant. Despite the promising results, the trials were deemed to have a moderate-to-high risk of bias, and the quality of evidence was generally low to very low. Thus, while oral magnesium supplements may be a cost-effective option for addressing insomnia symptoms in older adults, further research is needed to establish its efficacy and safety conclusively.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8053283/.
Nielsen FH, Johnson LK, Zeng H. Magnesium supplementation improves indicators of low magnesium status and inflammatory stress in adults older than 51 years with poor quality sleep. Magnes Res. 2010 Dec;23(4):158-68. doi: 10.1684/mrh.2010.0220. Epub 2011 Jan 4. PMID: 21199787.
Magnesium supplementation improves indicators of low magnesium status and inflammatory stress in adults older than 51 years with poor quality sleep
Low magnesium levels have been linked to various conditions with chronic inflammatory stress components, potentially exacerbated by factors like disrupted sleep. In a study involving 100 adults with poor sleep quality, supplementation with magnesium citrate significantly increased erythrocyte magnesium levels and decreased plasma C-reactive protein (CRP) concentrations in those with baseline values over 3.0 mg/L. However, overall sleep quality improvements were observed regardless of magnesium supplementation, complicating the determination of magnesium’s direct impact on sleep quality. These findings underscore the need for further investigation into the relationship between magnesium status and sleep quality to elucidate whether low magnesium levels contribute to poor sleep or vice versa.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21199787/.
Cao Y, Zhen S, Taylor AW, Appleton S, Atlantis E, Shi Z. Magnesium Intake and Sleep Disorder Symptoms: Findings from the Jiangsu Nutrition Study of Chinese Adults at Five-Year Follow-Up. Nutrients. 2018 Sep 21;10(10):1354. doi: 10.3390/nu10101354. PMID: 30248967; PMCID: PMC6212970.
Magnesium Intake and Sleep Disorder Symptoms: Findings from the Jiangsu Nutrition Study of Chinese Adults at Five-Year Follow-Up
Dietary magnesium intake has been linked to improvements in insomnia symptoms in clinical trials, but its association with sleep disorder symptoms at the population level remains unclear. Using data from the Jiangsu Nutrition Study involving 1487 adults, we found that higher magnesium intake was associated with a reduced likelihood of daytime falling asleep in women, but not in men, after adjusting for various factors. However, no significant associations were observed between magnesium intake and daytime sleepiness or night snoring in either gender. These findings suggest potential long-term benefits of dietary magnesium intake in mitigating daytime falling asleep, particularly in women.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6212970/.
Rondanelli M, Opizzi A, Monteferrario F, Antoniello N, Manni R, Klersy C. The effect of melatonin, magnesium, and zinc on primary insomnia in long-term care facility residents in Italy: a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011 Jan;59(1):82-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2010.03232.x. PMID: 21226679.
The effect of melatonin, magnesium, and zinc on primary insomnia in long-term care facility residents in Italy: a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial
The double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial aimed to assess the effectiveness of nightly administration of melatonin, magnesium, and zinc in improving primary insomnia among long-term care facility residents. Forty-three participants aged 78.3 ± 3.9 received either the food supplement or placebo for 8 weeks. Results showed significantly better sleep quality in the supplemented group, as evidenced by improved overall Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index scores and enhancements in secondary endpoints such as total sleep time and quality-of-life measures. This suggests that the treatment regimen has potential benefits for improving sleep quality and overall well-being in this population.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://agsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2010.03232.x.
Al Wadee Z, Ooi SL, Pak SC. Serum Magnesium Levels in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 14;10(9):2273. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092273. PMID: 36140382; PMCID: PMC9496273.
Serum Magnesium Levels in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
The aim of this systematic review was to assess the impact of obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) on serum magnesium (Mg) levels and its potential health consequences. Analysis of six clinical studies revealed that OSA patients may have lower serum Mg levels compared to healthy controls, with OSA severity negatively affecting Mg levels. While mean serum Mg levels in OSA patients did not significantly differ from the normal range, low Mg levels correlated with worsened cardiovascular risk biomarkers. Treatment of OSA coincided with improved Mg levels and severity. Sleep deprivation in OSA patients may contribute to Mg deficiency, increasing the risk of inflammation and cardiovascular and metabolic diseases.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9496273/.
Saba S, Faizi F, Sepandi M, Nehrir B. Effect of short-term magnesium supplementation on anxiety, depression and sleep quality in patients after open-heart surgery. Magnes Res. 2022 Apr 1;35(2):62-70. English. doi: 10.1684/mrh.2022.0503. PMID: 36354243.
Effect of short-term magnesium supplementation on anxiety, depression and sleep quality in patients after open-heart surgery
This study aimed to assess the impact of magnesium supplementation on anxiety, depression, and sleep quality in patients following open-heart surgery. Sixty participants were divided into control and intervention groups, with the intervention group receiving 500 mg of magnesium daily for five days post-surgery. Results showed a significant increase in magnesium levels and a decrease in anxiety and depression scores, along with improved sleep quality in the intervention group compared to controls. These findings suggest the potential benefits of magnesium supplementation in post-cardiac surgery patients to alleviate anxiety, depression, and enhance sleep quality.
You can read the full article at https://www.jle.com/fr/revues/mrh/e-docs/effect_of_short_term_magnesium_supplementation_on_anxiety_depression_and_sleep_quality_in_patients_after_open_heart_surgery_323411/article.phtml.
Hornyak M, Voderholzer U, Hohagen F, Berger M, Riemann D. Magnesium therapy for periodic leg movements-related insomnia and restless legs syndrome: an open pilot study. Sleep. 1998 Aug 1;21(5):501-5. doi: 10.1093/sleep/21.5.501. PMID: 9703590.
Magnesium therapy for periodic leg movements-related insomnia and restless legs syndrome: an open pilot study
In an open clinical and polysomnographic study involving 10 patients experiencing insomnia due to periodic limb movements during sleep (PLMS) or mild-to-moderate restless legs syndrome (RLS), oral magnesium therapy was administered over 4-6 weeks. Following treatment, PLMS associated with arousals decreased significantly, and there was a moderate reduction in PLMS without arousal. Sleep efficiency also improved notably. These findings suggest that magnesium supplementation could be a beneficial alternative therapy for insomnia related to mild or moderate RLS or PLMS, warranting further placebo-controlled investigations to elucidate its role in RLS pathophysiology.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://academic.oup.com/sleep/article/21/5/501/2725976?login=false.
Djokic G, Vojvodić P, Korcok D, Agic A, Rankovic A, Djordjevic V, Vojvodic A, Vlaskovic-Jovicevic T, Peric-Hajzler Z, Matovic D, Vojvodic J, Sijan G, Wollina U, Tirant M, Thuong NV, Fioranelli M, Lotti T. The Effects of Magnesium – Melatonin – Vit B Complex Supplementation in Treatment of Insomnia. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019 Aug 30;7(18):3101-3105. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2019.771. PMID: 31850132; PMCID: PMC6910806.
The Effects of Magnesium – Melatonin – Vit B Complex Supplementation in Treatment of Insomnia
Insomnia, characterized by difficulty falling or staying asleep, often results in daytime sleepiness and a sense of unwellness. Common treatments include GABAA receptor modulators or melatonin agonists, but our study aimed to assess the efficacy of a magnesium-melatonin-vitamin B complex supplement for insomnia. Sixty patients diagnosed with insomnia were randomly assigned to receive either the supplement or no treatment for three months. Results showed a significant reduction in insomnia severity with the supplement, indicating its potential as a beneficial treatment for insomnia regardless of its cause.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6910806/.
Mori H, Tack J, Suzuki H. Magnesium Oxide in Constipation. Nutrients. 2021 Jan 28;13(2):421. doi: 10.3390/nu13020421. PMID: 33525523; PMCID: PMC7911806.
Magnesium Oxide in Constipation
Magnesium oxide, traditionally employed as a laxative in East Asia, has seen renewed interest due to its convenience, affordability, and safety. However, recent clinical findings stress the importance of considering optimal dosage, serum levels, potential interactions, and side effects, particularly in elderly and renal-impaired patients. This review aims to assess the evidence supporting magnesium oxide’s efficacy for constipation treatment while offering practical insights into its benefits and drawbacks.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7911806/.
Mori S, Tomita T, Fujimura K, Asano H, Ogawa T, Yamasaki T, Kondo T, Kono T, Tozawa K, Oshima T, Fukui H, Kimura T, Watari J, Miwa H. A Randomized Double-blind Placebo-controlled Trial on the Effect of Magnesium Oxide in Patients With Chronic Constipation. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2019 Oct 30;25(4):563-575. doi: 10.5056/jnm18194. PMID: 31587548; PMCID: PMC6786451.
A Randomized Double-blind Placebo-controlled Trial on the Effect of Magnesium Oxide in Patients With Chronic Constipation
In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, the therapeutic effects of magnesium oxide (MgO) were evaluated in Japanese patients with chronic constipation (CC). Thirty-four female patients were assigned either placebo or MgO (0.5 g × 3/day) for 28 days. The MgO group showed significant improvement in overall constipation symptoms, spontaneous bowel movements, stool form, colonic transit time, abdominal symptoms, and quality of life compared to the placebo group. MgO proved to be an effective treatment for Japanese CC patients with mild to moderate symptoms, enhancing defecation status and shortening colonic transit time.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6786451/.
Zhang L, Du Z, Li Z, Yu F, Li L. Association of dietary magnesium intake with chronic constipation among US adults: Evidence from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Food Sci Nutr. 2021 Sep 29;9(12):6634-6641. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2611. PMID: 34925793; PMCID: PMC8645769.
Association of dietary magnesium intake with chronic constipation among US adults: Evidence from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
The study aimed to explore the relationship between dietary magnesium intake and chronic constipation in the general population using data from the NHANES 2007-2010. A total of 9,519 participants were included, and their bowel habits were assessed through questionnaires. Results showed an inverse association between dietary magnesium intake and chronic constipation defined by stool frequency, particularly among men. However, no significant association was found between magnesium intake and constipation defined by stool consistency. Further longitudinal studies are required to validate these findings.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8645769/.
Hassanein SMA, Deifallah SM, Bastawy HA. Efficacy of oral magnesium therapy in the treatment of chronic constipation in spastic cerebral palsy children: a randomized controlled trial. World J Pediatr. 2021 Feb;17(1):92-98. doi: 10.1007/s12519-020-00401-0. Epub 2021 Jan 22. PMID: 33481179.
Efficacy of oral magnesium therapy in the treatment of chronic constipation in spastic cerebral palsy children: a randomized controlled trial
In children with spastic cerebral palsy (sCP), chronic constipation is prevalent and impactful. A prospective, double-blinded randomized control trial involving 100 children aged 2-12 years with sCP aimed to assess the efficacy and safety of oral magnesium sulfate for treating constipation. Administering oral magnesium sulfate daily for 1 month significantly improved constipation scores, stool frequency, and consistency compared to the placebo group (P < 0.001), with 68% experiencing effective treatment versus 9.5% in the placebo group. Moreover, painful bowel evacuation attempts decreased notably in the magnesium sulfate group, highlighting its potential in alleviating constipation and reducing maternal caregiving time.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12519-020-00401-0.
Dupont C, Hébert G. Magnesium Sulfate-Rich Natural Mineral Waters in the Treatment of Functional Constipation-A Review. Nutrients. 2020 Jul 10;12(7):2052. doi: 10.3390/nu12072052. PMID: 32664341; PMCID: PMC7400933.
Magnesium Sulfate-Rich Natural Mineral Waters in the Treatment of Functional Constipation-A Review
Functional constipation (FC) presents a significant challenge due to its chronic nature and impact on quality of life. While first-line treatments emphasize physical activity and dietary adjustments, many patients require pharmacological interventions. Magnesium sulfate, historically used for its laxative properties, has gained attention in FC management. Although clinical studies demonstrating its efficacy were lacking until recently, the review of available data suggests that magnesium sulfate-rich natural mineral waters could offer a safe and effective natural treatment option for FC.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7400933/.
Kinnunen O, Salokannel J. Constipation in elderly long-stay patients: its treatment by magnesium hydroxide and bulk-laxative. Ann Clin Res. 1987;19(5):321-3. PMID: 3126699.
Constipation in elderly long-stay patients: its treatment by magnesium hydroxide and bulk-laxative
In a trial involving 64 geriatric long-stay patients aged 65 years or older who were using laxatives, magnesium hydroxide demonstrated greater efficacy compared to bulk-laxative. The mean daily dose of magnesium hydroxide was 25 ml, while for bulk-laxative, it was 8.7 g. Magnesium hydroxide resulted in a more frequent bowel habit (13.2 vs. 10.4/4 weeks, p < 0.001) and reduced the need for additional laxative bisacodyl compared to bulk-laxative (2.3 vs. 3.3/4 weeks, p < 0.01). Stool consistency also improved with magnesium hydroxide treatment. Although two patients showed elevated serum magnesium levels after magnesium hydroxide treatment, there were no clinical signs of hypermagnesemia. Overall, the study suggests that magnesium hydroxide is more effective than bulk-laxative for treating constipation in elderly long-stay patients.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3126699/.
Morishita D, Tomita T, Mori S, Kimura T, Oshima T, Fukui H, Miwa H. Senna Versus Magnesium Oxide for the Treatment of Chronic Constipation: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021 Jan 1;116(1):152-161. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000942. PMID: 32969946.
Magnesium Oxide for the Treatment of Chronic Constipation: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
In the first prospective, double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial comparing a stimulant laxative with an osmotic agent for chronic idiopathic constipation, patients were randomly assigned to receive senna (1.0 g), magnesium oxide (MgO, 1.5 g), or placebo for 28 days. The primary endpoint was overall symptom improvement, with secondary endpoints including spontaneous bowel movement (SBM), complete SBM, and patient assessment of constipation quality of life (QOL). Results showed a significant response rate for overall improvement in both the senna and MgO groups compared to placebo, along with greater improvements in SBM and complete SBM. Moreover, significant enhancements in constipation QOL were observed with senna and MgO treatment. The study suggests that both senna and MgO are effective and safe options for constipation management.
You can read the abstract of tne article at https://journals.lww.com/ajg/abstract/2021/01000/senna_versus_magnesium_oxide_for_the_treatment_of.27.aspx.
Benninga MA; MENA Infant Constipation Study Group; Vandenplas Y. The Magnesium-Rich Formula for Functional Constipation in Infants: a Randomized Comparator-Controlled Study. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2019 May;22(3):270-281. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2019.22.3.270. Epub 2019 Apr 18. PMID: 31110960; PMCID: PMC6506425.
The Magnesium-Rich Formula for Functional Constipation in Infants: a Randomized Comparator-Controlled Study
In this open-label, interventional, and comparator-controlled study, the effectiveness of magnesium (Mg)-enriched formula versus a control formula was compared in constipated infants aged ≤6 months. Infants were randomized to receive either formula for 30 days, with stool consistency and frequency monitored by parents and clinical examinations conducted by physicians. Results showed that after 7 days, significantly more infants fed the Mg-rich formula had stools with normal consistency and increased frequency compared to the control group. Moreover, a higher proportion of infants responded completely to the Mg-rich formula, and parents expressed high satisfaction with the treatment. This study suggests that the Mg-rich formula effectively improves stool consistency and frequency in constipated infants.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6506425/.
Garrison SR, Korownyk CS, Kolber MR, Allan GM, Musini VM, Sekhon RK, Dugré N. Magnesium for skeletal muscle cramps. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 21;9(9):CD009402. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009402.pub3. PMID: 32956536; PMCID: PMC8094171.
Magnesium for skeletal muscle cramps
This review assesses the efficacy of magnesium supplementation for skeletal muscle cramps compared to placebo or other treatments. Eleven trials with 735 participants were analyzed, focusing on various populations including those with pregnancy-associated leg cramps and idiopathic cramps. Results suggest that magnesium supplementation does not significantly reduce cramp frequency or intensity in older adults with idiopathic cramps, while evidence for pregnancy-associated cramps is conflicting. Adverse events, mainly gastrointestinal, were more common with magnesium supplementation. Overall, magnesium supplementation may not offer meaningful prophylaxis for skeletal muscle cramps in older adults, but further research is needed for specific populations like pregnant individuals and those with disease-associated cramps.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8094171/.
Moretti A. What is the role of magnesium for skeletal muscle cramps? A Cochrane Review summary with commentary. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2021 Mar 1;21(1):1-3. PMID: 33657750; PMCID: PMC8020016.
What is the role of magnesium for skeletal muscle cramps? A Cochrane Review summary with commentary
Muscle cramps, characterized by sudden and painful contractions of skeletal muscle fibers, can occur without an apparent cause (idiopathic) or be linked to various diseases. While the exact mechanisms are not fully understood, neurological factors are implicated, particularly in conditions like poliomyelitis and neuropathies. Systemic disorders like metabolic imbalances and electrolyte disturbances, including hypomagnesemia, are also associated with cramps. Magnesium, essential for nerve transmission and muscle function, is often supplemented to prevent cramps, with potential benefits for musculoskeletal health and exercise performance. However, the efficacy of magnesium supplementation in preventing or treating muscle cramps remains uncertain.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8020016/.
Reno AM, Green M, Killen LG, O’Neal EK, Pritchett K, Hanson Z. Effects of Magnesium Supplementation on Muscle Soreness and Performance. J Strength Cond Res. 2022 Aug 1;36(8):2198-2203. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000003827. Epub 2020 Oct 1. PMID: 33009349.
Effects of Magnesium Supplementation on Muscle Soreness and Performance
In this double-blind study, the effects of magnesium (Mg) supplementation (350 mg·d -1 , 10 days) on muscle soreness and performance were investigated. College-aged male ( n = 9) and female ( n = 13) participants completed eccentric bench press sessions inducing fatigue/soreness followed by performance sessions (total volume and repetitions to failure [RTF] [65, 75, and 85% of 1 repetition maximum]) 48 hours later with perceptual measures. Mg supplementation significantly reduced muscle soreness compared to baseline at 24, 36, and 48 hours post-trial, with no significant change observed for the placebo group. Performance outcomes approached significance, particularly for total RTF and at 65% and 75% RTF (Mg vs. placebo). Perceptual responses, including session rating of perceived exertion and acute rating of perceived exertion, favored the Mg group. Additionally, perceived recovery after supplementation improved significantly for Mg compared to baseline, while no significant change was observed for the placebo group. These findings suggest that Mg supplementation may reduce muscle soreness and improve perceived recovery, with some evidence for enhancing performance.
You can read the full article at https://journals.lww.com/nsca-jscr/abstract/2022/08000/effects_of_magnesium_supplementation_on_muscle.19.aspx.
Barna O, Lohoida P, Holovchenko Y, Bazylevych A, Velychko V, Hovbakh I, Bula L, Shechter M. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study assessing the efficacy of magnesium oxide monohydrate in the treatment of nocturnal leg cramps. Nutr J. 2021 Oct 31;20(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12937-021-00747-9. PMID: 34719399; PMCID: PMC8559389.
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study assessing the efficacy of magnesium oxide monohydrate in the treatment of nocturnal leg cramps
In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter study, the efficacy and safety of magnesium oxide monohydrate (MOMH) were assessed for the treatment of nocturnal leg cramps (NLC). Conducted in Ukraine from February to August 2018, eligible subjects received MOMH 226 mg or placebo once daily at bedtime for 60 days. The study found a significant decrease in the number and duration of NLC episodes in both groups compared to baseline, with MOMH demonstrating a higher reduction compared to placebo. MOMH treatment also led to greater improvements in sleep quality. These findings suggest that MOMH is effective, safe, and well-tolerated for treating NLC.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8559389/.
Frusso R, Zárate M, Augustovski F, Rubinstein A. Magnesium for the treatment of nocturnal leg cramps: a crossover randomized trial. J Fam Pract. 1999 Nov;48(11):868-71. PMID: 10907623.
Magnesium for the treatment of nocturnal leg cramps: a crossover randomized trial
In a crossover randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial conducted at a university-based ambulatory clinic in Buenos Aires, Argentina, the efficacy of magnesium in treating nocturnal leg cramps was evaluated. Ninety-three subjects underwent a 4-week washout period with placebo, followed by randomization to receive either magnesium citrate or placebo for 1 month, with a subsequent crossover. Forty-two patients completed the 4-month study, with no significant differences observed between magnesium and placebo in the number, duration, severity, or sleep disturbance caused by nocturnal leg cramps. The study concluded that magnesium was not effective in treating these cramps, attributing any observed improvements to a period-effect bias, including the natural course of the condition, regression to the mean, and placebo effects.
You can read the full article at https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10907623/.
Ceneviva GD, Thomas NJ, Kees-Folts D. Magnesium sulfate for control of muscle rigidity and spasms and avoidance of mechanical ventilation in pediatric tetanus. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2003 Oct;4(4):480-4. doi: 10.1097/01.PCC.0000090015.03962.8B. PMID: 14525647.
Magnesium sulfate for control of muscle rigidity and spasms and avoidance of mechanical ventilation in pediatric tetanus
In this case report, we detail the successful use of intravenous magnesium sulfate to manage muscle spasms and severe generalized rigidity in a 12-year-old child with moderate to severe tetanus. Administered in a pediatric intensive care unit setting, continuous infusion of magnesium sulfate effectively alleviated symptoms without the need for prolonged deep sedation, mechanical ventilation, or neuromuscular blockade. No adverse effects were observed, highlighting magnesium sulfate as a potential therapeutic option for managing tetanus-associated muscle spasms and rigidity when close monitoring of neurological, cardiovascular, and respiratory function is feasible.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://journals.lww.com/pccmjournal/abstract/2003/10000/magnesium_sulfate_for_control_of_muscle_rigidity.15.aspx.
Roffe C, Sills S, Crome P, Jones P. Randomised, cross-over, placebo controlled trial of magnesium citrate in the treatment of chronic persistent leg cramps. Med Sci Monit. 2002 May;8(5):CR326-30. PMID: 12011773.
Randomised, cross-over, placebo controlled trial of magnesium citrate in the treatment of chronic persistent leg cramps
This study investigates the efficacy of magnesium citrate in treating nocturnal leg cramps in non-pregnant individuals through a randomized, double-blind, cross-over placebo-controlled trial. Volunteers experiencing regular leg cramps received magnesium citrate or placebo for 6 weeks each. While there was no significant difference in cramp severity or duration between the groups, there was a trend towards fewer cramps with magnesium. Additionally, more participants reported that magnesium helped alleviate their symptoms compared to placebo. However, diarrhea was noted as a side effect of magnesium. These findings suggest that magnesium may be beneficial for treating nocturnal leg cramps, but further research is warranted for conclusive evidence.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://medscimonit.com/abstract/index/idArt/420841.
Su HC, Lin CP, Ho WJ, Chou SH, Wu CT, Chiang HY, Chu PH. Factors affecting the intensity of chronic musculoskeletal pain in patients with cardiovascular disease and evaluation of the efficacy of magnesium emulsion cream for muscle cramps. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Oct 27;102(43):e35532. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035532. PMID: 37904395; PMCID: PMC10615485.
Factors affecting the intensity of chronic musculoskeletal pain in patients with cardiovascular disease and evaluation of the efficacy of magnesium emulsion cream for muscle cramps
This study examined factors influencing chronic musculoskeletal pain (CMP) intensity in patients with cardiovascular disease (CVD) and evaluated the effectiveness of Ice Power Magnesium In Strong Cream for muscle cramps. Analysis of 396 patients revealed older age, female sex, hypertension, and calcium supplement use as significant factors for higher CMP intensity. In a subgroup of 73 patients with muscle cramps, the cream significantly reduced pain scores at weeks 2 and 4 compared to baseline. These findings suggest Ice Power Magnesium In Strong Cream’s efficacy in alleviating lower extremity muscle cramp pain alongside identifying key factors influencing CMP intensity in CVD patients.
You can read the full article athttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10615485/.
Liu J, Song G, Zhao G, Meng T. Effect of oral magnesium supplementation for relieving leg cramps during pregnancy: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Jul;60(4):609-614. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2021.05.006. PMID: 34247796.
Effect of oral magnesium supplementation for relieving leg cramps during pregnancy: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Leg cramps are a common issue during pregnancy, affecting 30%-50% of pregnant women. They can cause significant pain, sleep disturbances, and hinder daily activities. Despite several randomized controlled trials (RCTs) examining magnesium supplements’ effects on relieving leg cramps, the results have been inconsistent. A review of four RCTs involving 332 pregnant women found that magnesium supplementation did not decrease the frequency of leg cramps after treatment or improve recovery compared to the control group. Additionally, magnesium supplementation showed no significant side effects. Overall, oral magnesium supplementation was deemed ineffective for treating leg cramps during pregnancy.
You can read the full article athttps://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1028455921001182?via%3Dihub.
Garrison SR, Birmingham CL, Koehler BE, McCollom RA, Khan KM. The effect of magnesium infusion on rest cramps: randomized controlled trial. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2011 Jun;66(6):661-6. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glq232. Epub 2011 Feb 2. PMID: 21289017.
The effect of magnesium infusion on rest cramps: randomized controlled trial
Leg cramps, a common discomfort during pregnancy affecting 30%-50% of women, can lead to significant pain, sleep disturbances, and disruptions in daily activities. Despite multiple randomized controlled trials (RCTs) investigating the efficacy of magnesium supplements in alleviating leg cramps, the findings remain inconsistent. A review of four RCTs involving 332 pregnant women found no significant reduction in the frequency of leg cramps or improvement in recovery with magnesium supplementation compared to control groups. Moreover, magnesium supplementation showed no significant side effects. Overall, oral magnesium supplementation was deemed ineffective for treating leg cramps during pregnancy.
You can read the full article at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1028455921001182?via%3Dihub.
Clinton CW, Braude BM, James MF. Painful muscle spasm reversed by magnesium sulphate. A case report. S Afr Med J. 1985 Aug 31;68(5):332-3. PMID: 4035497.
Painful muscle spasm reversed by magnesium sulphate.A case report
A 25-year-old paraplegic man with a history of T3/T4 vertebral compression fracture experienced severe and painful spasms in the left hamstring muscle group lasting 2 hours, resulting in extreme knee flexion and positioning of the left foot posterior to the right buttock. Immediate relief was achieved with a 2 g intravenous injection of magnesium sulfate. Potential mechanisms of magnesium’s action in alleviating muscle spasms are deliberated.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4035497/.
Supakatisant C, Phupong V. Oral magnesium for relief in pregnancy-induced leg cramps: a randomised controlled trial. Matern Child Nutr. 2015 Apr;11(2):139-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1740-8709.2012.00440.x. Epub 2012 Aug 22. PMID: 22909270; PMCID: PMC6860204.
Oral magnesium for relief in pregnancy-induced leg cramps: a randomised controlled trial
Leg cramps are prevalent among pregnant women, yet standard treatments remain elusive. This double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial aimed to assess the efficacy of oral magnesium in alleviating pregnancy-induced leg cramps. Eighty-six healthy pregnant women, experiencing leg cramps at least twice weekly, participated, with 80 completing the study. Those assigned to magnesium bisglycinate chelate (300 mg/day) showed a significantly higher reduction in cramp frequency (86.0% vs. 60.5%, P=0.007) and intensity (69.8% vs. 48.8%, P=0.048) compared to the placebo group. Side effects like nausea and diarrhea did not significantly differ between the groups. These findings suggest that oral magnesium supplementation may effectively mitigate the frequency and intensity of pregnancy-induced leg cramps, offering a potential treatment option for affected women.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6860204/.
Sebo P, Cerutti B, Haller DM. Effect of magnesium therapy on nocturnal leg cramps: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials with meta-analysis using simulations. Fam Pract. 2014 Feb;31(1):7-19. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmt065. Epub 2013 Nov 26. PMID: 24280947.
Effect of magnesium therapy on nocturnal leg cramps: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials with meta-analysis using simulations
Nocturnal leg cramps (NLC) are a common concern in primary care, often causing significant pain and sleep disruption. This systematic review aimed to evaluate magnesium’s efficacy in treating NLC and its side-effect profile compared to placebo. Seven randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were analyzed, involving 361 participants, with three trials focused on pregnant women. The difference in the median number of leg cramps per week between magnesium and placebo groups was minimal overall, with slightly more gastrointestinal side effects observed with magnesium. However, evidence strength was weak due to small study sizes and short follow-up, suggesting further well-designed RCTs are needed to clarify magnesium’s role in NLC treatment, particularly in pregnant women.
You can read the full article at https://academic.oup.com/fampra/article/31/1/7/438649?login=false.
Steward CJ, Zhou Y, Keane G, Cook MD, Liu Y, Cullen T. One week of magnesium supplementation lowers IL-6, muscle soreness and increases post-exercise blood glucose in response to downhill running. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2019 Dec;119(11-12):2617-2627. doi: 10.1007/s00421-019-04238-y. Epub 2019 Oct 17. PMID: 31624951.
One week of magnesium supplementation lowers IL-6, muscle soreness and increases post-exercise blood glucose in response to downhill running
Nocturnal leg cramps (NLC) are a prevalent issue, often leading to significant discomfort and sleep disturbances. This systematic review aimed to assess the effectiveness of magnesium in alleviating NLC and its side effects compared to a placebo. Seven randomized controlled trials (RCTs), involving 361 participants, were analyzed, with three trials focusing on pregnant women. Overall, the difference in the median number of leg cramps per week between magnesium and placebo groups was minimal, with slightly more gastrointestinal side effects observed with magnesium. However, the evidence strength was weak due to small study sizes and short follow-up durations, warranting further well-designed RCTs to ascertain magnesium’s efficacy in NLC treatment, particularly among pregnant women.
You can read the full article at https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00421-019-04238-y.
Tangvoraphonkchai K, Davenport A. Magnesium and Cardiovascular Disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018 May;25(3):251-260. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2018.02.010. PMID: 29793664.
Magnesium and Cardiovascular Disease
Magnesium, abundant intracellularly, is crucial for cellular function and metabolism, serving as an enzyme cofactor, regulating ion channels, and supporting energy production. In the heart, magnesium modulates neuronal excitation, cardiac conduction, and muscle contraction by regulating ion transporters. Additionally, it influences vascular tone, atherosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular cell activity, potentially impacting cardiovascular disease development. Kidney disorders can disrupt magnesium balance, increasing cardiovascular risk. While low magnesium levels correlate with heart issues, supplementation trials yield inconsistent results, suggesting caution in routine use except for confirmed or suspected hypomagnesemia-induced arrhythmias.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://www.akdh.org/article/S1548-5595(18)30040-5/fulltext.
- Kolte D, Vijayaraghavan K, Khera S, Sica DA, Frishman WH. Role of magnesium in cardiovascular diseases. Cardiol Rev. 2014 Jul-Aug;22(4):182-92. doi: 10.1097/CRD.0000000000000003. PMID: 24896250.
Role of magnesium in cardiovascular diseases
Magnesium, as the fourth most abundant cation in the body, regulates vital cardiovascular functions, impacting vascular tone, endothelial function, and myocardial excitability. Its involvement in physiological processes underlies its significance in cardiovascular health, influencing conditions like hypertension, atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease, heart failure, and arrhythmias. This review highlights magnesium’s vasodilatory, anti-inflammatory, anti-ischemic, and antiarrhythmic effects, emphasizing its role in preventing and treating cardiovascular disorders.
You can read the full article at https://journals.lww.com/cardiologyinreview/abstract/2014/07000/role_of_magnesium_in_cardiovascular_diseases.5.aspx.
Rosique-Esteban N, Guasch-Ferré M, Hernández-Alonso P, Salas-Salvadó J. Dietary Magnesium and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review with Emphasis in Epidemiological Studies. Nutrients. 2018 Feb 1;10(2):168. doi: 10.3390/nu10020168. PMID: 29389872; PMCID: PMC5852744.
Dietary Magnesium and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review with Emphasis in Epidemiological Studies
Magnesium (Mg), an essential dietary element, plays a crucial role in various biological processes. Recent evidence from epidemiological studies, randomized controlled trials (RCTs), and meta-analyses suggests a link between Mg intake and cardiovascular diseases (CVD). This review synthesizes findings on the association between Mg intake and major CV risk factors, as well as CVD, emphasizing the role of circulating Mg levels. High Mg intake appears to correlate with a reduced risk of major CV risk factors, stroke, and total CVD, while higher circulating Mg levels are associated with a lower risk of specific CVDs like ischemic and coronary heart disease. Further research, including RCTs and prospective studies, is needed to explore potential protective effects of Mg against other CVDs and CVD-related mortality.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5852744/.
Del Gobbo LC, Imamura F, Wu JH, de Oliveira Otto MC, Chiuve SE, Mozaffarian D. Circulating and dietary magnesium and risk of cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013 Jul;98(1):160-73. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.112.053132. Epub 2013 May 29. PMID: 23719551; PMCID: PMC3683817.
Circulating and dietary magnesium and risk of cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies
Clinical hypomagnesemia and experimental dietary magnesium restriction have been linked to increased cardiac arrhythmias, but the impact of circulating or dietary magnesium at typical concentrations or intakes on cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk, including fatal ischemic heart disease (IHD), remains uncertain. Through a systematic review and meta-analysis of 16 studies comprising 313,041 individuals, associations between circulating and dietary magnesium and CVD incidence were explored. Higher circulating magnesium levels were associated with a 30% lower CVD risk, while dietary magnesium intake showed a 22% reduced risk of IHD. However, the association with fatal IHD was nonlinear, suggesting an inverse association with dietary magnesium intake up to ∼250 mg/d. These findings underscore the potential importance of magnesium in CVD prevention, warranting further clinical trials for validation.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3683817/.
DiNicolantonio JJ, Liu J, O’Keefe JH. Magnesium for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease. Open Heart. 2018 Jul 1;5(2):e000775. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2018-000775. PMID: 30018772; PMCID: PMC6045762.
Magnesium for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease
Magnesium, a vital intracellular cation, plays a crucial role in cellular physiology, enzyme activity, and ion channel regulation, particularly in the heart where it modulates neuronal excitation, intracardiac conduction, and myocardial contraction. Additionally, magnesium influences vascular tone, atherogenesis, thrombosis, and endothelial function, impacting cardiovascular disease (CVD) pathogenesis. Kidney disorders can disrupt magnesium homeostasis, affecting CVD risk. While low serum magnesium levels correlate with increased CVD risk, supplementation trials have yielded inconsistent results, underscoring the uncertainty surrounding routine magnesium supplementation in CVD prevention, barring cases of proven or suspected hypomagnesemia linked to cardiac arrhythmias.
You can read the full article at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1548559518300405#:~:text=Magnesium%20also%20has%20a%20role,the%20pathogenesis%20of%20cardiovascular%20disease..
Houston M. The role of magnesium in hypertension and cardiovascular disease. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2011 Nov;13(11):843-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2011.00538.x. Epub 2011 Sep 26. PMID: 22051430; PMCID: PMC8108907.
The role of magnesium in hypertension and cardiovascular disease
Daily magnesium intake ranging from 500 mg to 1000 mg may lead to a reduction in blood pressure by up to 5.6/2.8 mm Hg, although clinical studies show varied outcomes, with some demonstrating no change in blood pressure. Combining increased magnesium and potassium intake with reduced sodium intake proves more effective in blood pressure reduction than single mineral supplementation and can rival the efficacy of antihypertensive medications. Enhanced intracellular magnesium and potassium levels, alongside reduced intracellular sodium and calcium, contribute to improved blood pressure response. Moreover, magnesium enhances the effectiveness of all antihypertensive drug classes. While the preventative or therapeutic role of magnesium intake in cardiovascular diseases like coronary heart disease, ischemic stroke, and cardiac arrhythmias awaits conclusive evidence, initial findings suggest potential benefits in improving insulin sensitivity, hyperglycemia, diabetes mellitus, left ventricular hypertrophy, and dyslipidemia. Additionally, genetic defects in magnesium transport may be associated with hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Oral magnesium functions as a natural calcium channel blocker, promotes nitric oxide production, ameliorates endothelial dysfunction, and facilitates vasodilation both directly and indirectly.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8108907/.
Bo S, Pisu E. Role of dietary magnesium in cardiovascular disease prevention, insulin sensitivity and diabetes. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2008 Feb;19(1):50-6. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e3282f33ccc. PMID: 18196987.
Role of dietary magnesium in cardiovascular disease prevention, insulin sensitivity and diabetes
The review aims to outline the evidence supporting the beneficial effects of magnesium on metabolic abnormalities, inflammation, and cardiovascular risk factors, alongside potential underlying mechanisms. It addresses controversies stemming from conflicting literature findings. While increased dietary magnesium intake appears to guard against diabetes, metabolic syndrome, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease, its impact on incident pathologies in prospective studies is modest. Magnesium supplementation’s effects on glucose metabolism, blood lipid levels, and ischemic heart disease vary inconsistently. Despite strong biological plausibility, in-vivo magnesium deficiency may only play a limited role, with factors like reverse causality and the association with other nutrients potentially confounding results.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://journals.lww.com/co-lipidology/abstract/2008/02000/role_of_dietary_magnesium_in_cardiovascular.10.aspx.
Chakraborti S, Chakraborti T, Mandal M, Mandal A, Das S, Ghosh S. Protective role of magnesium in cardiovascular diseases: a review. Mol Cell Biochem. 2002 Sep;238(1-2):163-79. doi: 10.1023/a:1019998702946. PMID: 12349904.
Protective role of magnesium in cardiovascular diseases: a review
A wealth of experimental, epidemiological, and clinical evidence underscores the crucial role of Mg2+ in cardiovascular pathology. Hypomagnesemia in humans often coincides with electrolyte imbalances like Na+, K+, and Ca2+. Dietary Mg2+ deficiency and metabolic abnormalities contribute significantly to various heart conditions, including ischemic heart disease, congestive heart failure, sudden cardiac death, atherosclerosis, arrhythmias, and diabetic ventricular complications. Mg2+ deficiency leads to coronary vasoconstriction, diminishing oxygen and nutrient delivery to cardiac cells. Experimental and clinical data suggest that Mg2+ depletion triggers intracellular Ca2+ elevation, oxidative stress, inflammation, and membrane permeability changes in cardiac cells. Mg2+ and Ca2+ compete for binding sites on key contractile proteins, modulating myocardial contractility. Alcohol-induced Mg2+ depletion exacerbates intracellular Ca2+ levels, fostering coronary artery spasm, arrhythmias, and cardiac dysfunction. Hypomagnesemia often coexists with hypokalemia in hypertensive or myocardial infarction patients and chronic alcoholics. While certain mechanisms remain contentious, Mg2+ supplementation exhibits evident benefits in cardiovascular protection, warranting further research for its potential role in mitigating cardiac disease morbidity and mortality.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12349904/.
Itokawa Y. [Magnesium intake and cardiovascular disease]. Clin Calcium. 2005 Feb;15(2):154-9. Japanese. PMID: 15692152.
Fang X, Wang K, Han D, He X, Wei J, Zhao L, Imam MU, Ping Z, Li Y, Xu Y, Min J, Wang F. Dietary magnesium intake and the risk of cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and all-cause mortality: a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. BMC Med. 2016 Dec 8;14(1):210. doi: 10.1186/s12916-016-0742-z. PMID: 27927203; PMCID: PMC5143460.
Dietary magnesium intake and the risk of cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and all-cause mortality: a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies
Numerous studies have explored the link between dietary magnesium intake and health outcomes, yielding inconclusive results. A dose-response meta-analysis of forty prospective cohort studies with over 1 million participants aimed to elucidate this association. While no significant correlation was found between increased dietary magnesium intake and total cardiovascular disease (CVD) or coronary heart disease (CHD) risk, a 22% reduction in heart failure risk and a 7% decrease in stroke risk were noted per 100 mg/day increment of magnesium intake. Additionally, magnesium intake was associated with a 19% lower risk of type 2 diabetes (T2D) and a 10% reduction in all-cause mortality. These findings suggest that boosting dietary magnesium may confer health benefits, particularly in reducing the risk of stroke, heart failure, diabetes, and overall mortality.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5143460/.
Gums JG. Magnesium in cardiovascular and other disorders. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2004 Aug 1;61(15):1569-76. doi: 10.1093/ajhp/61.15.1569. PMID: 15372830.
Magnesium in cardiovascular and other disorders
Magnesium, often overlooked but crucial for physiological function, participates in over 300 enzymatic reactions, impacting energy metabolism, protein synthesis, and hormonal processes. Its deficiency, increasingly common due to dietary changes and medication use, is linked to conditions like hypertension, heart failure, and diabetes. Clinical studies suggest magnesium supplementation benefits these conditions. Clinicians should consider supplementation in at-risk patients and address underlying causes of deficiency to mitigate potential pathological processes.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://academic.oup.com/ajhp/article-abstract/61/15/1569/5143665?redirectedFrom=fulltext&login=false.
Chiuve SE, Sun Q, Curhan GC, Taylor EN, Spiegelman D, Willett WC, Manson JE, Rexrode KM, Albert CM. Dietary and plasma magnesium and risk of coronary heart disease among women. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013 Mar 18;2(2):e000114. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.113.000114. PMID: 23537810; PMCID: PMC3647257.
Dietary and plasma magnesium and risk of coronary heart disease among women
Magnesium is linked to a reduced risk of sudden cardiac death, potentially through antiarrhythmic pathways, but its direct relation to coronary heart disease (CHD) risk remains unclear. In a prospective study among women from the Nurses’ Health Study, higher magnesium intake was not significantly associated with total or nonfatal CHD risk, but it showed an inverse association with fatal CHD. Plasma magnesium levels above 2.0 mg/dL were also linked to a lower CHD risk, although not independently of other cardiovascular biomarkers. These findings suggest a potential role for magnesium in reducing fatal CHD risk, possibly mediated by hypertension.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3647257/.
de Valk HW. Magnesium in diabetes mellitus. Neth J Med. 1999 Apr;54(4):139-46. doi: 10.1016/s0300-2977(99)00005-4. PMID: 10218382.
Magnesium in diabetes mellitus
Magnesium deficiency is common in patients with diabetes mellitus due to factors such as glucosuria-related hypermagnesiuria, nutritional factors, and hyperinsulinemia-related hypermagnesiuria. Although plasma magnesium levels are inversely related to insulin sensitivity, oral magnesium supplementation has not shown consistent benefits in improving glycemic control in patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. However, magnesium supplementation has been found to improve insulin sensitivity and secretion in type 2 diabetes patients. While there are indications that magnesium may reduce blood pressure and the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, further research is needed to clarify its efficacy in retinopathy prevention and blood pressure reduction.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10218382/.
Veronese N, Dominguez LJ, Pizzol D, Demurtas J, Smith L, Barbagallo M. Oral Magnesium Supplementation for Treating Glucose Metabolism Parameters in People with or at Risk of Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients. 2021 Nov 15;13(11):4074. doi: 10.3390/nu13114074. PMID: 34836329; PMCID: PMC8619199.
Oral Magnesium Supplementation for Treating Glucose Metabolism Parameters in People with or at Risk of Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trials
Numerous studies have investigated the impact of oral magnesium (Mg) supplementation on glucose metabolism in individuals with or at risk of diabetes. Data synthesis from these studies revealed that Mg supplementation effectively reduced fasting plasma glucose levels in diabetic individuals and improved plasma glucose levels and insulin sensitivity markers in those at high risk of diabetes, compared to placebo. These findings suggest a beneficial role of Mg supplementation in managing glucose parameters in diabetic individuals and improving insulin sensitivity in those at risk of diabetes.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8619199/.
Barbagallo M, Dominguez LJ. Magnesium and type 2 diabetes. World J Diabetes. 2015 Aug 25;6(10):1152-7. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i10.1152. PMID: 26322160; PMCID: PMC4549665.
Magnesium and type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes often coincides with deficiencies in both extracellular and intracellular magnesium (Mg), with many diabetic patients experiencing chronic latent Mg deficits or clinical hypomagnesemia, especially in cases of poorly controlled glycemic profiles. Insulin and glucose play pivotal roles in Mg metabolism, with intracellular Mg crucial for regulating insulin action, glucose uptake, and vascular tone. Reduced intracellular Mg levels can lead to impaired insulin action and worsened insulin resistance. Mechanisms such as low Mg intake and increased urinary Mg loss contribute to Mg depletion in type 2 diabetes. While most clinical studies suggest benefits of Mg supplementation on metabolic profiles in diabetics, further large-scale prospective studies are warranted to solidify the potential role of dietary Mg supplementation in mitigating diabetes risk.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4549665/#:~:text=Type%202%20diabetes%20is%20frequently,with%20poorly%20controlled%20glycemic%20profiles.
Rodríguez-Morán M, Simental Mendía LE, Zambrano Galván G, Guerrero-Romero F. The role of magnesium in type 2 diabetes: a brief based-clinical review. Magnes Res. 2011 Dec;24(4):156-62. doi: 10.1684/mrh.2011.0299. PMID: 22198525.
The role of magnesium in type 2 diabetes: a brief based-clinical review
In recent years, an increasing body of experimental evidence has highlighted magnesium’s crucial role in glucose metabolism, suggesting its potential in reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes. While large epidemiological studies have linked low dietary magnesium intake to an elevated risk of type 2 diabetes, findings from randomized controlled clinical trials evaluating the benefits of magnesium supplementation on glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity remain inconsistent. This article reviewed evidence from epidemiological studies and clinical trials obtained from electronic databases like Medline, Embase, and the Cochrane Controlled Trials Register up to June 2011, revealing a consistent inverse relationship between dietary magnesium intake and the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in epidemiological studies, although clinical trial results are limited and contentious.
You can read the full article at https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22198525/.
Zhao B, Deng H, Li B, Chen L, Zou F, Hu L, Wei Y, Zhang W. Association of magnesium consumption with type 2 diabetes and glucose metabolism: A systematic review and pooled study with trial sequential analysis. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020 Mar;36(3):e3243. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3243. Epub 2019 Dec 11. PMID: 31758631.
Association of magnesium consumption with type 2 diabetes and glucose metabolism: A systematic review and pooled study with trial sequential analysisAssociation of magnesium consumption with type 2 diabetes and glucose metabolism: A systematic review and pooled study with trial sequential analysis
Preventing type 2 diabetes (T2D) through diet or supplementation poses challenges. This article aims to establish definitive links between magnesium intake and T2D incidence while assessing the impact of magnesium supplementation on glucose metabolism. A review of databases until May 15, 2019, yielded 26 relevant publications involving 35 cohorts. High magnesium intake was associated with a 22% lower risk of T2D, with each 100 mg increase in daily intake reducing risk by 6%. Analysis of 26 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) further indicated that magnesium supplementation significantly reduced fasting plasma glucose, 2-hour oral glucose tolerance test results, fasting insulin levels, insulin resistance, triglyceride levels, and blood pressure. Trial sequential analysis confirmed the stability of these benefits, suggesting that magnesium supplementation could be beneficial for individuals at risk of or diagnosed with T2D.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/dmrr.3243.
Verma H, Garg R. Effect of magnesium supplementation on type 2 diabetes associated cardiovascular risk factors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2017 Oct;30(5):621-633. doi: 10.1111/jhn.12454. Epub 2017 Feb 2. PMID: 28150351.
Effect of magnesium supplementation on type 2 diabetes associated cardiovascular risk factors: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of mortality in individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D). This study conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to assess the impact of magnesium supplementation on cardiovascular risk factors associated with T2D. Data from various databases were analyzed, revealing significant improvements in fasting plasma glucose, high-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein, plasma triglycerides, and systolic blood pressure following magnesium supplementation. Subgroup analysis indicated a more pronounced effect in diabetic subjects with hypomagnesemia. These findings suggest that magnesium supplementation may mitigate the risk of cardiovascular diseases associated with T2D, underscoring the need for further large-scale RCTs to establish clinical guidelines.
You can read the full article at https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jhn.12454.
Salhi H, El Ouahabi H. Magnesium status in patients with Type 2 diabetes (about 170 cases). Ann Afr Med. 2021 Jan-Mar;20(1):64-68. doi: 10.4103/aam.aam_49_19. PMID: 33727515; PMCID: PMC8102897.
Magnesium status in patients with Type 2 diabetes (about 170 cases)
Magnesium (Mg) is crucial for various physiological functions in the body and is associated with metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, and Type-2 diabetes due to lower intake and serum concentrations. This case-control study conducted at our endocrinology department aimed to assess the relationship between serum Mg levels and common complications of diabetes mellitus and other biochemical indices. The study included 170 patients classified into low Mg (Group 1, n = 85) and normal Mg (Group 2, n = 85) groups. Results revealed significant correlations between serum Mg levels and age, sex, diabetes duration, body mass index, hypertension, and glycosylated hemoglobin. Additionally, a negative correlation was observed between Mg levels and nephropathy, indicating a potential link with glycemic control and high blood pressure. However, further research is necessary to validate these findings.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8102897/.
Batar PK. Study of Serum Magnesium Level in Diabetes Mellitus and it’s Correlation with Micro and Macro Complications. J Assoc Physicians India. 2022 Apr;70(4):11-12. PMID: 35443371.
Study of Serum Magnesium Level in Diabetes Mellitus and it’s Correlation with Micro and Macro Complications
The multi-system effects of diabetes mellitus, including retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy, and cardiovascular diseases, are significant public health concerns. Although numerous studies have explored the association between magnesium (Mg) and diabetes and its complications, findings have been inconsistent. This cross-sectional study, conducted at the Department of Medicine, S.P. Medical College & Associated Group of Hospitals, Bikaner, aimed to estimate the serum magnesium levels in the development and progression of Type 2 diabetes and its complications. The study found a significant association between hypomagnesemia and diabetic complications, particularly microvascular complications such as nephropathy, neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular disease. Thus, measuring serum magnesium levels in patients with uncontrolled blood sugar could be beneficial, as supplementation may help mitigate microvascular complications.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35443371/.
Veronese N, Watutantrige-Fernando S, Luchini C, Solmi M, Sartore G, Sergi G, Manzato E, Barbagallo M, Maggi S, Stubbs B. Effect of magnesium supplementation on glucose metabolism in people with or at risk of diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of double-blind randomized controlled trials. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2016 Dec;70(12):1354-1359. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2016.154. Epub 2016 Aug 17. Erratum in: Eur J Clin Nutr. 2016 Dec;70(12 ):1463. PMID: 27530471.
Effect of magnesium supplementation on glucose metabolism in people with or at risk of diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of double-blind randomized controlled trials
Although higher dietary intakes of magnesium (Mg) have been associated with lower diabetes incidence, research on Mg supplementation in individuals with or at risk of diabetes is limited. Therefore, we conducted a comprehensive literature review to investigate the effect of oral Mg supplementation on glucose and insulin-sensitivity parameters compared to placebo in participants with diabetes or at high risk of diabetes. Our analysis of eighteen randomized controlled trials revealed that Mg supplementation significantly reduced fasting plasma glucose in individuals with diabetes and improved plasma glucose levels after a 2-hour oral glucose tolerance test in those at high risk of diabetes. Additionally, Mg supplementation showed promising trends in reducing insulin resistance. These findings suggest that Mg supplementation may have a beneficial impact on glucose metabolism in individuals with diabetes and those at high risk of diabetes.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://www.nature.com/articles/ejcn2016154.
de Valk HW, Verkaaik R, van Rijn HJ, Geerdink RA, Struyvenberg A. Oral magnesium supplementation in insulin-requiring Type 2 diabetic patients. Diabet Med. 1998 Jun;15(6):503-7. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9136(199806)15:6<503::AID-DIA596>3.0.CO;2-M. PMID: 9632126.
Oral magnesium supplementation in insulin-requiring Type 2 diabetic patients
Oral magnesium (Mg) supplementation has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity and secretion in individuals with Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM). In this study, fifty moderately controlled patients with Type 2 DM receiving insulin were randomly assigned to receive either 15 mmol Mg or placebo daily for three months. Although plasma Mg concentration and urinary Mg excretion increased significantly with Mg supplementation compared to placebo, there were no significant differences observed in glycaemic control, plasma lipid levels, or blood pressure between the two groups. However, there was a trend towards a decrease in diastolic pressure associated with increased plasma Mg concentration.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9632126/.
de Lordes Lima M, Cruz T, Pousada JC, Rodrigues LE, Barbosa K, Canguçu V. The effect of magnesium supplementation in increasing doses on the control of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1998 May;21(5):682-6. doi: 10.2337/diacare.21.5.682. PMID: 9589224.
The effect of magnesium supplementation in increasing doses on the control of type 2 diabetes
The objective of this clinical randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial was to assess whether magnesium supplementation, specifically magnesium oxide (MgO), could enhance metabolic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Conducted at Bahia Federal University Hospital in Brazil, the study involved 128 patients with type 2 diabetes who received either placebo, 20.7 mmol MgO, or 41.4 mmol MgO daily for 30 days. While no significant improvements were observed in glycemic control with lower doses of Mg, supplementation with 41.4 mmol Mg tended to increase plasma, cellular, and urine Mg levels and led to a notable decrease in fructosamine levels, indicating a potential benefit in improving metabolic control in these patients.
You can read the full article at https://diabetesjournals.org/care/article/21/5/682/22876/The-Effect-of-Magnesium-Supplementation-in.
Nielsen FH. Magnesium deficiency and increased inflammation: current perspectives. J Inflamm Res. 2018 Jan 18;11:25-34. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S136742. PMID: 29403302; PMCID: PMC5783146.
Magnesium deficiency and increased inflammation: current perspectives
Animal studies have revealed that magnesium deficiency triggers an inflammatory response characterized by leukocyte and macrophage activation, cytokine release, and free radical production. This response is primarily mediated by elevated cellular calcium levels, which prime cells for inflammation. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and acute-phase reactants have been linked to magnesium deficiency-induced chronic low-grade inflammation. Adequate magnesium levels generally do not affect inflammatory markers, but deficiency is associated with conditions like cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Given the prevalence of magnesium deficiency in regions with insufficient dietary intake, addressing this deficiency is crucial for overall health and well-being.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5783146/.
Maier JA, Castiglioni S, Locatelli L, Zocchi M, Mazur A. Magnesium and inflammation: Advances and perspectives. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jul;115:37-44. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.11.002. Epub 2020 Nov 18. PMID: 33221129.
Magnesium and inflammation: Advances and perspectives
Magnesium, crucial for metabolism and tissue balance, also governs immune functions, impacting both innate and adaptive systems. Insufficient magnesium primes immune cells, heightens oxidative burst, and triggers cytokine release, fostering inflammation. Undiagnosed low magnesium levels exacerbate immune reactivity, contributing to the pathogenesis of numerous chronic ailments. Recent advancements underscore the association between magnesium deficiency, inflammation, and disease, shedding light on underlying mechanisms for enhanced comprehension.
You can read the full article at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1084952120301713?via%3Dihub.
Veronese N, Pizzol D, Smith L, Dominguez LJ, Barbagallo M. Effect of Magnesium Supplementation on Inflammatory Parameters: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients. 2022 Feb 5;14(3):679. doi: 10.3390/nu14030679. PMID: 35277037; PMCID: PMC8838086.
Effect of Magnesium Supplementation on Inflammatory Parameters: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Studies suggest that magnesium (Mg) supplementation could offer various health benefits, potentially through its impact on serum inflammatory parameters. To assess this, a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) investigating Mg supplementation’s effects on serum inflammation markers was conducted. Among 2484 papers screened, 17 RCTs (889 participants) were included, showing a low risk of bias. Meta-analysis revealed that Mg supplementation significantly decreased serum C reactive protein (CRP) levels and increased nitric oxide (NO) levels. Additionally, Mg supplementation demonstrated reductions in other inflammatory markers like plasma fibrinogen, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase type 5, tumor necrosis factor-ligand superfamily member 13B, ST2 protein, and IL-1, indicating its potential in mitigating inflammation.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8838086/.
Shahi A, Aslani S, Ataollahi M, Mahmoudi M. The role of magnesium in different inflammatory diseases. Inflammopharmacology. 2019 Aug;27(4):649-661. doi: 10.1007/s10787-019-00603-7. Epub 2019 Jun 6. PMID: 31172335.
The role of magnesium in different inflammatory diseases
Magnesium deficiency (MgD) is implicated in inflammation within the human body through various mechanisms, including phagocytic cell activation, calcium channel opening, N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor activation, and nuclear factor (NF)-κB activation. Additionally, MgD induces systemic stress responses via neuroendocrinological pathways. This inflammation contributes to pro-atherogenic changes in lipoprotein metabolism, endothelial dysfunction, and elevated blood pressure. Studies suggest magnesium’s crucial role in the pathophysiology of inflammatory diseases, with clinical trials and laboratory studies supporting its functional significance. Highlighted inflammatory diseases where magnesium plays a role include diabetes, asthma, preeclampsia, atherosclerosis, heart damage, and rheumatoid arthritis.
You can read the full article at https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31172335/#:~:text=Magnesium%20deficiency%20(MgD)%20can%20cause,nuclear%20factor%20(NF)%2D%CE%BAB..
Nielsen FH. Effects of magnesium depletion on inflammation in chronic disease. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2014 Nov;17(6):525-30. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000093. PMID: 25023192.
Effects of magnesium depletion on inflammation in chronic disease
This review aims to provide updated evidence supporting the notion that subclinical magnesium deficiency, often induced by low dietary intake, is a contributing factor to chronic inflammatory stress and the development of chronic diseases like cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Recent findings indicate that both inadequate magnesium intake (<250 mg/day) and low serum magnesium concentrations (≤ 0.75 mmol/l) are associated with elevated serum C-reactive protein levels, a marker of inflammation. Attaining adequate magnesium levels through diet or supplementation tends to mitigate this inflammatory response. Individuals with obesity or chronic diseases are frequently found to be deficient in magnesium. Overall, subclinical magnesium deficiency is a significant concern for health and well-being, highlighting the importance of addressing magnesium intake levels.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://journals.lww.com/co-clinicalnutrition/abstract/2014/11000/effects_of_magnesium_depletion_on_inflammation_in.7.aspx.
Mazur A, Maier JA, Rock E, Gueux E, Nowacki W, Rayssiguier Y. Magnesium and the inflammatory response: potential physiopathological implications. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2007 Feb 1;458(1):48-56. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2006.03.031. Epub 2006 Apr 19. PMID: 16712775.
Magnesium and the inflammatory response: potential physiopathological implications
This review aims to synthesize experimental evidence demonstrating magnesium’s modulation of cellular processes involved in inflammation. Experimental magnesium deficiency in rats induces a clinical inflammatory syndrome characterized by leukocyte and macrophage activation, cytokine release, and free radical production. Alterations in extracellular magnesium levels affect inflammatory responses, likely through its role as a natural calcium antagonist, modulating intracellular calcium concentrations. Mechanisms implicated include priming of phagocytic cells, calcium channel opening, NMDA receptor activation, and NFkappaB activation. Additionally, magnesium deficiency triggers systemic stress responses via neuroendocrinological pathways. The interplay between the nervous and immune systems, exacerbated by magnesium deficiency, leads to heightened immune and oxidative stress responses, contributing to various pathological conditions such as atherosclerosis, endothelial dysfunction, and hypertension. While further human studies are needed, these findings in animal models suggest inflammation as a crucial link in understanding magnesium’s role in pathological conditions.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0003986106001366?via%3Dihub.
Ashique S, Kumar S, Hussain A, Mishra N, Garg A, Gowda BHJ, Farid A, Gupta G, Dua K, Taghizadeh-Hesary F. A narrative review on the role of magnesium in immune regulation, inflammation, infectious diseases, and cancer. J Health Popul Nutr. 2023 Jul 27;42(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s41043-023-00423-0. Erratum in: J Health Popul Nutr. 2023 Nov 2;42(1):117. PMID: 37501216; PMCID: PMC10375690.
Ashique S, Kumar S, Hussain A, Mishra N, Garg A, Gowda BHJ, Farid A, Gupta G, Dua K, Taghizadeh-Hesary F. A narrative review on the role of magnesium in immune regulation, inflammation, infectious diseases, and cancer. J Health Popul Nutr. 2023 Jul 27;42(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s41043-023-00423-0. Erratum in: J Health Popul Nutr. 2023 Nov 2;42(1):117. PMID: 37501216; PMCID: PMC10375690.
Nielsen FH. Magnesium, inflammation, and obesity in chronic disease. Nutr Rev. 2010 Jun;68(6):333-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2010.00293.x. PMID: 20536778.
Magnesium, inflammation, and obesity in chronic disease
Approximately 60% of adults in the United States fall short of the estimated average requirement for magnesium intake, yet widespread pathological conditions directly linked to magnesium deficiency are uncommon. However, low magnesium levels have been linked to various pathological conditions with chronic inflammatory stress components. Human studies show that magnesium deficiencies are typically marginal to moderate, while animal experiments suggest that these deficiencies can be influenced by other factors affecting inflammatory and oxidative stress, a pattern also observed in recent human studies. This interplay may hold significance in conditions like obesity, characterized by chronic low-grade inflammation and higher prevalence of low magnesium levels. Marginal-to-moderate magnesium deficiency exacerbating chronic inflammatory stress likely contributes significantly to chronic diseases such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, osteoporosis, diabetes mellitus, and cancer.
You can read the full article at https://academic.oup.com/nutritionreviews/article/68/6/333/1828430?login=false.
Rayssiguier Y, Mazur A. [Magnesium and inflammation: lessons from animal models]. Clin Calcium. 2005 Feb;15(2):245-8. Japanese. PMID: 15692164.
[Magnesium and inflammation: lessons from animal models]
Approximately 60% of adults in the United States fall short of the estimated average requirement for magnesium intake, yet widespread pathological conditions directly linked to magnesium deficiency are uncommon. However, low magnesium levels have been linked to various pathological conditions with chronic inflammatory stress components. Human studies show that magnesium deficiencies are typically marginal to moderate, while animal experiments suggest that these deficiencies can be influenced by other factors affecting inflammatory and oxidative stress, a pattern also observed in recent human studies. This interplay may hold significance in conditions like obesity, characterized by chronic low-grade inflammation and higher prevalence of low magnesium levels. Marginal-to-moderate magnesium deficiency exacerbating chronic inflammatory stress likely contributes significantly to chronic diseases such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, osteoporosis, diabetes mellitus, and cancer.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15692164/.
Talebi S, Miraghajani M, Hosseini R, Mohammadi H. The Effect of Oral Magnesium Supplementation on Inflammatory Biomarkers in Adults: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Dose-response Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022 Apr;200(4):1538-1550. doi: 10.1007/s12011-021-02783-2. Epub 2021 Jun 18. PMID: 34143369.
The Effect of Oral Magnesium Supplementation on Inflammatory Biomarkers in Adults: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Dose-response Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials
This comprehensive systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis examined the impact of oral magnesium supplementation on inflammatory biomarkers in adults, including CRP, IL-6, and TNF-α. Utilizing major databases and assessing study quality, 18 eligible studies involving 927 participants were analyzed. Results showed no significant effect of magnesium supplementation on serum CRP, IL-6, or TNF-α levels compared to controls. Subgroup analysis and dose-response assessment also revealed no significant non-linear associations between magnesium dosage or duration and inflammatory marker concentrations. Overall, the findings suggest that oral magnesium supplementation may not confer favorable effects on CRP, IL-6, and TNF-α in adults.
You can read the full article at https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12011-021-02783-2.
Simental-Mendia LE, Sahebkar A, Rodriguez-Moran M, Zambrano-Galvan G, Guerrero-Romero F. Effect of Magnesium Supplementation on Plasma C-reactive Protein Concentrations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(31):4678-4686. doi: 10.2174/1381612823666170525153605. PMID: 28545353.
Effect of Magnesium Supplementation on Plasma C-reactive Protein Concentrations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Previous clinical trials investigating magnesium supplementation’s impact on inflammatory markers have produced conflicting outcomes. This systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials aimed to assess the effect of oral magnesium supplementation on plasma C-reactive protein (CRP) concentrations. Using various databases, 11 studies were analyzed, revealing that overall, magnesium treatment did not significantly alter plasma CRP levels. However, subgroup analysis based on baseline CRP values showed a notable reduction in CRP levels among individuals with baseline CRP values exceeding 3 mg/L, suggesting a potential adjunctive role for magnesium supplements in managing low-grade chronic systemic inflammation.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28545353/.
Pitzer Mutchler A, Huynh L, Patel R, Lam T, Bain D, Jamison S, Kirabo A, Ray EC. The role of dietary magnesium deficiency in inflammatory hypertension. Front Physiol. 2023 May 24;14:1167904. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1167904. PMID: 37293263; PMCID: PMC10244581.
The role of dietary magnesium deficiency in inflammatory hypertension
Approximately 30% of adults have inadequate magnesium (Mg2+) intake, often exacerbated by medications like diuretics, potentially contributing to hypertension. We investigated the impact of Mg2+ deficiency on blood pressure regulation and inflammatory pathways in antigen-presenting cells. Mice on a Mg2+-depleted diet exhibited elevated blood pressure, increased plasma IL-1β levels, and upregulated NLRP3, IL-1β, and IsoLG expression in antigen-presenting cells from various organs. These findings suggest that Mg2+ depletion activates the NLRP3 inflammasome and promotes IsoLG formation, contributing to hypertension. Increasing Mg2+ intake may offer therapeutic benefits in reducing hypertension and cardiovascular risk.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10244581/.
López-Baltanás R, Encarnación Rodríguez-Ortiz M, Canalejo A, Díaz-Tocados JM, Herencia C, Leiva-Cepas F, Torres-Peña JD, Ortíz-Morales A, Muñoz-Castañeda JR, Rodríguez M, Almadén Y. Magnesium supplementation reduces inflammation in rats with induced chronic kidney disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 2021 Aug;51(8):e13561. doi: 10.1111/eci.13561. Epub 2021 Apr 18. PMID: 33870500.
Magnesium supplementation reduces inflammation in rats with induced chronic kidney disease
Inflammation is prevalent in chronic kidney disease (CKD), particularly linked to cardiovascular complications. Observational data suggest an association between low magnesium (Mg) levels and inflammation. Using a CKD rat model, we explored Mg’s potential modulatory role in uraemia-induced inflammation. Uraemic rats on a normal Mg diet exhibited systemic inflammation and oxidative stress, alongside elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines in aortic tissue, all mitigated by Mg supplementation. In vitro studies with vascular smooth muscle cells corroborated these findings, showing Mg’s ability to suppress inflammation and oxidative stress. These results underscore the potential of Mg supplementation in managing inflammation in CKD, suggesting its therapeutic value in clinical settings.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/eci.13561.
Xie C, Li X, Wu J, Liang Z, Deng F, Xie W, Zhu M, Zhu J, Zhu W, Geng S, Zhong C. Anti-inflammatory Activity of Magnesium Isoglycyrrhizinate Through Inhibition of Phospholipase A2/Arachidonic Acid Pathway. Inflammation. 2015 Aug;38(4):1639-48. doi: 10.1007/s10753-015-0140-2. PMID: 25691139.
Anti-inflammatory Activity of Magnesium Isoglycyrrhizinate Through Inhibition of Phospholipase A2/Arachidonic Acid Pathway
Glycyrrhiza glabra (licorice) exhibits diverse pharmacological properties, including anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective effects. Magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate (MgIG), a derivative of licorice, is used to treat inflammatory liver diseases, yet its anti-inflammatory mechanism remains unclear. Our study investigated MgIG’s inhibitory effects on the phospholipase A2 (PLA2)/arachidonic acid (AA) pathway and the release of inflammatory lipid mediators in RAW264.7 macrophages. Results demonstrated MgIG’s suppression of LPS-induced PLA2 activation and production of AA metabolites, including prostaglandins, thromboxane, and leukotrienes. Additionally, MgIG inhibited LPS-induced AA-metabolizing enzymes such as COX-2, COX-1, and 5-LOX. These findings suggest that MgIG’s anti-inflammatory effects may involve modulation of COXs and 5-LOX pathways in AA metabolism.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10753-015-0140-2.
Success Stories
 before after
before after
At the age of 60, I look and feel better than I ever have in my entire life! Switching my health program and hormone replacement therapy regimen over to Genemedics was one of the best decisions I’ve ever made in my life! Genemedics and Dr George have significantly improved my quality of life and also dramatically improved my overall health. I hav...
Nick Cassavetes ,60 yrs old
Movie Director (“The Notebook”, “John Q”, “Alpha Dog”), Actor and Writer
 Before After
Before After
I am now in my mid-sixties and feel better than I did in my 20’s. Many people have commented that I actually look 20 years younger since I started the program at Genemedics.
Calling Dr. George has proven to be one of the best decisions I have made in my life. Doctors and society convince us that developing various health issues and negative sy...
Pamela Hill ,66 yrs old
Call 800-277-4041 for a Free Consultation
- Usually takes 15-30 minutes
- Completely confidential
- No obligation to purchase anything
- We will discuss your symptoms along with your health and fitness goals
- Free post-consult access for any additional questions you may have
About
Genemedics® Health Institute is a global premier institute dedicated to revolutionizing health and medicine through healthy lifestyle education, guidance and accountability in harmony with functional medicine. Our physician-supervised health programs are personally customized to help you reach your health and fitness goals while looking and feeling better than ever.
Quick Links
Our Services
Our Locations
© Copyright Genemedics Health Institute. All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy.

