GENEMEDICS APP
GENEMEDICS NUTRITION
Ginsenoside Rg3
Author: Dr. George Shanlikian, M.D. | Last Updated: February 1st, 2024
- Home
- >
- Health Library
- >
- Ginsenoside Rg3
- 5-amino-1MQ
- Aminophylline
- Aniracetam
- ARA 290
- Argireline + Leuphasyl
- BPC-157
- Bremelanotide
- Cerebrolysin
- CJC-1295
- Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide
- Dihexa
- Elampretide (SS-31)
- Epithalon
- FG Loop Peptide (FGL)
- GHK-Cu
- Ginsenoside Rg3
- Glycyrrhetinic Acid
- Ipamorelin
- Kisspeptin
- KPV
- LL-37
- Melanotan 1
- Melanotan 2
- Mitochondrial ORF of the twelve S c (MOTS-c)
- MK-677 (IBUTAMOREN)
- Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+)
- Nicotinamide Riboside
- NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide)
- Noopept
- Pegylated Mechano Growth Factor
- Selank
- Semax
- Sermorelin
- SRT2104
- Tesamorelin
- Thymosin Alpha 1
- Thymosin Beta 4
- Tiger 17
- Valproic Acid
- Valproic acid + PTD-DBM
- Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide
- Zinc-Thymulin
- Potential Benefits of Ginsenoside Rg3
- Key Takeaways of Ginsenoside Rg3
- What is Ginsenoside Rg3?
- How Ginsenoside Rg3 Works
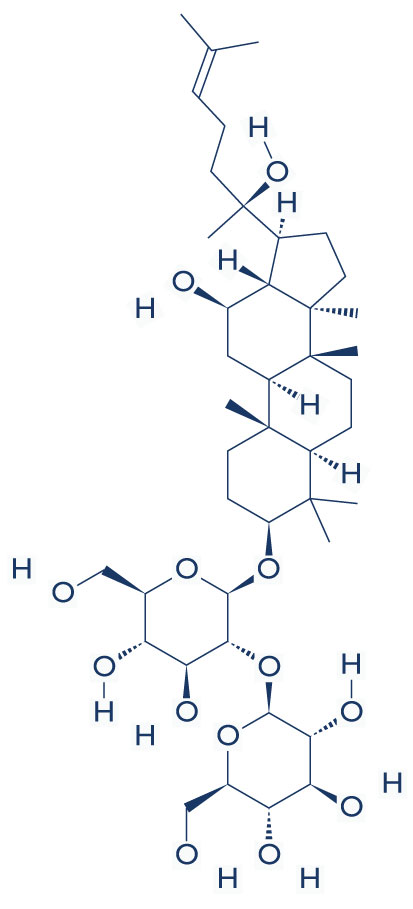
- Chemical Structure of Ginsenoside Rg3
- Research on Ginsenoside Rg3
- Associated Side Effects of Ginsenoside Rg3
- Ginsenoside Rg3 Dosage
- Ginsenoside Rg3 Supplement Availability
- Ginsenoside Rg3 Interactions with Drugs and Nutrients
- FAQs
- Blog
- Reference
Book a Free Consultation
Table of Contents
- Potential Benefits of Ginsenoside Rg3
- Key Takeaways of Ginsenoside Rg3
- What is Ginsenoside Rg3?
- How Ginsenoside Rg3 Works
- Chemical Structure of Ginsenoside Rg3
- Research on Ginsenoside Rg3
- Associated Side Effects of Ginsenoside Rg3
- Ginsenoside Rg3 Dosage
- Ginsenoside Rg3 Supplement Availability
- Ginsenoside Rg3 Interactions with Drugs and Nutrients
- FAQs
- Blog
- Reference
Potential Benefits of Ginsenoside Rg3
Ginsenoside Rg3 is a potent compound known for its diverse health benefits, including improving memory, reducing heart disease risk, regulating blood pressure, enhancing immune function, aiding in weight loss, accelerating wound healing, preventing cancer, elevating mood, and stabilizing blood sugar levels. Its multifaceted effects have been supported by numerous studies, making it a valuable component in holistic health approaches. With such a range of advantages, the ginsenoside Rg3 benefits are increasingly recognized and sought after in the world of natural remedies.
- Improves memory and prevents brain disorders [1-18]
- Lowers the risk of heart disease [19-31]
- Lowers blood pressure [26, 32-33]
- Boosts immune function [34-39]
- Helps lose weight [40-42]
- Accelerates wound healing [43-49]
- Prevents cancer [50-79]
- Improves mood [18, 80-81]
- Improves blood sugar levels and treats diabetic symptoms [82-95]
Key Takeaways of Ginsenoside Rg3
- Ginsenoside Rg3, derived from Panax ginseng, possesses a myriad of health benefits, including improved memory, cardiovascular protection, immune function enhancement, and potential cancer prevention.
- Ginsenoside Rg3 works through a multifaceted approach, including anti-cancer mechanisms, neuroprotective effects, cardioprotective roles, and metabolic regulation, among others.
- Ginsenoside Rg3 stands out for its neuroprotective properties against oxidative stress and inflammation, as well as its cardioprotective role in reducing oxidative stress and arterial plaque formation.
- While ginsenoside Rg3 has been associated with some side effects, they are very uncommon, and there’s a possibility that they might not be directly related to the use of the compound.
- Ginsenoside Rg3 not only neutralizes free radicals due to its antioxidant properties but also modulates the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, supporting overall cellular health and reducing inflammation.
What is Ginsenoside Rg3?
Ginsenoside Rg3 is a natural product derived from Panax ginseng, particularly abundant in red ginseng. It is one of the active compounds found in certain species of the ginseng plant. As more people recognize its health benefits, there is a rising interest in the ginsenoside Rg3 supplement in the market. Ginsenoside Rg3 plays an essential role in nerve cell and cardiovascular protection. Additionally, it is known for its potent anti-cancer effects and brain-boosting properties.
The mechanisms by which ginsenoside Rg3 exerts its therapeutic effects are multifaceted, encompassing anti-cancer, neuroprotective, cardioprotective, immune-modulating, metabolic-regulating, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory actions, among others. Given its wide array of benefits, many individuals are considering the addition of a ginsenoside Rg3 supplement to their daily regimen. This compound has garnered attention in the medical and scientific communities due to its diverse range of potential health benefits.
How Ginsenoside Rg3 Works
Ginsenoside Rg3 is one of the active compounds found in certain species of the ginseng plant. The mechanisms by which ginsenoside Rg3 exerts its therapeutic effects are multifaceted and are still the subject of ongoing research. Here are some insights into how ginsenoside Rg3 works:
- Anti-cancer Mechanism: Ginsenoside Rg3 has been shown to inhibit tumor growth and metastasis, demonstrating the anticancer effects of ginsenoside. One of the mechanisms through which it acts is that ginsenoside Rg3 induces apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells. This apoptosis-inducing property is crucial for its anti-cancer effects. Furthermore, besides the fact that ginsenoside Rg3 induces apoptosis, it also inhibits tumor angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels that feed the tumor), emphasizing once again the anticancer effects of ginsenoside. Additionally, it suppresses the invasive and migratory capabilities of cancer cells.
- Neuroprotective Effects: Ginsenoside Rg3 can protect nerve cells against oxidative stress induced by various external and internal factors. Additionally, it guards against inflammation, potentially aiding in memory enhancement and the prevention of brain disorders.
- Cardioprotective Role: It may protect the heart and blood vessels by reducing oxidative stress, and inflammation, and preventing the formation of plaques in arteries.
- Immune Modulation: Ginsenoside Rg3 can enhance the activity of certain immune cells, thereby boosting the body’s defense mechanisms. Through its unique properties, ginsenoside Rg3 enhances the body’s natural ability to ward off potential threats. Additionally, studies suggest that ginsenoside Rg3 enhances the overall immune response, further fortifying the body against foreign invaders.
- Metabolic Regulation: Ginsenoside Rg3 has been shown to have a role in regulating blood sugar levels, making it potentially beneficial for diabetic patients. It might improve insulin sensitivity and reduce insulin resistance.
- Antioxidant Action: Like many ginsenosides, Rg3 possesses antioxidant properties, which means it can neutralize free radicals in the body, reducing oxidative stress and potential damage to cells.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Ginsenoside Rg3 can modulate the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and thereby reduce inflammation in the body.
- Wound Healing: It may promote wound healing by accelerating the proliferation and migration of skin cells, as well as promoting angiogenesis in wound sites.
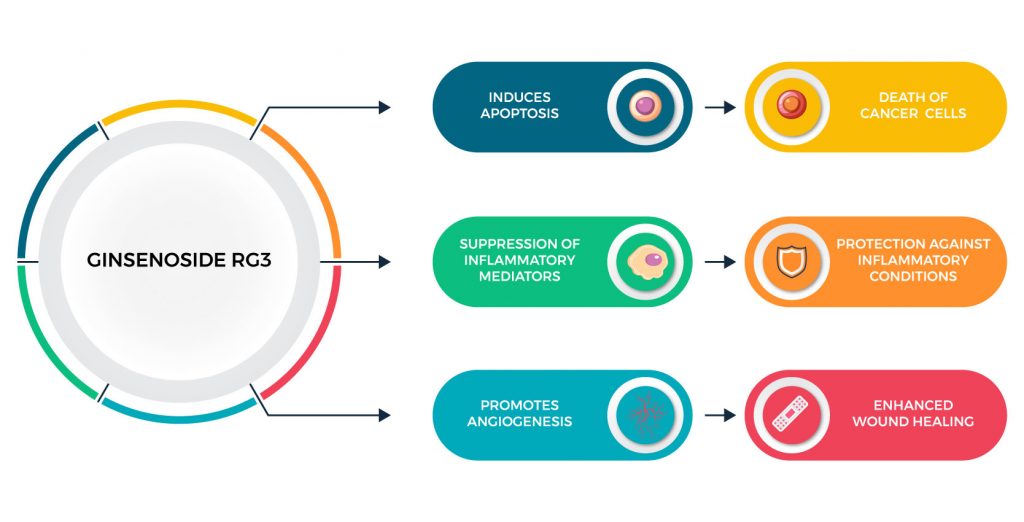
Chemical Structure of Ginsenoside Rg3
Research on Ginsenoside Rg3
A. Improves Memory and Prevents Brain Disorders
A convincing number of studies suggest that ginsenoside Rg3 can improve memory and prevent brain disorders through its neuroprotective effects:
- In mice, oral administration of ginsenoside Rg3 for 4 days significantly reversed memory impairment induced by ethanol. [1]
- In cultured rat brain cells, ginsenoside Rg3 protected against glutamate-induced neurodegeneration. [2]
- A cell study reported that pretreatment of brain cells with ginsenoside Rg3 resulted in an increased survival rate via its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. [3]
- In an animal model of brain inflammation, ginsenoside Rg3 supplementation at 20 and 30 mg/kg oral doses significantly reduced inflammation by reducing the levels of inflammatory substances such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) and IL-6 mRNA. [4]
- In rats with cognitive impairment, ginsenoside Rg3 treatment restored learning and memory functions. [5]
- A cell study also reported that ginsenoside Rg3 prevented brain inflammation by reducing inflammatory stimuli in the majority of brain tissues. [6]
- A study conducted on animal models of Alzheimer’s disease found that ginsenoside Rg3 can help prevent or slow the development of neurological disorders due to its anti-inflammatory activity in the brain. [7]
- A cell study found that ginsenoside Rg3 can help prevent Alzheimer’s disease by reducing the levels of abnormal protein structures in the brain. [8]
- In a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease, ginsenoside Rg3 prevented cognitive impairment by improving mitochondrial dysfunction. [9-11]
- In mice and rats, ginsenoside Rg3 ameliorated scopolamine-induced learning deficits through the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase activity and NF-κB signaling in the brain. [12-13]
- Studies reported that ginsenoside Rg3 exerts its neuroprotective effects by suppressing oxidative stress, enhancing neurotransmission, and reducing inflammation. [14-16]
- In mice, ginsenoside Rg3 (25-200 mg/kg) reversed scopolamine-induced memory impairment and learning deficits. [17]
- In rats exposed to chronic unpredictable stress, ginsenoside Rg3 (20 and 40 mg/kg) produced anti-anxiety effects. [18]
B. Lowers the Risk of Heart Disease

Studies suggest that ginsenoside Rg3 offers cardioprotective effects:
- In rats, ginsenoside Rg3 administration protected against heart impairment. [19]
- In mice with heart injury, ginsenoside Rg3 treatment prevented the development of heart attack. [20]
- In rats, ginsenoside Rg3 delayed the progression of cardiovascular disease (CVD). [21]
- In mice with isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction (heart attack), ginsenoside Rg3 protected against further heart injury. [22]
- In rats with insufficient blood flow to the heart, ginsenoside Rg3 improved cardiac function by attenuating programmed cell death (apoptosis) and inflammation. [23-25]
- In hypertensive rats, ginsenoside Rg3 exerted cardioprotective effects. [26]
- In rats, ginsenoside Rg3 improved cardiac adaptations to exercise by regulating mitochondria dynamic remodeling and enhancing the quantity and quality of mitochondria. [27]
- A test tube study found that ginsenoside Rg3 significantly inhibited collagen-induced platelet aggregation, suggesting that it can help prevent blood clot formation in the heart. [28]
- In rabbits, ginsenoside Rg3 alleviated antithyroid cancer drug vandetanib-induced QT interval prolongation (abnormal heart rhythm. [29]
- A study found that ginsenoside Rg3 mitigated doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and enhanced its anticancer efficacy. [30]
- In mice with narrowing of the heart arteries, ginsenoside Rg3 improved cardiac function by restoring normal heart signals. [31]
C. Lowers Blood Pressure

Evidence shows that Rg3 has antihypertensive properties:
- In hypertensive rats, ginsenoside Rg3 lowered blood pressure by attenuating renin-angiotensin system (RAS) activity. [26]
- In rats, daily oral administration of ginsenoside Rg3 lowered systolic and diastolic blood pressure. [32]
- A review of several studies showed that ginsenoside Rg3 is beneficial in treating hypertensive patients. [33]
D. Boosts Immune Function

Studies report that Rg3 also has immune-boosting properties:
- In an animal study, treatment with ginsenoside Rg3 has been shown to protect the animals from the lethality of the H1N1 virus. [34]
- In mice, ginsenoside Rg3 treatment stimulated an immune response by boosting the levels of specific immune cells such as immunoglobulin G. [35-36]
- In mouse B cells, treatment with ginsenoside Rg3 has been shown to increase the levels of immunoglobulin A. [37]
- A cell study found that ginsenoside Rg3 inhibited Th17 differentiation and Th17-mediated neuroinflammation, suggesting that it can help treat Th17-related autoimmune diseases. [38]
- In mice with hepatocellular carcinoma, a specific type of liver cancer, ginsenoside Rg3 treatment enhanced cellular immunity. This improvement may be attributed to the stimulation of lymphocytes, Th1-type cytokines interleukin-2, and interferon-γ levels. Studies on hepatocellular carcinoma further highlight the potential therapeutic applications of ginsenoside Rg3 in addressing liver cancer or liver-related malignancies. [39]
E. Helps Lose Weight

Evidence shows that ginsenoside Rg3 can help promote fat loss. Furthermore, there’s increasing interest in exploring the potential of ginsenoside Rg3 for weight loss, given its apparent ability to target fat cells and enhance metabolic functions.
- A review of mice studies suggested that ginsenoside Rg3 could potentially reduce body fat percentage. [40]
- A study in obese mice showed that ginsenoside Rg3 treatment resulted in better metabolism. [41]
- In mice fed with a high-fat diet, ginsenoside Rg3 treatment for 8 weeks significantly reduced body weight by promoting white fat burning. [42]
F. Accelerates Wound Healing
There’s also a good deal of evidence supporting the beneficial effects of ginsenoside Rg3 on wound healing. Some studies have pointed out that ginsenoside Rg3 can influence the activity of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which plays a key role in tissue repair and regeneration. Furthermore, by modulating the epidermal growth factor receptor, ginsenoside Rg3 might enhance the cellular mechanisms associated with wound recovery and skin restoration:
- Studies showed that ginsenoside Rg3 consumption can help improve wound healing through its anti-inflammatory effects. [43-44]
- Studies also reported that ginsenoside Rg3 can help prevent the formation of raised scars after an injury. [45-47]
- A study also found that ginsenoside Rg3 can help prevent keloid scar formation by promoting collagen synthesis. [48]
- In animals with experimental wounds, ginsenoside Rg3 induced the repair of tissue damage in the early stage and inhibited scar formation in the late stage of wound healing. [49]
G. Prevents Cancer

Ginsenoside Rg3, a naturally occurring compound found in certain species of the ginseng plant, has been studied extensively for its anti-cancer properties. It operates through multiple pathways to prevent the development and progression of cancer. One of the primary mechanisms is its ability to induce apoptosis, or programmed cell death, in cancerous cells. This not only curtails the growth of tumors but also prevents the abnormal cells from replicating and spreading, such as in the case of ovarian cancer metastasis.
Additionally, Rg3 has been observed to inhibit angiogenesis—the process by which tumors develop their blood supply—which is crucial for their growth and metastasis. By targeting these fundamental aspects of cancer cell survival and expansion, ginsenoside Rg3 demonstrates a robust defense against the establishment and progression of various cancers including inhibiting cancer cell proliferation.
Moreover, ginsenoside Rg3 enhances the efficacy of chemotherapy while potentially reducing its adverse side effects. It appears to sensitize cancer cells to the cytotoxic effects of chemotherapeutic drugs, thereby requiring lower doses for the same therapeutic effect, which could lead to a reduction in the drugs’ toxic impacts on healthy cells.
Furthermore, Rg3 exerts a modulatory influence on the immune system, boosting the body’s natural defense mechanisms to identify and destroy cancer cells via an enhanced immune response. This modulation can lead to a reduction in cancer cell proliferation, as the immune system becomes more efficient at targeting and eliminating malignant cells. By fostering an environment that is less conducive to cancer growth and by amplifying the body’s inherent cancer-fighting capabilities, ginsenoside Rg3 presents a multi-faceted approach to cancer prevention, warranting further investigation and integration into cancer treatment regimens.
A substantial body of high-quality research indicates that ginsenoside Rg3 exhibits potent anti-cancer effects against various human cancer cells. In particular, it has shown activity against gallbladder cancer cells by disrupting their growth signals. The compound has been found to be effective in preventing the proliferation and survival of colon cancer cell lines, where it interferes with cancer cell metabolism and DNA replication.
Studies involving gallbladder cancer cells have further elucidated the pathways through which ginsenoside Rg3 exerts its effects, revealing the compound’s capacity to inhibit cancer cells via modulation of signal transduction and gene expression. Additionally, its therapeutic effects on cancer mda mb 231 cells highlight its promise in targeting aggressive forms of breast cancer. By stymieing the migration and invasiveness of these cells, ginsenoside Rg3 contributes to a broader anti-cancer strategy.
Research has also focused on the way ginsenoside Rg3 tackles thyroid cancer metastasis, where it has been seen to prevent the spread of cancerous cells, further indicating its potential as a valuable adjunct in cancer treatment protocols. The comprehensive impact of ginsenoside Rg3 on cancer mda mb 231 cells, colon cancer cell lines, and other human cancer cells underlines its significance as a powerful compound in the fight against cancer.
- Research revealed that ginsenoside Rg3 can act against tumor cells, exhibiting the capability to inhibit tumor growth. In multiple studies, its effects on tumor cells were profound, especially in colon cancer cells, where it was observed to have strong anti-tumor properties. This compound not only hampers tumor growth but also notably targets the growth, proliferation, and colon cancer cell migration, making it a significant find in cancer research. It provides a basis for developing potential therapeutic agents that can inhibit the advancement and spread of cancer, particularly in cases of colon cancer. [50]
- Another study highlighted the potential effects of rg3 on cancer prevention, showing that ginsenoside Rg3 can assist in preventing esophageal cancer, including esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Specifically, the effects of rg3 on certain cancer cell mechanisms, especially in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, helped inhibit the proliferation of these harmful cells. Furthermore, it was observed that this compound can significantly diminish the growth of prostate cancer cells, providing another promising avenue in the fight against cancer cell growth. [51]
- In mice-bearing H460 lung cancer cells, a type of non-small cell lung cancer, and hypoxic lung cancer cells, a 28-day oral regimen with ginsenoside Rg3 at 100 mg/kg notably reduced tumor growth. Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits the progression and growth of these specific cancer types. Further research has indicated that ginsenoside Rg3 can be particularly effective against non-small cell lung cancers, which constitute a significant proportion of lung cancer cases. This efficacy stems from the ability of ginsenoside Rg3 to inhibit tumor cell proliferation and migration. Furthermore, ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits several mechanisms that these cancer cells use to thrive and spread. [52]
- Human esophageal cancer cells, human gastric cancer cells, and even other types of cancer cells, including gastric cancer cells, witnessed protective benefits from ginsenoside Rg3. Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits the growth mechanisms in esophageal cancer cells, promoting programmed cell death. Similarly, studies on human gastric cancer cell lines showed that ginsenoside Rg3 slows down cancer cell growth, offering potential therapeutic benefits for those with gastric malignancies. Furthermore, ginsenoside Rg3 shows promise in targeting the specific pathways that contribute to human gastric cancer cell growth. Additional research is needed to uncover more about its potential against various stages of gastric cancer. [53]
- Numerous research papers have suggested that ginsenoside Rg3 can amplify the therapeutic impact of anti-cancer drugs while concurrently decreasing their side effects. This was especially observed in ovarian cancer cells and human breast cancer samples. In relation to human breast cancer cells, ginsenoside Rg3 showed promise in inhibiting growth and progression. Some studies focused on human breast cancer MDA samples and breast cancer MDA MB lines, revealing potential molecular targets for ginsenoside Rg3’s action. Notably, metastatic breast cancer, which is a form of advanced breast cancer that spreads to other parts of the body, has been another area of investigation for ginsenoside Rg3. Some studies have indicated its potential efficacy against triple-negative breast cancer, a particularly aggressive form of breast cancer that lacks the usual receptors targeted by many treatments. Considering the challenges of treating metastatic breast cancer, researchers are hopeful about the benefits of ginsenoside Rg3. Research is ongoing to explore how ginsenoside Rg3 interacts with triple-negative breast cancer cells and its potential as a therapeutic agent for this challenging condition. [54-64]
- In experiments with human colorectal cancer cells, ginsenoside Rg3 thwarted cancer growth and its subsequent progression. This compound showed a marked ability to inhibit colorectal tumor growth, demonstrating its potential therapeutic effects. Its effects were also seen in colon cancer cells, where it further suppressed colorectal tumor growth, and in small-cell lung cancer specimens. [65-68]
- For patients diagnosed with lung cancer, including both non-small cell lung and small cell lung cancer, ginsenoside Rg3 not only extended overall survival but also obstructed the growth and viability of cancer cells. Studies specifically looking into non-small cell lung cancer also highlighted the potential benefits of ginsenoside Rg3 in enhancing treatment outcomes. [69-71]
- Patients and animals afflicted with breast cancer, specifically human breast cancer mda, demonstrated promising results upon treatment with ginsenoside Rg3. When analyzing mda mb 231 cells, a specific line of breast cancer cells, there was a notable response to ginsenoside Rg3 treatment. In the context of metastatic breast cancer, especially involving mda mb 231 cells, ginsenoside Rg3 showcased potential in combating the spread of the disease. Studies focusing on breast cancer MDA mb, including evaluations on mda mb 231 cells, found a noticeable reduction in tumor expansion. Furthermore, it triggered programmed cell death and delayed the progression of breast cancer. [72-74]
- There’s evidence that ginsenoside Rg3 stunts the proliferation of malignant cells, demonstrating a strong inhibitory effect of ginsenoside on their growth. Particularly, in prostate cancer cells and hypoxic lung cancer cells, the inhibitory effect of ginsenoside plays a crucial role by altering the immunosuppressive microenvironment. [75]
- In mouse studies, ginsenoside Rg3 obstructed the migration and invasion of liver cancer cells, including hepatocellular carcinoma, by augmenting the protein ARHGAP9. This compound has shown promise in inhibiting the growth of cancer cell, particularly in the liver, where hepatocellular carcinoma is a prevalent type. Simultaneously, its effectiveness was noted against small-cell lung cancer types. Research continues to examine its impact on various cancer cell lines, including hepatocellular carcinoma, to understand its full therapeutic potential. [76]
- One cell study shed light on how ginsenoside Rg3 arrested the growth and dissemination of several thyroid cancer cell lines. Notably, this research also indicated that the compound was effective in targeting the cancer cell’s metabolic pathways, hindering their proliferation. Moreover, ginsenoside Rg3 was found to be particularly potent against prostate and colon cancer cells, suggesting its broad-spectrum activity against various cancer cell types. [77]
- It’s worth noting that ginsenoside Rg3 has also been documented to restrict the growth dynamics of prostate cancer cell line, small cell lung cancer samples, and non-small cell lung cancer. In particular, rg3 inhibits the aggressive behavior of these cancer types. This suggests that rg3 inhibits not only the growth but also the metastatic potential of prostate cancer cells, non-small cell lung cancer cells, and other malignant cells. The anti-cancer effects of ginsenoside Rg3 on these cells have gained significant attention in recent research. [78]
- In a laboratory model of ovarian cancer, including detailed studies on ovarian cancer cells, the effects of ginsenoside Rg3 were thoroughly examined, revealing the effects of Rg3 in impeding metastasis. Specifically, ginsenoside Rg3 showed a notable capacity to inhibit the progression and dissemination of ovarian cancer cells, suggesting its potential as a promising adjunct in ovarian cancer treatment. This compound’s action against ovarian cancer could offer a new avenue for therapeutic strategies. Additionally, the impact of ginsenoside Rg3 extended to human breast cancer samples, where it effectively thwarted the growth and proliferation of cancer cells. The consistent efficacy across different types of cancer, including ovarian cancer, underscores the potential of ginsenoside Rg3 as a valuable component in comprehensive cancer treatment protocols. [79]
H. Improves Mood

Studies show that Rg3 also has antidepressant effects. Ginsenoside Rg3 induces positive changes in mood by modulating neurotransmitter levels in the brain. Moreover, research suggests that ginsenoside Rg3 induces a protective effect against stress-related disorders, further highlighting its potential benefits in mental health.
- In rats exposed to chronic unpredictable stress, ginsenoside Rg3 administration at 20 and 40 mg/kg produced anti-anxiety effects. [18]
- In a mouse study, ginsenoside Rg3 induced positive effects on immunoregulation, which in turn helped in reducing signs of depression. Researchers believe that the benefits might be linked to the changes ginsenoside Rg3 induced in the immune system’s response, impacting brain functions associated with mood. [80]
- A review of studies highlighted the potent effect of Rg3 in traditional herbal remedies. It showed that ginsenoside Rg3 treatment, particularly the effect of Rg3 on neuroprotective functions, reduced depressive symptoms in patients with low mood. Some researchers believe the effect of Rg3 on brain pathways could be a potential reason behind its mood-enhancing capabilities. Furthermore, considering the overall effect of Rg3 in holistic health, its role in mental well-being is increasingly being recognized. [81]
I. Improves Blood Sugar Levels and Treats Diabetic Symptoms
Ginsenoside Rg3 has been extensively studied for its therapeutic properties. Research indicates that ginsenoside Rg3 induces positive changes in metabolic functions, leading to improved blood sugar regulation. Furthermore, ginsenoside Rg3 induces enhancements in the way the body utilizes the insulin hormone and ensures effective blood sugar transport. This suggests its potential in treating symptoms of diabetes and maintaining optimal blood sugar levels:
- In mice, ginsenoside Rg3 suppressed the blood sugar levels from rising by enhancing insulin secretion 30 minutes after administration. [82]
- A study found that ginsenoside Rg3 enhanced the transport of blood sugar within the cells. [83]
- In type 2 diabetic mice, ginsenoside Rg3 lowered blood sugar by increasing insulin levels. [84]
- In diabetic rats, ginsenoside Rg3 protected against lung injury caused by high blood sugar levels. [85]
- In diabetic rat models, ginsenoside Rg3 protected the kidney against damage due to inflammation. [86]
- A cell study reported that ginsenoside Rg3 improved insulin signaling and blood sugar uptake. [87]
- In western diet-fed mice, ginsenoside Rg3 alleviated diabetic complications such as elevated blood sugar, triglyceride, and low-density lipoprotein (bad cholesterol) levels. [88]
- In animal models of diabetes, ginsenoside Rg3 protected the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas against cell death. [89-90]
- In diabetic rats, ginsenoside Rg3 significantly ameliorated kidney dysfunction. [91]
- In mice fed with a high-fat diet, ginsenoside Rg3 ameliorated obesity-induced insulin resistance. [92]
- In a mice model with diabetic atherosclerosis (plaque formation within the heart arteries), ginsenoside Rg3 inhibited the migration of the plaques. [93]
- In mice, ginsenoside Rg3 significantly ameliorated insulin resistance through activation of the AMPK pathway. [94]
- In streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats, ginsenoside Rg3 improved erectile function. [95]
Associated Side Effects of Ginsenoside Rg3
Ginsenoside Rg3 side effects are very uncommon. There have been some side effects associated with the use of this drug wherein the patient had one of the issues listed below at some point while being on ginsenoside Rg3. However, these side effects weren’t confirmed to be associated with the treatment and could have been a coincidence and not related to the use of ginsenoside Rg3. Despite this, it was listed as a side effect associated with ginsenoside Rg3 even though these associated side effects are very uncommon.
Side effects associated with ginsenoside Rg3 may include the following:
- Decreased appetite
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Rashes
Ginsenoside Rg3 Dosage
The appropriate dosage of Ginsenoside Rg3 can vary widely depending on several factors, including the age, health status of the individual, the form of the product, and the purpose for which it is being used.
For clinical applications, especially in cancer treatment, the dosages can vary based on the type and stage of cancer, and are often determined by the healthcare provider within the context of a clinical trial or a specialized treatment protocol. For instance, doses in the range of 20-60 mg per day have been used in some clinical studies for anti-cancer purposes, where rg3 induced apoptotic cell death is a desired outcome to prevent the proliferation of cancerous cells.
For general health supplements, the dosages might be lower. However, there is no universally accepted standard dose for Rg3 due to the variability in ginseng preparations and the concentration of active components.
Research indicates that Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits colorectal tumor growth by interfering with cell growth pathways, thereby offering a therapeutic advantage in colorectal cancer management. The compound’s ability to inhibit colorectal tumor growth has been a focus of numerous studies, reflecting its potential role in integrative oncology. Additionally, the influence of Ginsenoside Rg3 on cell growth does not limit its action to malignant cells alone; its impact on normal cell growth must be considered to avoid unintended consequences on healthy tissues.
It’s critical to note that natural products are not always necessarily safe and dosages can be important. Just because ginsenosides are natural compounds, it does not mean that they can be taken in any amount without potential risks. Overdosing on Ginsenoside Rg3 can lead to side effects such as gastrointestinal issues, sleep problems, and possible interactions with other medications, which may impact cell growth in non-targeted tissues.
Before starting any new supplement, including Ginsenoside Rg3, it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider who can provide guidance based on your specific health needs and conditions. They can also monitor for potential interactions with other medications and advise on the correct dosage for your situation, to ensure that cell growth is regulated safely and effectively.
Ginsenoside Rg3 Supplement Availability
Ginsenoside Rg3 supplements are typically found in specialty health food stores, online supplement retailers, or stores that specialize in herbal and traditional medicines. Availability can vary based on your region and local regulations regarding supplements.
Here’s what to consider when looking for ginsenoside Rg3 supplements:
- Quality and Purity: Look for supplements that have been tested for quality and purity. Some companies provide certificates of analysis (COAs) for their products.
- Form: Ginsenoside Rg3 is available in various forms, such as capsules, tablets, powders, and sometimes as a liquid extract.
- Concentration: Pay attention to the concentration of Rg3, as this can vary significantly between products.
- Source: Look for products that specify the source of the ginsenoside Rg3, as this can affect the type and purity of the compound.
- Brand Reputation: Choose brands with good reputations and reviews from consumers.
- Legal Status: In some countries, the sale of certain supplements may be regulated or restricted, so check the legal status of ginsenoside Rg3 in your country.
- Consult Healthcare Providers: Before taking any new supplement, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare provider, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
Ginsenoside Rg3 Interactions with Drugs and Nutrients
Interactions with Drugs
Ginsenoside Rg3, like many bioactive compounds derived from herbal medicines, can interact with pharmaceutical drugs, often influencing their pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics. For instance, its modulatory effects on liver enzymes such as cytochrome P450 can affect the metabolism of certain drugs, potentially leading to either an increase or decrease in their active levels in the bloodstream. This means that medications with a narrow therapeutic index, such as warfarin or some antiepileptics, may require close monitoring and dosage adjustments when taken concurrently with ginsenoside Rg3 supplements. Additionally, given its potential antiplatelet and anticoagulant effects, there might be an increased risk of bleeding when ginsenoside Rg3 is combined with anticoagulant drugs like heparin or antiplatelet agents such as aspirin.
Interactions with Nutrients
The interactions between ginsenoside Rg3 and various nutrients can also be significant, particularly in the realms of absorption and bioavailability. Certain minerals, for example, may compete with ginsenoside Rg3 for absorption in the gastrointestinal tract, potentially reducing the efficacy of either the nutrient or the ginsenoside. Conversely, some vitamins (like Vitamin C) might enhance the absorption of ginsenosides. On the other hand, dietary fiber could bind to ginsenoside Rg3, thereby decreasing its bioavailability. Therefore, timing and dietary composition might be crucial when consuming ginsenoside Rg3 to maximize its benefits without compromising the nutritional value of one’s diet.
Potential for Adverse Interactions
Despite its therapeutic properties, the potential for adverse interactions between ginsenoside Rg3 and other drugs or nutrients underscores the necessity for professional oversight. Individuals taking prescription medications for chronic conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, or mood disorders, should consult healthcare providers before starting any ginsenoside Rg3 supplementation. This is particularly important because ginsenoside Rg3 might alter the effects of hypoglycemic drugs or antihypertensive agents. Moreover, as the research into ginsenoside Rg3 is still evolving, health professionals must stay informed about the latest findings to guide their patients appropriately in the context of polypharmacy and complex dietary habits.
FAQ
What is the effect of ginsenosides?
Ginsenosides, the primary active compounds found in ginseng, have garnered attention for their range of therapeutic effects. Research has particularly highlighted that ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits the growth and metastasis of certain cancer cells, demonstrating a potential role in oncology. With its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and neuroprotective properties, ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits not only the proliferation of malignancies but also mediates protective mechanisms in neuronal and cardiovascular tissues.
What is the antioxidant activity of ginsenosides?
Ginsenosides, particularly due to the effect of ginsenoside Rg3, have strong antioxidant activity. This activity, stemming from the effect of ginsenoside Rg3, means they can neutralize free radicals in the body. By reducing oxidative stress and potential cellular damage, the effect of ginsenoside Rg3 demonstrates its importance in the overall benefits of ginsenosides. Additionally, this reduction in oxidative stress may inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells, indicating a potential for ginsenoside Rg3 in contributing to cancer prevention strategies.
What is 20 s ginsenoside Rg3?
20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 is one of the stereoisomers of ginsenoside Rg3 found in the ginseng plant. Ginsenosides, the major active ingredients of ginseng, are a diverse group of steroidal saponins. They can exist in different stereoisomeric forms because of the difference in spatial arrangement around their chiral centers. Specifically, ginsenoside Rg3 has two stereoisomers: 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 and 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg3.
Among the two, 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 is often reported to have stronger pharmacological effects. Studies have shown that this compound possesses various therapeutic properties, including anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective, and neuroprotective activities.
What is the solubility of ginsenosides?
Ginsenosides are mainly soluble in water and alcohol, but their solubility can vary based on their specific structure and type.
What happens when you take ginseng every day?
Taking ginseng daily can help boost energy levels, improve cognitive function, and enhance the immune system. However, excessive or long-term use may lead to side effects.
How does ginseng help the brain?
Ginseng and its components, especially ginsenosides, have been shown to improve cognitive function, protect nerve cells against oxidative stress and inflammation, and potentially aid in memory enhancement.
What are the side effects of taking ginseng vitamins?
Potential side effects of ginseng, especially when consumed in the form of red ginseng extract, include headaches, digestive problems, sleep disturbances, nervousness, and elevated blood pressure. It’s essential to understand the source and formulation of the ginseng product being consumed.
How do you feel after taking ginseng?
Most people report feeling more energetic and alert after taking ginseng. The compound ginsenoside Rg3 promotes increased energy and vitality in many individuals. Additionally, ginsenoside Rg3 promotes better mental clarity, which could be a reason behind the heightened alertness. With its potential benefits, ginsenoside Rg3 promotes overall well-being when consumed. It’s not just the ginseng, but specifically how ginsenoside Rg3 promotes these positive effects that have caught the attention of many researchers.
What are the sources of ginsenosides?
The primary source of ginsenosides is the ginseng plant, especially the roots.
How much ginsenosides per day?
The recommended daily dose varies, but generally, it’s between 1 to 2 grams of raw ginseng root. However, always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Who should not take ginseng?
People with high blood pressure, pregnant and nursing women, and those taking certain medications (like blood thinners) should avoid ginseng or consult with a doctor before use.
Is ginseng better in the morning or night?
Ginseng is often recommended in the morning or early afternoon due to its energizing effects which might interfere with sleep if taken at night.
How many times a week should I take ginseng?
This varies based on personal needs and the advice of a healthcare provider, but many people take ginseng daily or at least several times a week.
What are the long-term side effects of ginseng?
Long term use of ginseng can lead to side effects like hormonal imbalances, insomnia, elevated blood pressure, and digestive issues.
Does ginseng work quickly?
The effects of ginseng can be felt shortly after taking it, but for some benefits, consistent and prolonged use might be required. Among these long-term benefits, studies have suggested that an active component of ginseng, ginsenoside Rg3, inhibits colorectal tumor growth. This indicates that regular consumption of ginseng, with its Rg3 content, could potentially contribute to colorectal health over time.
Which ginseng is best?
The “best” ginseng depends on the desired effect. Panax ginseng is often used for energy and cognitive benefits, while American ginseng might be preferred for immune support.
Is ginseng good or bad for the heart?
Ginseng has cardioprotective effects and can be beneficial for heart health, but excessive intake can increase blood pressure. Always consult with a doctor.
What is the best time of day to take ginseng?
Morning or early afternoon is usually recommended to avoid potential sleep disturbances.
Does ginseng affect your kidneys?
While ginseng has been used traditionally to support kidney health, excessive or prolonged intake can stress the kidneys. Consultation with a doctor is essential.
How much ginseng is safe daily?
Typically, 1 to 2 grams of raw ginseng root is considered safe, but the appropriate amount varies by individual and product concentration.
Does ginseng detox your body?
Ginseng has antioxidant properties that can support the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Are ginsenosides steroids?
Ginsenosides are steroid-like compounds, but they’re not steroids in the traditional sense.
What percentage of ginseng is ginsenosides?
The percentage can vary, but typically, dried ginseng root contains 2-3% ginsenosides.
Which ginseng has the most ginsenosides?
Korean Red Ginseng, a form of Panax ginseng, is often considered to have the highest ginsenoside content.
What ginseng is best for brain health?
Panax ginseng, especially Korean Red Ginseng, is commonly recommended for cognitive benefits.
Are ginsenosides saponins?
Yes, ginsenosides are a type of saponin found in ginseng plants.
Does ginseng grow naturally?
Yes, ginseng grows naturally in various regions, including North America and Asia, but cultivated varieties also exist.
Are ginsenosides polysaccharides?
No, ginsenosides are saponins. Ginseng does contain beneficial polysaccharides, but these are distinct from ginsenosides.
Does ginseng affect the immune system?
Yes, ginseng can modulate and boost the immune system.
Can I take ginseng with other vitamins?
Generally, ginseng can be taken with vitamins, but always consult with a healthcare provider regarding potential interactions.
Is ginseng bad for blood pressure?
Ginseng can affect blood pressure. Some people experience an increase, so those with hypertension should be cautious and consult with a doctor.
Can I take ginseng on an empty stomach?
Ginseng can be taken on an empty stomach, but some people may experience stomach upset and prefer to take it with food.
Does ginseng interact with any medications?
Ginseng can be taken on an empty stomach, but some people may experience stomach upset and prefer to take it with food.
Does ginseng interact with any medications?
Yes, ginseng can interact with medications, especially blood thinners, diabetes medications, and antidepressants. Always consult with a healthcare provider.
Is ginseng acidic or alkaline?
Ginseng is generally considered slightly acidic.
Is ginseng good for females?
Yes, ginseng can offer benefits for females, including energy boosts and hormonal balance. However, specific effects can vary by individual.
Which ginseng is best for anti-aging?
Korean Red Ginseng is often touted for its anti-aging benefits due to its high ginsenoside content.
Is ginseng good for acid reflux?
There’s limited evidence on this, and while some believe it may help, others find it can exacerbate symptoms. Always consult with a doctor.
Can ginseng cause heart palpitations?
In some individuals, excessive intake can cause side effects including heart palpitations.
How many times a week should I take ginseng?
The frequency can vary based on personal needs and advice from a healthcare provider, but many take ginseng daily or several times a week.
Is ginseng good for your face?
Ginseng has anti-aging and antioxidant properties that can be beneficial for skin health.
Is ginseng a blood thinner?
Ginseng can interact with blood-thinning medications and may have blood-thinning effects on its own. Always consult with a healthcare provider.
Is ginseng good for creatinine?
There’s limited research, but some studies suggest ginseng might help reduce creatinine levels in individuals with kidney issues.
Is ginseng safe for liver?
Moderate consumption of ginseng is generally safe, but excessive or prolonged intake can stress the liver.
Does ginseng increase uric acid?
There’s limited evidence on this, and more research is needed to draw conclusions.
What is the best time of day to take ginseng?
Morning or early afternoon is usually recommended due to its energizing effects.
How does ginseng help sleep?
While ginseng can be energizing, some forms, like American ginseng, may have calming effects that can potentially aid sleep.
How long does it take for ginseng to work?
The effects of ginseng can be felt shortly after intake, with initial energizing effects often reported. However, for some benefits, such as capturing circulating tumor cells—a process critical for limiting the spread of cancer—consistent use over weeks or months might be required. Ginseng’s active compounds, including ginsenosides, have been studied for their ability to interfere with cancer progression because they induce apoptosis of human cancer cells. This programmed cell death is essential for eliminating malignant cells and preventing the development of tumors. Therefore, the full spectrum of ginseng’s therapeutic effects, especially in the context of cancer prevention and treatment, often emerges with long-term use.
Why do athletes take ginseng?
Athletes often take ginseng for its energy-boosting, anti-fatigue, and potential performance-enhancing properties.
How many times a week should I take ginseng?
The frequency can vary, but many individuals take ginseng daily or at least several times a week, based on personal needs and the advice of a healthcare provider. Additionally, research into the benefits of ginseng has shown that one of its active components, ginsenoside Rg3, induces apoptosis of human cancer cells, which may be beneficial in developing treatments for various cancers.
What are the potential benefits of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3?
20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 has been researched for its various therapeutic properties. These include anti-cancer activities, cardioprotective effects, anti-inflammatory benefits, and neuroprotective properties. It is often reported to possess stronger pharmacological effects than its isomeric counterpart.
How does 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 differ from 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg3?
Both 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 and 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg3 are stereoisomers, meaning they have the same molecular formula but differ in the spatial arrangement of their atoms. Among the two, 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 is often considered to have more potent pharmacological activities based on various studies.
How is 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 sourced?
20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 is naturally sourced from certain species of the ginseng plant, particularly from its roots. It can be extracted and purified using various techniques to obtain a concentrated form suitable for research or therapeutic applications.
Are there any side effects associated with 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 consumption?
While 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 is generally considered safe when consumed within recommended dosages, like any compound, excessive or inappropriate use might lead to adverse effects. It’s crucial to follow recommended guidelines or consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation.
Can 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 be used in combination with other treatments?
Preliminary research indicates that 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 can enhance the therapeutic effects of certain treatments, particularly by inhibiting cell growth in the context of cancer therapies. Ginsenoside Rg3 attenuates the proliferation of malignant cells, offering a potential adjunctive benefit to conventional treatments by potentially slowing tumor metastasis. Moreover, ginsenoside Rg3 attenuates the aggressive nature of cancer cells, which might complement the action of other therapeutic agents aimed at mitigating tumor metastasis. However, it is crucial to always consult with a healthcare professional before combining it with other treatments to ensure safety and efficacy.
How does 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 impact immune function?
Studies suggest that 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3, often referred to as 20 S RG3, may modulate the immune system by enhancing the activity of certain immune cells, thereby potentially bolstering the body’s defense mechanisms against pathogens and diseases. The presence of 20 S RG3 in ginseng is believed to be a key factor in its health benefits. Additionally, 20 S RG3 has been the subject of numerous studies aiming to harness its therapeutic properties for improving immune function.
Ongoing research is delving deeper into how 20 S RG3 can be utilized in immune system enhancement. The potential for 20 S RG3 to contribute to novel treatments in immunotherapy is an exciting development in the field of medicine. As scientists continue to study 20 S RG3, they are uncovering more about its role in regulating both innate and adaptive immune responses.
It’s also worth noting that 20 S RG3 might have synergistic effects when combined with other immune-boosting compounds, although such combinations would require careful study to understand their interactions fully. Lastly, the potential of 20 S RG3 in improving vaccine efficacy is another area of interest, providing a promising avenue for further investigation.
Reference
Bao HY, Zhang J, Yeo SJ, Myung CS, Kim HM, Kim JM, Park JH, Cho J, Kang JS. Memory enhancing and neuroprotective effects of selected ginsenosides. Arch Pharm Res. 2005 Mar;28(3):335-42. doi: 10.1007/BF02977802. PMID: 15832823.
In this study, the effects of ginsenosides Rg3(R), Rg3(S), and Rg5/Rk1, isolated from processed Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer, on memory dysfunction in mice were investigated. When administered orally for four days, all three ginsenosides demonstrated significant improvements in memory impairment induced by ethanol or scopolamine. Notably, Rg5/Rk1 exhibited the most effective enhancement of memory function, with treated mice showing 1.2 times longer latency periods than the control group in both models. Additionally, the ginsenosides displayed potent inhibition of excitotoxicity induced by glutamate or N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) but were ineffective against oxidative neuronal damage caused by H2O2 or xanthine/xanthine oxidase. These findings suggest that Rg3(S) and Rg5/Rk1 can reverse memory dysfunction and possess neuroprotective properties against excitotoxicity.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15832823/.
Kim, Y. C., Kim, S. R., Markelonis, G. J., and Oh, T. H., Ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg3 protect cultured rat cortical cells from glutamate-induced neurodegeneration.J. Neurosci. Res., 53, 426–432 (1998).
Ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg3 protect cultured rat cortical cells from glutamate-induced neurodegeneration
In this study, researchers explored the neuroprotective properties of natural compounds derived from Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer against glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in rat cortical cell cultures. They found that ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg3 effectively attenuated glutamate-induced neuronal cell damage, reducing neuronal death and inhibiting the overproduction of nitric oxide. Additionally, these compounds preserved superoxide dismutase levels, reduced malondialdehyde formation associated with lipid peroxidation, and diminished calcium influx in glutamate-treated cells, collectively indicating their significant neuroprotective effects against oxidative damage caused by excess glutamate exposure.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/%28SICI%291097-4547%2819980815%2953%3A4%3C426%3A%3AAID-JNR4%3E3.0.CO%3B2-8?sid=nlm%3Apubmed.
Joo SS, Yoo YM, Ahn BW, Nam SY, Kim YB, Hwang KW, Lee DI. Prevention of inflammation-mediated neurotoxicity by Rg3 and its role in microglial activation. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Jul;31(7):1392-6. doi: 10.1248/bpb.31.1392. PMID: 18591781.
Prevention of inflammation-mediated neurotoxicity by Rg3 and its role in microglial activation
This study investigated the potential therapeutic effects of Rg3, a by-product from the steaming of red ginseng, on neurodegenerative diseases by focusing on inflammation and apoptosis. Rg3 demonstrated a significant reduction in inflammatory cytokine expression in Abeta42-treated BV-2 microglial cells and inhibited the binding of NF-kappaB p65 to its DNA consensus sequences, resulting in decreased TNF-alpha expression in activated microglia. Furthermore, Rg3 enhanced the survival rate of Neuro-2a neuroblastoma cells exposed to TNF-alpha, suggesting its ability to reduce neurotoxicity by suppressing chronic inflammation through microglial inhibition and promoting MSRA expression, potentially contributing to phagocytosis of Abeta42 peptides in neurodegenerative diseases.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/bpb/31/7/31_7_1392/_article.
Park SM, Choi MS, Sohn NW, Shin JW. Ginsenoside Rg3 attenuates microglia activation following systemic lipopolysaccharide treatment in mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(9):1546-52. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b12-00393. PMID: 22975507.
Ginsenoside Rg3 attenuates microglia activation following systemic lipopolysaccharide treatment in mice
This study explored the immune-modulating effects of ginsenoside Rg3, a prominent component of Panax ginseng, on neuroinflammation induced by systemic lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment in mice. Ginsenoside Rg3, administered orally at doses of 20 and 30 mg/kg prior to LPS injection, significantly reduced the up-regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6) in brain tissue and mitigated the morphological activation of microglia. Additionally, the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in brain tissue was reduced with ginsenoside Rg3 treatment, highlighting its potential as a modulator of neuroinflammation in vivo.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/bpb/35/9/35_b12-00393/_article.
Jang SK, Yu JM, Kim ST, Kim GH, Park DW, Lee DI, Joo SS. An Aβ42 uptake and degradation via Rg3 requires an activation of caveolin, clathrin and Aβ-degrading enzymes in microglia. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Jul 5;758:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.03.071. Epub 2015 Apr 4. PMID: 25848967.
An Aβ42 uptake and degradation via Rg3 requires activation of caveolin, clathrin and Aβ-degrading enzymes in microglia
This study delved into the biochemical and mechanistic roles of ginsenoside Rg3 in human microglia and animal models, focusing on its potential to restore memory and learning impaired by amyloid β peptide 1-42 (Aβ42). Rg3 was found to enhance the expression of macrophage scavenger receptor class A (SRA), leading to increased Aβ42 uptake in both rats and human microglial cells. Additionally, Rg3 promoted endocytic biogenesis through clathrin and caveolin1, activating signaling pathways, and stimulated the expression of neprilysin (NEP) and insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE), suggesting its potential as a therapy for Alzheimer’s disease by facilitating Aβ peptide uptake and degradation.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0014299915003106?via%3Dihub.
Available at http://koreascience.or.kr/article/JAKO201201052161301.page.
Lee B, Sur B, Park J, Kim SH, Kwon S, Yeom M, Shim I, Lee H, Hahm DH. Ginsenoside rg3 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced learning and memory impairments by anti-inflammatory activity in rats. BiomolTher (Seoul). 2013 Sep 30;21(5):381-90. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2013.053. PMID: 24244826; PMCID: PMC3825202.
Ginsenoside rg3 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced learning and memory impairments by anti-inflammatory activity in rats
This study aimed to investigate the potential of ginsenoside Rg3 (GRg3) in alleviating learning and memory impairments and reducing inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) injection in rat brains. The research found that daily administration of GRg3 significantly improved LPS-induced cognitive deficits, as demonstrated in behavioral tests, and reduced the expression of pro-inflammatory markers such as tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, and cyclooxygenase-2 in the hippocampus. These findings suggest that GRg3’s anti-inflammatory properties may make it effective in preventing or slowing the progression of neurological disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease, by enhancing cognitive and memory functions.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3825202/.
Aalinkeel R, Kutscher HL, Singh A, Cwiklinski K, Khechen N, Schwartz SA, Prasad PN, Mahajan SD. Neuroprotective effects of a biodegradable poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-ginsenoside Rg3 nanoformulation: a potential monotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease? J Drug Target. 2018 Feb;26(2):182-193. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2017.1354002. Epub 2017 Jul 17. PMID: 28697660.
Neuroprotective effects of a biodegradable poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-ginsenoside Rg3 nanoformulation: a potential nanotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease
This study explores the potential of ginsenoside Rg3, a compound found in ginseng with memory-enhancing and antioxidant properties, as a neuroprotective treatment for Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The researchers developed biodegradable nanoparticles encapsulating Rg3 and Thioflavin T, a diagnostic agent for Aβ plaques, to enhance its delivery to the brain and investigate its neuroprotective effects. This innovative nanotherapeutic approach shows promise not only for AD but also for addressing other neurological diseases by improving the solubility and pharmacokinetics of natural therapeutic agents.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/1061186X.2017.1354002.
Zhang, Y., Yang, X., Wang, S., & Song, S. (2019). Ginsenoside Rg3 Prevents Cognitive Impairment by Improving Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Rat Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 67(36), 10048–10058. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b03793.
Ginsenoside Rg3 Prevents Cognitive Impairment by Improving Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Rat Model of Alzheimer’s Disease
This study investigates the potential benefits of ginsenoside Rg3 (GRg3), a significant bioactive component in ginseng, in rats with Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The research evaluates GRg3’s impact on cognitive function and antioxidant capacity, using metabolomic analysis and apoptosis assessment to uncover underlying mechanisms related to mitochondrial dysfunction. The results suggest that GRg3 may have a preventive and delaying effect on AD by regulating energy metabolism, electron transport chain, amino acid metabolism, purine metabolism, and antiapoptotic pathways, positioning it as a promising complementary and functional food for AD prevention.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b03793.
Sheng C, Peng W, Xia ZA, Wang Y, Chen Z, Su N, Wang Z. The impact of ginsenosides on cognitive deficits in experimental animal studies of Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Oct 24;15:386. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0894-y. PMID: 26497388; PMCID: PMC4619356.
The impact of ginsenosides on cognitive deficits in experimental animal studies of Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review
In this systematic review, the efficacy of ginsenoside treatment in addressing cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) was investigated using experimental rodent AD models. Twelve eligible studies were analyzed, with overall study quality rated as poor. The meta-analysis indicated a statistically significant positive impact of ginsenosides on cognitive performance in these models, with ginsenoside Rg1 showing the most substantial effect on the acquisition and retention of memory. Interestingly, studies involving female animals demonstrated a higher effect size for both acquisition and retention memory compared to male animals. However, the authors emphasize the need for additional well-designed and well-reported animal studies to inform future clinical investigations.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmid/26497388/.
Sheng, C., Peng, W., Xia, Z. A., Wang, Y., Chen, Z., Su, N., & Wang, Z. (2015). The impact of ginsenosides on cognitive deficits in experimental animal studies of Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. BMC complementary and alternative medicine, 15, 386. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-015-0894-y.
The impact of ginsenosides on cognitive deficits in experimental animal studies of Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review
In this systematic review, the effectiveness of ginsenoside treatment for addressing cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) remains unexplored. The study conducted a comprehensive evaluation of ginsenosides’ impact on cognitive deficits using experimental rodent AD models. Twelve studies met the inclusion criteria from a pool of 283 publications, but the overall quality of these studies was deemed poor. The meta-analysis indicated that ginsenosides had a statistically significant positive influence on cognitive performance in experimental AD models. Notably, ginsenoside Rg1 demonstrated the most substantial effect on the acquisition and retention memory in AD models, with studies involving female animals showing a higher effect size for both memory aspects compared to male animals. The authors stress the need for additional well-designed and well-documented animal studies to guide future clinical investigations.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4619356/.
Kim, J., Shim, J., Lee, S., Cho, W. H., Hong, E., Lee, J. H., Han, J. S., Lee, H. J., & Lee, K. W. (2016). Rg3-enriched ginseng extract ameliorates scopolamine-induced learning deficits in mice. BMC complementary and alternative medicine, 16, 66. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-016-1050-z.
Rg3-enriched ginseng extract ameliorates scopolamine-induced learning deficits in mice
This study aimed to assess the impact of ginsenoside Rg3-enriched ginseng extract (Rg3GE) on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. Mice received Rg3GE for 14 days and were subjected to scopolamine-induced memory impairment for 6 days. The Morris water maze test revealed that mice treated with Rg3GE and scopolamine did not exhibit scopolamine-induced deficits in the acquisition of spatial memory. Additionally, Rg3GE administration inhibited the scopolamine-induced increase in acetylcholinesterase activity and activation of the NF-κB pathway in the hippocampus. These findings suggest that Rg3GE may mitigate scopolamine-induced memory deficits by modulating acetylcholinesterase activity and NF-κB signaling in the hippocampus.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4758096/.
Peña, I. D., Yoon, S. Y., Kim, H. J., Park, S., Hong, E. Y., Ryu, J. H., Park, I. H., & Cheong, J. H. (2014). Effects of ginseol k-g3, an Rg3-enriched fraction, on scopolamine-induced memory impairment and learning deficit in mice. Journal of ginseng research, 38(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2013.11.003.
Effects of ginseol k-g3, an Rg3-enriched fraction, on scopolamine-induced memory impairment and learning deficit in mice
This study aimed to address the challenges associated with ginsenoside production, focusing on the Rg3 compound, which has potential cognitive benefits but is costly to extract. The researchers developed ginseol k-g3, an Rg3-enriched fraction, and evaluated its impact on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. Ginseol k-g3 demonstrated a significant reversal of cognitive impairment in passive avoidance and Morris water maze tests, particularly in reference or long-term memory tasks. Unlike acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, ginseol k-g3 did not inhibit acetylcholinesterase activity. These findings suggest that ginseol k-g3 may enhance cognitive function and warrant further investigation into its mechanism of action.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3915335/.
Bao, H. Y., Zhang, J., Yeo, S. J., Myung, C. S., Kim, H. M., Kim, J. M., Park, J. H., Cho, J., & Kang, J. S. (2005). Memory enhancing and neuroprotective effects of selected ginsenosides. Archives of pharmacal research, 28(3), 335–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977802.
Memory enhancing and neuroprotective effects of selected ginsenosides
This study investigated the effects of ginsenosides Rg3(R), Rg3(S), and Rg5/Rk1 from processed Panax ginseng on memory dysfunction in mice using a passive avoidance test. The results showed that these ginsenosides, when orally administered, significantly improved memory impairments induced by ethanol or scopolamine. Among them, Rg5/Rk1 was the most effective in enhancing memory function, even in normal conditions, and the ginsenosides also exhibited neuroprotective effects against excitotoxicity, particularly Rg3(S) and Rg5/Rk1. These findings suggest the potential of these ginsenosides in addressing memory issues and protecting against excitotoxicity-related neuronal damage.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15832823/.
H. Singh, J. Du, P. Singh, G.T. Mavlonov, T.H. Yi. Development of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles via direct conjugation with ginsenosides and its in-vitro study. J Photochem Photobiol B: Biol, 185 (2018), pp. 100-110.
Development of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles via direct conjugation with ginsenosides and its in-vitro study
In this study, superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) were directly conjugated with ginsenosides CK and Rg3 using a cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and efficient method. Characterization confirmed the successful formation of SPION conjugates. These conjugates, termed SPION-CK and SPION-Rg3, exhibited non-cytotoxicity in normal HaCaT keratinocyte cells and demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties by reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS), nitric oxide, and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) levels in lipopolysaccharide-activated RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. These findings suggest that SPIONs conjugated with ginsenosides CK and Rg3 have the potential for use as carriers for delivering ginsenosides in the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
You can read the full article at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1011134418302641?via%3Dihub.
Ratan, Z. A., Haidere, M. F., Hong, Y. H., Park, S. H., Lee, J. O., Lee, J., & Cho, J. Y. (2021). Pharmacological potential of ginseng and its major component ginsenosides. Journal of ginseng research, 45(2), 199–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2020.02.004.
Pharmacological potential of ginseng and its major component ginsenosides
Ginseng, a traditional herb with a long history of use in Asian countries, contains various active compounds, notably ginsenosides, which have been studied for their potential health benefits including antioxidant, anticancer, and immune-boosting effects, as well as their impact on conditions like cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and neurological disorders. While ginseng holds promise for drug development, further high-quality research is needed, and it should be used with caution due to possible interactions with other medications. This article provides an overview of the bioactive compounds, global distribution, and therapeutic potential of Panax genus plants.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8020288/.
Peña ID, Yoon SY, Kim HJ, Park S, Hong EY, Ryu JH, Park IH, Cheong JH. Effects of ginseol k-g3, an Rg3-enriched fraction, on scopolamine-induced memory impairment and learning deficit in mice. J Ginseng Res. 2014 Jan;38(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2013.11.003. Epub 2013 Dec 11. PMID: 24558303; PMCID: PMC3915335.
Effects of ginseol k-g3, an Rg3-enriched fraction, on scopolamine-induced memory impairment and learning deficit in mice
The study aimed to overcome the cost and potency limitations of ginsenosides like Rg1, Rb1, and Rg3 by preparing an Rg3-enriched fraction called ginseol k-g3. This fraction significantly improved memory impairment induced by scopolamine in mice, particularly in tasks related to reference or long-term memory, and showed stronger effects in memory tests compared to Rg3 or Red ginseng. Importantly, ginseol k-g3 didn’t inhibit acetylcholinesterase activity, and its mechanism of action in reversing memory deficits is yet to be fully understood.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3915335/.
Xu, J. N., Chen, L. F., Su, J., Liu, Z. L., Chen, J., Lin, Q. F., Mao, W. D., & Shen, D. (2018). The anxiolytic-like effects of ginsenoside Rg3 on chronic unpredictable stress in rats. Scientific reports, 8(1), 7741. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-26146-5.
The anxiolytic-like effects of ginsenoside Rg3 on chronic unpredictable stress in rats
This study aimed to assess the anxiolytic effects of ginsenoside Rg3 (GRg3). GRg3, administered at doses of 20 and 40 mg/kg, demonstrated anxiolytic-like activities by reversing behavioral changes observed in tests like the elevated plus maze and novelty-suppressed feeding. It also normalized the levels of certain neurosteroids, serotonin, and hormones in the brain, suggesting its potential in alleviating anxiety-related symptoms and modulating the neuroendocrine system.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5958129/.
Available at https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2016/6967853/.
Ginsenoside Rg3 Improves Cardiac Function after Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion via Attenuating Apoptosis and Inflammation
This study aimed to investigate the impact of ginsenoside Rg3 on cardiac function impairment caused by myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) in rats. Ginsenoside Rg3 was found to enhance left ventricular function parameters, reduce apoptosis, and lower the levels of inflammatory markers in the left ventricles of I/R-induced rats. These results suggest that ginsenoside Rg3 may be effective in improving cardiac function after myocardial I/R injury, primarily through its anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory properties.
You can read the full article at https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2016/6967853/.
Available at https://cdt.amegroups.com/article/view/37868/30147.
Ginsenoside Rg3 protects heart against isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction by activating AMPK-mediated autophagy
Panax ginseng is a well-known traditional medicinal herb, and ginsenoside Rg3 (Rg3) is considered a key active compound within it. This study explored the molecular mechanisms underlying the beneficial effects of Rg3 in a mouse heart injury model induced by isoproterenol (ISO). Rg3 was found to significantly reduce ISO-induced myocardial injury, as evidenced by lowered levels of serum markers like BNP and LDH. These cardioprotective effects were linked to enhanced autophagy and activation of the AMPK signaling pathway. Inhibition of AMPK reversed the protective effects of Rg3, suggesting that Rg3’s benefits in myocardial injury may be mediated through AMPK-dependent autophagy, with potential implications for myocardial infarction treatment.
You can read the full article at https://cdt.amegroups.org/article/view/37868/30147.
Lim, Dong Yoon1; Koh, Young Youp2 PS 04-21 GINSENOSIDE-RG3 INHIBITS CATECHOLAMINE SECRETION FROM THE PERFUSED RAT ADRENAL GLAND, Journal of Hypertension: September 2016 – Volume 34 – Issue – p e138-e139. doi: 10.1097/01.hjh.0000500255.90789.ef.
PS 04-21 GINSENOSIDE-RG3 INHIBITS CATECHOLAMINE SECRETION FROM THE PERFUSED RAT ADRENAL GLAND
The study aimed to investigate the impact of ginsenoside-Rg3 (Rg3) on catecholamine (CA) secretion from isolated rat adrenal glands and its underlying mechanism. Rg3 dose-dependently and time-dependently inhibited CA secretion triggered by various stimulants, including ACh, DMPP, high K+, veratridine, Bay-K-8644, and cyclopiazonic acid. Notably, Rg3’s inhibitory effect on ACh-induced CA secretion was partially reversed when co-administered with L-NAME, suggesting the involvement of nitric oxide (NO). Rg3 also increased NO release from the adrenal medulla. When used in combination with fimasartan, Rg3’s inhibitory effects on CA secretion were further enhanced. These findings indicate that Rg3 inhibits CA secretion through multiple mechanisms involving calcium and sodium influx, calcium release, and NO production, suggesting potential clinical applications in cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension.
You can read the full article at https://journals.lww.com/jhypertension/abstract/2016/09001/ps_04_21_ginsenoside_rg3_inhibits_catecholamine.383.aspx.
Sun, G. Z., Meng, F. J., Cai, H. Q., Diao, X. B., Zhang, B., & Bai, X. P. (2020). Ginsenoside Rg3 protects heart against isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction by activating AMPK mediated autophagy. Cardiovascular diagnosis and therapy, 10(2), 153–160. https://doi.org/10.21037/cdt.2020.01.02.
Ginsenoside Rg3 protects heart against isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction by activating AMPK mediated autophagy
In a study focusing on Panax ginseng and its active component, ginsenoside Rg3 (Rg3), researchers explored its potential cardioprotective effects. They used an isoproterenol-induced mouse heart injury model and assessed myocardial damage with ELISA kits measuring brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and caspase-3. They also investigated the role of AMPK-mediated autophagy in Rg3’s protective mechanism by employing an AMPK inhibitor alongside Rg3. Western blot analysis was used to measure NLRP3 inflammasome-related molecules. The results showed that Rg3 significantly reduced myocardial injury induced by isoproterenol, as indicated by decreased BNP and LDH levels. Additionally, Rg3 enhanced the expression of autophagy-related proteins and activated the AMPK downstream signaling pathway. Notably, inhibiting AMPK reversed Rg3’s myocardial protective effects, suggesting that Rg3 may ameliorate myocardial injury through AMPK-mediated autophagy. These findings provide valuable translational evidence for Rg3’s potential use in treating myocardial infarction (MI).
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7225426/.
Zhang, L. P., Jiang, Y. C., Yu, X. F., Xu, H. L., Li, M., Zhao, X. Z., & Sui, D. Y. (2016). Ginsenoside Rg3 Improves Cardiac Function after Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion via Attenuating Apoptosis and Inflammation. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, 2016, 6967853. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6967853.
Ginsenoside Rg3 Improves Cardiac Function after Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion via Attenuating Apoptosis and Inflammation
This study aimed to assess the impact of ginsenoside Rg3, a major constituent isolated from Panax ginseng, on cardiac function impairment induced by myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) in rats. Sprague-Dawley rats underwent myocardial I/R, and various parameters, including echocardiographic and hemodynamic measurements, along with histopathological examination, were conducted. Ginsenoside Rg3 treatment resulted in increased left ventricular fractional shortening and ejection fraction, while also mitigating elevations in left ventricular end-diastolic pressure and reductions in left ventricular systolic pressure and ±dp/dt in myocardial I/R rats. Additionally, Rg3 reduced apoptosis by inhibiting caspase-3 activation and significantly lowered TNF-α and IL-1β levels in the left ventricles of myocardial I/R rats. These findings suggest that ginsenoside Rg3 improves cardiac function impairment induced by myocardial I/R, primarily through its anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory properties.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5220470/.
Wang, Y., Hu, Z., Sun, B., Xu, J., Jiang, J., & Luo, M. (2015). Ginsenoside Rg3 attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via Akt/endothelial nitric oxide synthase signaling and the B‑cell lymphoma/B‑cell lymphoma‑associated X protein pathway. Molecular medicine reports, 11(6), 4518–4524. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3336.
Ginsenoside Rg3 attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via Akt/endothelial nitric oxide synthase signaling and the B‑cell lymphoma/B‑cell lymphoma‑associated X protein pathway
This study explored the potential cardioprotective effects of ginsenoside Rg3 (GSRg3) extracted from Panax ginseng in both in vitro and in vivo models of cardiac injury. The research demonstrated that GSRg3 pretreatment significantly improved cardiac function, reduced myocardial infarct size, and lowered markers of myocardial injury in rats subjected to ischemia/reperfusion injury. In vitro experiments revealed that GSRg3 reduced apoptosis in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes by inhibiting caspase-3 and caspase-9 activation, while enhancing Akt/eNOS signaling and the Bcl-2/Bax ratio. These findings suggest that GSRg3 may offer cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis through multiple pathways.
You can read the full article at https://www.spandidos-publications.com/mmr/11/6/4518.
Tu, C., Wan, B., & Zeng, Y. (2020). Ginsenoside Rg3 alleviates inflammation in a rat model of myocardial infarction via the SIRT1/NF-κB pathway. Experimental and therapeutic medicine, 20(6), 238. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2020.9368.
Ginsenoside Rg3 alleviates inflammation in a rat model of myocardial infarction via the SIRT1/NF-κB pathway
Inflammation plays a critical role in myocardial infarction (MI), and ginsenoside Rg3 (Rg3), known as an activator of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), has demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects through the NF-κB pathway. In this study using an MI rat model, Rg3 was investigated for its potential to mitigate inflammation in MI by modulating the SIRT1/NF-κB pathway. Rg3 treatment not only improved ECG values and reduced cardiac enzymes like LDH, CK-MB, and cTnI levels in MI rats but also lowered pro-inflammatory markers (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6) while increasing the anti-inflammatory marker IL-10. Rg3 also attenuated myocardial damage and apoptosis, altered cytokine gene expression, and influenced key proteins (SIRT1, RelB, p-p65/p65) associated with the SIRT1/NF-κB pathway in the heart tissues of MI rats. This suggests that Rg3 mitigates inflammation in MI via the SIRT1/NF-κB pathway.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7646702/.
Jiang Y, Li M, Lu Z, Wang Y, Yu X, Sui D, Fu L. Ginsenoside Rg3 induces ginsenoside Rb1-comparable cardioprotective effects independent of reducing blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Exp Ther Med. 2017 Nov;14(5):4977-4985. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5198. Epub 2017 Sep 22. PMID: 29201202; PMCID: PMC5704305.
Ginsenoside Rg3 induces ginsenoside Rb1-comparable cardioprotective effects independent of reducing blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats
In this study, the rare ginsenoside Rg3, known for its anti-tumor properties in China, was compared with ginsenoside Rb1, a compound with cardiovascular protective effects, in a 6-week experiment involving spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). Both Rg3 and Rb1 were found to alleviate cardiac dysfunction and ventricular remodeling in the SHR rats, as observed through echocardiography and histopathological examinations. Interestingly, despite not lowering blood pressure, these compounds demonstrated independent cardioprotective effects. Additionally, Rb1 and Rg3 were shown to attenuate renin angiotensin system (RAS) activity in the myocardium, as evidenced by immunohistochemistry, while serum RAS activity remained unchanged. Moreover, levels of various pro-inflammatory markers in the myocardium were reduced by Rb1 and Rg3 treatment, potentially mediated by the modulation of RAS activity, shedding light on the mechanisms underlying their cardioprotective effects.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5704305/.
Sun, M., Huang, C., Wang, C., Zheng, J., Zhang, P., Xu, Y., Chen, H., & Shen, W. (2013). Ginsenoside Rg3 improves cardiac mitochondrial population quality: mimetic exercise training. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 441(1), 169–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.10.039.
Ginsenoside Rg3 improves cardiac mitochondrial population quality: mimetic exercise training
Recent findings suggest that exercise training may influence mitochondrial quality control by improving mitochondrial dynamics. Ginsenoside Rg3, a component of Panax ginseng known for its tonic and restorative properties, has had its underlying molecular mechanism for beneficial effects unclear until now. In this study, we compared the impact of Rg3 supplementation and aerobic exercise on mitochondrial adaptation in the cardiac muscle of Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats. Both aerobic exercise and Rg3 boosted levels of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor coactivator 1 alpha (PGC-1α) and nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) proteins in the cardiac muscle. PGC-1α activation led to increased mitochondrial DNA copy number and complex protein levels, while Nrf2 activation enhanced detoxifying enzyme levels. Additionally, aerobic exercise promoted mitochondrial autophagy pathway activity, akin to the effects of Rg3. These findings reveal that Rg3 mimics the cardiac benefits of exercise by regulating mitochondrial dynamics and enhancing mitochondrial quantity and quality.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0006291X13017117?via%3Dihub.
Jeong, D., Irfan, M., Kim, S. D., Kim, S., Oh, J. H., Park, C. K., Kim, H. K., & Rhee, M. H. (2017). Ginsenoside Rg3-enriched red ginseng extract inhibits platelet activation and in vivo thrombus formation. Journal of ginseng research, 41(4), 548–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2016.11.
Ginsenoside Rg3-enriched red ginseng extract inhibits platelet activation and in vivo thrombus formation
Korean Red Ginseng has a long history of use for various health benefits, and ginsenosides, its active compounds, have shown anticancer, antiaging, and anti-inflammatory properties. Ginsenoside Rg3, derived from red ginseng, has been found to exhibit antiplatelet activity alongside its other health benefits. Platelets are important for blood clotting but also contribute to cardiovascular diseases. In this study, a ginsenoside Rg3-enriched red ginseng extract (Rg3-RGE) was prepared and tested. The results showed that Rg3-RGE effectively reduced platelet activation in vitro, inhibiting aggregation, calcium mobilization, and ATP release. It also impacted signaling pathways and reduced mortality in a mouse model of acute pulmonary thromboembolism. These findings suggest that Rg3-RGE could potentially serve as a therapeutic agent against platelet-related cardiovascular disorders.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5628340/.
Zhang, J., Luo, D., Li, F., Li, Z., Gao, X., Qiao, J., Wu, L., & Li, M. (2021). Ginsenoside Rg3 Alleviates Antithyroid Cancer Drug Vandetanib-Induced QT Interval Prolongation. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity, 2021, 3520034. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/3520034.
Ginsenoside Rg3 Alleviates Antithyroid Cancer Drug Vandetanib-Induced QT Interval Prolongation
The inhibition of the hERG potassium channel is responsible for acquired long QT syndromes, a dangerous cardiac condition. Vandetanib, a multikinase inhibitor used to treat advanced medullary thyroid cancer, can prolong the QT interval, limiting its clinical use. Ginsenoside Rg3 has been found to impact hERG K(+) channel activity. This study aimed to investigate whether Rg3 could reverse vandetanib-induced QT interval prolongation. Results showed that vandetanib prolonged the QT interval, but Rg3 alleviated this effect in Langendorff-perfused hearts, reduced action potential duration in cardiomyocytes, and mitigated hERG current inhibition. These findings suggest that ginsenoside Rg3 could be a promising cardioprotective agent against vandetanib-induced cardiac arrhythmia by targeting the hERG channel.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8516564/.
Li, L., Ni, J., Li, M., Chen, J., Han, L., Zhu, Y., Kong, D., Mao, J., Wang, Y., Zhang, B., Zhu, M., Gao, X., & Fan, G. (2017). Ginsenoside Rg3 micelles mitigate doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and enhance its anticancer efficacy. Drug delivery, 24(1), 1617–1630. https://doi.org/10.1080/10717544.2017.1391893.
Ginsenoside Rg3 micelles mitigate doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and enhance its anticancer efficacy
Doxorubicin is a potent chemotherapy agent but comes with the risk of causing cardiotoxicity due to increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Ginsenoside Rg3, known for its antioxidant and cardioprotective properties, has limited solubility and bioavailability. In this study, Rg3 was encapsulated using Pluronic F127 to enhance its solubility and bioavailability. Co-administering Rg3 in Pluronic F127 micelles with doxorubicin not only reduced cardiotoxicity by improving mitochondrial and metabolic function, calcium handling, and reducing ROS production but also enhanced doxorubicin’s anticancer efficacy. This approach offers a promising strategy to develop a supportive treatment that reduces chemotherapy toxicity while improving its effectiveness.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8241051/.
Liu, Z., Bian, X., Gao, W., Su, J., Ma, C., Xiao, X., Yu, T., Zhang, H., Liu, X., & Fan, G. (2021). Rg3 promotes the SUMOylation of SERCA2a and corrects cardiac dysfunction in heart failure. Pharmacological research, 172, 105843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105843.
Rg3 promotes the SUMOylation of SERCA2a and corrects cardiac dysfunction in heart failure
SUMOylation of the SERCA2a protein has a crucial role in the disrupted calcium cycle seen in heart failure. Ginsenoside Rg3, a primary active component of Panax ginseng, has diverse cardiovascular effects but its impact on abnormal calcium regulation in heart failure hasn’t been explored. This study revealed a new role for Rg3 in improving calcium homeostasis and cardiac function in mice with heart failure. Rg3 increased SUMOylation of SERCA2a, enhancing its activity. Rg3 also reduced calcium overload in heart cells, but this effect was dependent on the presence of SUMO1. Furthermore, blocking SUMOylation sites on SERCA2a hindered Rg3’s positive impact, resulting in endoplasmic reticulum stress and ROS generation. These findings suggest that regulating SERCA2a SUMOylation with Rg3 could offer a novel therapeutic approach for heart failure treatment.
You can read the full article at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1043661821004278?via%3Dihub.
Available at https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/1934578X19900712.
Lee H, Kong G, Tran Q, Kim C, Park J, Park J. Relationship BetweenGinsenoside Rg3 and Metabolic Syndrome. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:130. Published 2020 Feb 25. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.00130.
Relationship BetweenGinsenoside Rg3 and Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a pressing public health concern often linked to a more affluent lifestyle, but its exact causes and effective treatments remain elusive. Researchers are now exploring the potential of natural compounds to mitigate metabolic syndrome. Ginsenoside, extracted from ginseng and its roots, is one such natural product gaining attention for its various applications in dietary supplements and cosmetics. Numerous studies have investigated the effects of ginsenoside, particularly Rg3, on conditions like obesity, diabetes, and hypertension associated with metabolic syndrome. This review discusses the potential of ginsenoside Rg3 from ginseng as a treatment for metabolic syndrome.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7052819/.
Available at https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0171936.
Available from https://academic.oup.com/intimm/article/24/7/465/821288.
Stereospecificity of ginsenoside Rg3 in promotion of the immune response to ovalbumin in mice
In our previous research, we found that ginsenoside Rg3 has immune-boosting properties. In this study, we compared two epimers, 20(R)-Rg3 and 20(S)-Rg3, for their ability to enhance the immune response against ovalbumin (OVA) in BALB/c mice. Both 20(R)-Rg3 and 20(S)-Rg3 showed adjuvant effects on OVA-induced immune responses, but 20(R)-Rg3 had a more pronounced impact. It significantly increased serum-specific IgG, IFN-γ, and IL-5 levels, and enhanced splenocyte proliferative responses and the expression of immune-related genes when compared to 20(S)-Rg3. This suggests that ginsenoside Rg3 has stereospecific immune-stimulating properties, with 20(R)-Rg3 displaying stronger adjuvant activity than 20(S)-Rg3
You can read the abstract of the article at https://academic.oup.com/intimm/article/24/7/465/821288.
Wei, X., Chen, J., Su, F., Su, X., Hu, T., & Hu, S. (2012). Stereospecificity of ginsenoside Rg3 in promotion of the immune response to ovalbumin in mice. International immunology, 24(7), 465–471. https://doi.org/10.1093/intimm/dxs043.
Stereospecificity of ginsenoside Rg3 in promotion of the immune response to ovalbumin in mice
In our prior investigation, we found that ginsenoside Rg3 enhances the immune response. This study compared two forms of Rg3, 20(R)-Rg3 and 20(S)-Rg3, for their immune-boosting effects against ovalbumin (OVA) in BALB/c mice. Both 20(R)-Rg3 and 20(S)-Rg3 exhibited adjuvant effects on OVA-induced immune responses, but 20(R)-Rg3 displayed a significantly stronger impact. It led to higher levels of serum-specific IgG, IFN-γ, and IL-5, and increased splenocyte proliferation and gene expression related to immunity compared to 20(S)-Rg3. This suggests that ginsenoside Rg3 has stereospecific immune-stimulating properties, with 20(R)-Rg3 showing greater adjuvant activity than 20(S)-Rg3.
You can read the full article at https://academic.oup.com/intimm/article/24/7/465/821288?login=false.
Park HY, Lee SH, Lee KS, Yoon HK, Yoo YC, Lee J, Choi JE, Kim PH, Park SR. Ginsenoside Rg1 and 20(S)-Rg3 Induce IgA Production by Mouse B Cells. Immune Netw. 2015 Dec;15(6):331-6. doi: 10.4110/in.2015.15.6.331. Epub 2015 Dec 24. PMID: 26770188; PMCID: PMC4700410.
Ginsenoside Rg1 and 20(S)-Rg3 Induce IgA Production by Mouse B Cells
Ginsenosides, the primary compounds found in ginseng known for their various health effects, have been studied for their impact on blood pressure, metabolism, and immune function. While ginseng and some ginsenosides have been recognized for their immunoregulatory effects on innate and T cell-mediated immune responses, their influence on the humoral immune response has remained less explored. This study investigated the direct effects of red ginseng extract (RGE) and specific ginsenosides on mouse B cell behavior, including proliferation, antibody production, and germline transcript (GLT) expression. While RGE had a modest impact on B cell proliferation but enhanced IgA production by LPS-stimulated B cells, ginsenosides Rg1 and 20(S)-Rg3 were found to selectively induce IgA production and the expression of GLTα transcripts in these B cells. This suggests that ginsenosides Rg1 and 20(S)-Rg3 may play a role in promoting the differentiation of B cells into IgA-producing cells by selectively inducing GLTα expression.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4700410/.
Park, Y. J., Cho, M., Choi, G., Na, H., & Chung, Y. (2020). A Critical Regulation of Th17 Cell Responses and Autoimmune Neuro-Inflammation by Ginsenoside Rg3. Biomolecules, 10(1), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010122.
A Critical Regulation of Th17 Cell Responses and Autoimmune Neuro-Inflammation by Ginsenoside Rg3
Among various helper T-cell subsets, Th17 cells are implicated in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases, making them a target for potential treatment. Ginsenoside Rg3, a potent component in Korean Red Ginseng (KRG), is known for its anti-inflammatory properties. However, its role in Th17 cells and Th17-mediated autoimmunity remained unclear. This study revealed that Rg3 effectively hindered the differentiation of Th17 cells from naive precursors in a dendritic cell-T cell co-culture system. While Rg3 had minimal impact on the secretion of certain cytokines from dendritic cells, it notably suppressed the expression of IL-17A and RORγt in T cells. Furthermore, Rg3 mitigated the onset and severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a disease associated with Th17-mediated inflammation. These findings suggest that Rg3 could be a potential candidate for addressing autoimmune diseases driven by Th17 cells.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7023269/.
Wu, R., Ru, Q., Chen, L., Ma, B., & Li, C. (2014). Stereospecificity of ginsenoside Rg3 in the promotion of cellular immunity in hepatoma H22-bearing mice. Journal of food science, 79(7), H1430–H1435. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.12518.
Stereospecificity of ginsenoside Rg3 in the promotion of cellular immunity in hepatoma H22-bearing mice
Previous research has established that ginsenoside Rg3 (Rg3) possesses various beneficial effects, including antitumor, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory properties. However, Rg3 comes in two stereoisomeric pairs, 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 [20(S)-Rg3] and 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg3 [20(R)-Rg3], with distinct pharmacological actions due to their differing chemical structures. This study compared the impact of these two epimers on the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma H22 tumors and the immune function of H22-bearing mice. The results showed that both 20(S)-Rg3 and 20(R)-Rg3 significantly inhibited tumor growth and enhanced cellular immunity in H22-bearing mice, with 20(R)-Rg3 exhibiting more pronounced effects. These findings suggest that Rg3 can inhibit tumor growth and boost cellular immunity in a stereospecific manner, with 20(R)-Rg3 showing greater potency, potentially holding clinical promise for cancer treatment and immune-related diseases.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://ift.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/1750-3841.12518.
Available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7052819/.
Relationship Between Ginsenoside Rg3 and Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome, linked to affluent lifestyles, poses a significant public health challenge with unclear pathogenesis and no effective treatment. Researchers are exploring natural compounds for metabolic syndrome management due to their proven versatility. Ginsenoside, derived from ginseng and ginseng root, exemplifies this trend and finds application in dietary supplements and cosmetics. Studies have revealed the positive effects of ginsenoside on metabolic conditions like obesity, diabetes, and hypertension. In this review, we delve into the potential of ginsenoside Rg3, a component of ginseng, as a therapeutic option for addressing metabolic syndrome.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7052819/.
Lee, J., Yoon, S., Lee, S., Lee, M., Jung, H., Kim, T., Yoon, S., Choi, I., Kim, I., Chung, S., Lee, H., Min, J., & Park, Y. (2017). Ginsenoside Rg3 ameliorated HFD-induced hepatic steatosis through downregulation of STAT5-PPARγ, Journal of Endocrinology, 235(3), 223-235. Retrieved Jan 22, 2021, from https://joe.bioscientifica.com/view/journals/joe/235/3/JOE-17-0233.xml.
Ginsenoside Rg3 ameliorated HFD-induced hepatic steatosis through downregulation of STAT5-PPARγ
The healthy expansion of adipose tissue plays a vital role in maintaining metabolic balance by storing excess energy. The STAT5-PPAR gamma pathway is known to regulate various aspects of adipocyte function. Ginsenoside Rg3, a component of ginseng, has shown pharmacological promise. In this study, the therapeutic effects of ginsenoside Rg3 were evaluated in pathological conditions both in vitro and in vivo. Rg3 demonstrated the ability to reduce adipose tissue size, hepatic steatosis, and triglyceride levels in mice on a high-fat diet. It also reduced lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 cells. Rg3 was found to regulate PPAR gamma through STAT5, impacting lipid metabolism-related genes. This study suggests that Rg3 has the potential to ameliorate obesity-related issues and improve adipose tissue function through the STAT5-PPAR gamma pathway, presenting a novel approach for addressing insulin resistance and lipotoxicity induced by obesity.
You can read the full article at https://joe.bioscientifica.com/view/journals/joe/235/3/JOE-17-0233.xml.
Available from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/348453543_Ginsenoside_rg3_reduces_body_weight_by_regulating_fat_content_and_browning_in_obese_mice.
Ginsenoside rg3 reduces body weight by regulating fat content and browning in obese mice
This study aimed to assess the impact of ginsenoside rg3 on the body weight of obese C57BL/6J mice and explore the underlying mechanisms, particularly those related to white fat browning. After 8 weeks of intervention with ginsenoside rg3, there was a significant reduction in body weight, body fat mass, food intake, and blood lipid levels compared to the obese model group. Histological analysis indicated an improvement in white adipocyte hypertrophy. Furthermore, ginsenoside rg3 increased the expression of genes and proteins associated with white fat browning, including PPARγ, PGC-1α, PRDM16, and UCP-1. These findings suggest that ginsenoside rg3’s weight-reducing effect may be linked to the promotion of white fat browning.
You can read the full article at https://www.researchgate.net/publication/348453543_Ginsenoside_rg3_reduces_body_weight_by_regulating_fat_content_and_browning_in_obese_mice.
Available at https://www.mdpi.com/2218-273X/10/3/444/htm.
Kang S, Park SJ, Lee AY, Huang J, Chung HY, Im DS. Ginsenoside Rg3 promotes inflammation resolution through M2 macrophage polarization. J Ginseng Res. 2018 Jan;42(1):68-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2016.12.012. Epub 2017 Jan 1. PMID: 29348724; PMCID: PMC5766702.
Ginsenoside Rg3 promotes inflammation resolution through M2 macrophage polarization
Ginsenosides are known for their various health benefits, including anti-inflammatory effects. This study investigated whether ginsenosides can modulate macrophage phenotypes to reduce inflammation. Among the studied ginsenosides, Ginsenoside Rg3 was identified as a proresolving compound that promotes the polarization of M2-type macrophages, known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Rg3 induced M2 marker gene expression, reduced M1 marker genes, and decreased NO levels in macrophages in vitro. In a zymosan-induced peritonitis mouse model, Rg3 accelerated the resolution of inflammation when administered at the peak of the inflammatory response. These findings highlight the potential of ginsenoside Rg3 to induce M2 macrophage polarization and expedite the resolution of inflammation, opening new possibilities in ginseng pharmacology.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5766702/.
Cheng L, Sun X, Hu C, Jin R, Sun B, Shi Y, Zhang L, Cui W, Zhang Y. In vivo inhibition of hypertrophic scars by implantable ginsenoside-Rg3-loaded electrospun fibrous membranes. ActaBiomater. 2013 Dec;9(12):9461-73. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2013.07.040. Epub 2013 Aug 9. PMID: 23938200.
In vivo inhibition of hypertrophic scars by implantable ginsenoside-Rg3-loaded electrospun fibrous membranes
Hypertrophic scarring (HS) poses significant clinical challenges, and effective early interventions are limited. This study introduces 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg3 (GS-Rg3), a Chinese drug that inhibits early HS formation and subsequent hyperplasia by inducing fibroblast apoptosis, reducing inflammation, and down-regulating VEGF expression in vivo. GS-Rg3-loaded poly(l-lactide) (PLA) fibrous membranes were successfully created using co-electrospinning to control drug release and enhance utilization. These membranes released GS-Rg3 over 3 months in vivo, with varying drug concentrations achievable by adjusting the fiber’s drug content. Histological analysis demonstrated that GS-Rg3/PLA significantly inhibited HS formation, improving dermis and epidermis thickness and reducing fibroblast proliferation. Immunohistochemistry and Masson’s trichrome staining further supported HS inhibition, with decreased collagen fibers and microvessels, while VEGF levels were notably lower in the GS-Rg3/PLA group. This study highlights GS-Rg3’s potential for early and long-term HS treatment, particularly when delivered using GS-Rg3/PLA electrospun membranes.
You can read the full article at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1742706113003887?via%3Dihub.
Tang M, Wang W, Cheng L, Jin R, Zhang L, Bian W, Zhang Y. The inhibitory effects of 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg3 on the proliferation, angiogenesis, and collagen synthesis of hypertrophic scar derived fibroblasts in vitro. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018 Mar;21(3):309-317. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2018.19451.5153. PMID: 29511498; PMCID: PMC5817175.
The inhibitory effects of 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg3 on the proliferation, angiogenesis, and collagen synthesis of hypertrophic scar derived fibroblasts in vitro
The study aimed to further investigate the potential therapeutic effects of Rg3, a traditional Chinese medicine, on hypertrophic scar (HS). HS specimens were obtained from patients, and primary cultured scar tissue cells were used in experiments. Hypertrophic scar fibroblasts (HSFs) treated with different Rg3 concentrations were assessed for various parameters. Results showed that Rg3 inhibited HSF proliferation, vascularization, and extracellular matrix deposition through the TGF-β/SMAD and Erk signaling pathways. These findings support Rg3 as a promising treatment option for HS based on in vitro evidence.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5817175/.
Cheng, L., , Sun, X., , Li, B., , Hu, C., , Yang, H., , Zhang, Y., , & Cui, W., (2013). Electrospun Ginsenoside Rg3/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) fibers coated with hyaluronic acid for repairing and inhibiting hypertrophic scars. Journal of materials chemistry. B, 1(35), 4428–4437. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tb20441c.
Many studies have focused on treating hypertrophic scars, often addressing them after formation, without considering early tissue damage repair and late-stage scar inhibition. In this study, a novel approach was employed by creating Ginsenoside Rg3 (Rg3) loaded poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) electrospun fibrous scaffolds with a subsequent hyaluronic acid (HA) coating. These hydrophilic Rg3/PLGA/HA scaffolds combined treatments to promote early wound healing and inhibit late-stage scar hyperplasia. The scaffolds exhibited improved hydrophilicity, proper porosity, stable fibrous structure, durability, and controlled drug release. In vivo results showed accelerated wound healing and significant scar inhibition, offering a promising combined therapeutic approach for hypertrophic scars.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2013/TB/c3tb20441c.
Cheng L, Sun X, Hu C, Jin R, Sun B, Shi Y, Cui W, Zhang Y. In vivo early intervention and the therapeutic effects of 20(s)-ginsenoside rg3 on hypertrophic scar formation. PLoS One. 2014 Dec 12;9(12):e113640. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113640. PMID: 25502572; PMCID: PMC4264739.
In vivo early intervention and the therapeutic effects of 20(s)-ginsenoside rg3 on hypertrophic scar formation
Current treatments for hypertrophic scars often target them after formation, missing the opportunity for early intervention during the inflammatory phase of wound healing. This study aimed to find an effective and safe drug for such early intervention. In vitro experiments showed that 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 (Rg3) could inhibit hypertrophic scar fibroblast proliferation and induce apoptosis. In vivo studies demonstrated that Rg3 effectively reduced inflammation without delaying wound healing, making it suitable for early intervention. Topical injection of 4 mg/mL Rg3 reduced hypertrophic scar formation by 34%. Histological and molecular analyses revealed that Rg3 inhibited fibroblast proliferation, reduced collagen fiber accumulation, and down-regulated VEGF expression in hypertrophic scar tissue, highlighting its potential as an early intervention and combined therapeutic drug.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4264739/.
Sun, X., Cheng, L., Zhu, W., Hu, C., Jin, R., Sun, B., Shi, Y., Zhang, Y., & Cui, W. (2014). Use of ginsenoside Rg3-loaded electrospun PLGA fibrous membranes as wound cover induces healing and inhibits hypertrophic scar formation of the skin. Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 115, 61–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.11.030.
Use of ginsenoside Rg3-loaded electrospun PLGA fibrous membranes as wound cover induces healing and inhibits hypertrophic scar formation of the skin
Effective prevention of hypertrophic scar formation on the skin involves a multifaceted approach, including early-stage skin regeneration promotion and later-stage hypertrophic inhibition. This study developed hydrophilic poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) electrospun fibrous membranes loaded with Ginsenoside-Rg3 (Rg3) and coated with chitosan (CS) using pressure-driven permeation (PDP) technology. These membranes combined the benefits of nanofibrous structures and drug carriers. The PDP method enhanced membrane hydrophilicity while maintaining Rg3 release kinetics. Animal wound experiments demonstrated earlier re-epithelialization and healing, and reduced scar formation with Rg3 treatment. Molecular analyses showed decreased VEGF, mRNA, and Collagen Type I expression in scars treated with Rg3. Overall, PLGA-Rg3/CS electrospun fibrous membranes offer a dual-functional approach for preventing hypertrophic skin scars by facilitating early tissue repair and inhibiting later-stage scar formation.
You can read the full article athttps://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0927776513007285?via%3Dihub.
Tang M, Bian W, Cheng L, Zhang L, Jin R, Wang W, Zhang Y. Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits keloid fibroblast proliferation, angiogenesis and collagen synthesis in vitro via the TGF‑β/Smad and ERK signaling pathways. Int J Mol Med. 2018 Mar;41(3):1487-1499. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3362. Epub 2018 Jan 4. PMID: 29328420; PMCID: PMC5819908.
Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits keloid fibroblast proliferation, angiogenesis and collagen synthesis in vitro via the TGF‑β/Smad and ERK signaling pathways
Numerous therapeutic options are available for keloid treatment, but they often come with side-effects and a high risk of recurrence. Seeking improved treatments, this study explored the potential of Ginsenoside Rg3 (Rg3) for targeting keloids. The research focused on human keloid fibroblasts (KFs) in vitro, investigating molecular and cellular mechanisms. Rg3 was found to inhibit transforming growth factor-β/Smad and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways in KFs, reducing their proliferation, migration, invasion, angiogenesis, and collagen synthesis. An ex vivo assay showed Rg3’s ability to inhibit angiogenesis and reduce collagen accumulation in keloids. These findings suggest that Rg3 may offer a promising treatment option for keloids.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5819908/.
Available at https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/25/21/4905/pdf.
Park D, Bae DK, Jeon JH, Lee J, Oh N, Yang G, Yang YH, Kim TK, Song J, Lee SH, Song BS, Jeon TH, Kang SJ, Joo SS, Kim SU, Kim YB. Immunopotentiation and antitumor effects of a ginsenosideRg₃-fortified red ginseng preparation in mice bearing H460 lung cancer cells. Environ ToxicolPharmacol. 2011 May;31(3):397-405. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2011.01.008. Epub 2011 Mar 8. PMID: 21787710.
Immunopotentiation and antitumor effects of a ginsenosideRg₃-fortified red ginseng preparation in mice bearing H460 lung cancer cells
The antitumor effects of a ginsenoside Rg(3)-fortified red ginseng preparation (Rg(3)-RGP) were investigated in human non-small cell lung carcinoma (H460) cells in vitro and in a nude mouse xenograft model. Additionally, the immunomodulatory effects of Rg(3)-RGP were assessed, showing that it enhanced the phagocytic activity of blood macrophages and splenocyte proliferation without affecting nitric oxide production. In tumor-bearing mice, oral treatment with Rg(3)-RGP significantly suppressed tumor growth, comparable to the effects of doxorubicin, but without causing adverse effects observed with doxorubicin, such as decreased body and testes weights and spermatogenic cell depletion. These findings suggest that Rg(3)-RGP exhibits antitumor activity through indirect immunomodulation and is well-tolerated.
You can read the full article at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1382668911000123?via%3Dihub.
Liu H, Zhao J, Fu R, Zhu C, Fan D. The ginsenoside Rk3 exerts anti-esophageal cancer activity in vitro and in vivo by mediating apoptosis and autophagy through regulation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. PLoS One. 2019 May 15;14(5):e0216759. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216759. PMID: 31091245; PMCID: PMC6519821.
The ginsenoside Rk3 exerts anti-esophageal cancer activity in vitro and in vivo by mediating apoptosis and autophagy through regulation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway
The rare ginsenoside Rk3, derived from ginseng and Panax notoginseng, exhibits anti-lung cancer activity, but its effects on human esophageal cancer were previously unexplored. This study investigated Rk3’s anticancer effects on Eca109 and KYSE150 cell lines and found that it significantly inhibited cell proliferation and colony formation. In a KYSE150 xenograft model, Rk3 effectively suppressed tumor growth with minimal organ toxicity. Rk3 induced G1 phase arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy, and the combination of autophagy inhibition partially abrogated apoptosis. Further analysis revealed that the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway played a role in Rk3-induced apoptosis and autophagy. These findings suggest Rk3 as a promising antitumor agent for esophageal cancer, shedding light on its potential mechanisms of action.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6519821/.
Hong, S., Cai, W., Huang, Z., Wang, Y., Mi, X., Huang, Y., Lin, Z., & Chen, X. (2020). Ginsenoside Rg3 enhances the anticancer effect of 5‑FU in colon cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncology reports, 44(4), 1333–1342. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2020.7728.
Ginsenoside Rg3 enhances the anticancer effect of 5‑FU in colon cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT pathway
Chemotherapy, commonly used for advanced colon cancer treatment, often has limited effectiveness due to its toxicity. Ginsenoside Rg3 (Rg3), derived from ginseng, is known for its anticancer effects across various malignancies. This study aimed to investigate whether Rg3 could enhance the anticancer effects of 5‑fluorouracil (5‑FU) in human colon cancer. The results showed that the combined treatment of Rg3 and 5‑FU significantly inhibited colon cancer cell proliferation, colony formation, invasion, and migration in vitro. It also enhanced apoptosis through the Apaf1/caspase 9/caspase 3 pathway and arrested the cell cycle at G0/G1 by promoting the expression of Cyclin D1, CDK2, and CDK4. Additionally, the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway was suppressed. In vivo, Rg3 synergized with 5‑FU to inhibit colon cancer growth in xenografts. These findings suggest that Rg3 enhances the anticancer effects of 5‑FU in colon cancer cells through the PI3K/AKT pathway.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7448421/.
Kim, D. G., Jung, K. H., Lee, D. G., Yoon, J. H., Choi, K. S., Kwon, S. W., Shen, H. M., Morgan, M. J., Hong, S. S., & Kim, Y. S. (2014). 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rg3 is a novel inhibitor of autophagy and sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma to doxorubicin. Oncotarget, 5(12), 4438–4451. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.2034.
20(S)-Ginsenoside Rg3 is a novel inhibitor of autophagy and sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma to doxorubicin
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths, with limited effective treatments. 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3, a steroidal saponin from Panax ginseng, is known to potentially enhance the effects of therapeutic drugs, though the mechanism is unclear. This study investigated Rg3’s ability to inhibit autophagy and sensitize HCC cells to doxorubicin in vitro. Rg3 was found to inhibit late-stage autophagy, possibly through gene expression changes. Doxorubicin-induced autophagy serves as a protective mechanism in HCC cells, making the combination of Rg3 and doxorubicin effective in killing cancer cells while sparing normal liver cells. In vivo, Rg3 was well-tolerated and synergized with doxorubicin to inhibit tumor growth in HCC xenografts, suggesting its potential as an autophagy inhibitor for clinical use in combination therapy for HCC treatment
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4147336/.
Yuan, Z., Jiang, H., Zhu, X., Liu, X., & Li, J. (2017). Ginsenoside Rg3 promotes cytotoxicity of Paclitaxel through inhibiting NF-κB signaling and regulating Bax/Bcl-2 expression on triple-negative breast cancer. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie, 89, 227–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.02.038.
Ginsenoside Rg3 promotes cytotoxicity of Paclitaxel through inhibiting NF-κB signaling and regulating Bax/Bcl-2 expression on triple-negative breast cancer
Taxane-based chemotherapy is a leading treatment for aggressive triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Ginsenoside Rg3, derived from Panax ginseng, possesses anti-cancer properties. This study aimed to assess Rg3’s chemosensitizing effects on TNBC cells and xenograft models, along with the underlying mechanism. Rg3 was found to enhance the cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by Paclitaxel in TNBC cells and xenografts. This effect was associated with the inhibition of NF-κB activation, decreased levels of NF-κB p65 and Bcl-2 proteins, increased levels of Bax and Caspase-3 proteins, and an elevated Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. These findings suggest that Rg3 can enhance the effectiveness of Paclitaxel in TNBC treatment by inhibiting NF-κB signaling and modulating Bax/Bcl-2 expression, making it a promising chemosensitizing agent for TNBC therapy.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0753332217304183?via%3Dihub.
Pan, L., Zhang, T., Sun, H., & Liu, G. (2019). Ginsenoside Rg3 (Shenyi Capsule) Combined with Chemotherapy for Digestive System Cancer in China: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, 2019, 2417418. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2417418.
Ginsenoside Rg3 (Shenyi Capsule) Combined with Chemotherapy for Digestive System Cancer in China: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review
In China, ginsenoside Rg3 is frequently used in conjunction with chemotherapy for digestive system cancers. This meta-analysis and systematic review aimed to provide a comprehensive evaluation of the efficacy and safety of combining ginsenoside Rg3 with chemotherapy in these cancer types. Eighteen randomized controlled trials involving 1531 patients were analyzed. The findings indicate that this combination therapy significantly enhances the objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), 1-year survival rate (SR), Karnofsky Performance Scale (KPS), while reducing gastrointestinal dysfunction and the decline in leucocyte count. Overall, ginsenoside Rg3 combined with chemotherapy demonstrates improved clinical efficacy and reduced treatment-related side effects in digestive system cancer.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6942834/.
Xu, T. M., Xin, Y., Cui, M. H., Jiang, X., & Gu, L. P. (2007). Inhibitory effect of ginsenoside Rg3 combined with cyclophosphamide on growth and angiogenesis of ovarian cancer. Chinese medical journal, 120(7), 584–588.
Inhibitory effect of ginsenoside Rg3 combined with cyclophosphamide on growth and angiogenesis of ovarian cancer
In this study, the potential synergistic effects of ginsenoside Rg3 and cyclophosphamide (CTX) on human ovarian cancer growth and angiogenesis were investigated. Female athymic mice were divided into four groups, receiving ginsenoside Rg3, CTX, a combination of both, or serving as controls after ovarian cancer cell transplantation. The combined treatment group demonstrated improved life quality, longer survival, reduced tumor size, lower proliferating cell nuclear antigen labelling index (PCNALI), decreased expression of vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF), and lower microvessel density (MVD) in tumor tissues compared to controls. Both ginsenoside Rg3 and the combination therapy with CTX showed significant inhibitory effects on ovarian cancer growth and angiogenesis, suggesting their potential in improving the quality of life and survival in mice with tumors.
You can read the full article at https://journals.lww.com/cmj/fulltext/2007/04010/inhibitory_effect_of_ginsenoside_rg3_combined_with.11.aspx.
Li, J., Liu, T., Zhao, L., Chen, W., Hou, H., Ye, Z., & Li, X. (2015). Ginsenoside 20(S)‑Rg3 inhibits the Warburg effect through STAT3 pathways in ovarian cancer cells. International journal of oncology, 46(2), 775–781. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2014.2767.
Ginsenoside 20(S)‑Rg3 inhibits the Warburg effect through STAT3 pathways in ovarian cancer cells
In this study, researchers investigated the impact of ginsenoside 20(S)-Rg3, a bioactive compound from Panax ginseng, on the Warburg effect, a metabolic process where cancer cells preferentially use glycolysis for energy. They found that 20(S)-Rg3 inhibits glycolysis in ovarian cancer cells by regulating key enzymes, hexokinase 2 (HK2) and pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2). Additionally, 20(S)-Rg3 downregulates p-STAT3 (Tyr705), affecting HK2 expression. Overexpression of STAT3 counteracted the suppression of the Warburg effect induced by 20(S)-Rg3. Furthermore, in a mouse xenograft model, 20(S)-Rg3 treatment reduced HK2 expression. These findings suggest that 20(S)-Rg3 can potentially serve as a therapeutic agent for ovarian cancer by targeting the STAT3/HK2 pathway and inhibiting the Warburg effect in cancer cells.
You can read the full article at https://www.spandidos-publications.com/ijo/46/2/775.
Kim, S. M., Lee, S. Y., Cho, J. S., Son, S. M., Choi, S. S., Yun, Y. P., Yoo, H. S., Yoon, D. Y., Oh, K. W., Han, S. B., & Hong, J. T. (2010). Combination of ginsenoside Rg3 with docetaxel enhances the susceptibility of prostate cancer cells via inhibition of NF-kappaB. European journal of pharmacology, 631(1-3), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.12.018.
Combination of ginsenoside Rg3 with docetaxel enhances the susceptibility of prostate cancer cells via inhibition of NF-kappaB
Ginsenoside Rg3 has garnered interest as a potential cancer preventive and therapeutic agent. In prostate cancer, constitutive activation of nuclear factor-kappa (NF-kappaB) contributes to chemotherapy resistance. This study aimed to determine if Rg3 could inhibit NF-kappaB activation, making prostate cancer cells more susceptible to chemotherapy. The combination of Rg3 (50 microM) with docetaxel (5 nM) was found to be more effective at inhibiting prostate cancer cell growth, inducing apoptosis, and causing G0/G1 arrest, along with significant NF-kappaB activity inhibition, compared to Rg3 or docetaxel alone. This combination also enhanced the expression of NF-kappaB target genes associated with apoptosis and suppressed cell cycle regulatory proteins. A similar effect was observed when Rg3 was combined with cisplatin and doxorubicin. These findings suggest that ginsenoside Rg3 can inhibit NF-kappaB and enhance prostate cancer cell susceptibility to various chemotherapeutics, positioning it as a potential anti-cancer agent.
You can read the full article at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S001429990901139X?via%3Dihub.
Kim, S. M., Lee, S. Y., Yuk, D. Y., Moon, D. C., Choi, S. S., Kim, Y., Han, S. B., Oh, K. W., & Hong, J. T. (2009). Inhibition of NF-kappaB by ginsenoside Rg3 enhances the susceptibility of colon cancer cells to docetaxel. Archives of pharmacal research, 32(5), 755–765. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-1515-4.
Inhibition of NF-kappaB by ginsenoside Rg3 enhances the susceptibility of colon cancer cells to docetaxel
Ginsenoside Rg3, a prominent component from Panax ginseng, has garnered interest for its potential as a cancer preventive or therapeutic agent. This study investigated whether Rg3 can inhibit NF-kappaB activity, a transcription factor persistently activated in colon cancer, leading to resistance against chemotherapy. Colon cancer cells (SW620 and HCT116) were treated with varying concentrations of Rg3 (25, 50, 75, 100 microM) to assess cell susceptibility and NF-kappaB activation. Rg3 dose-dependently inhibited cancer cell growth, induced apoptosis, and reduced NF-kappaB activity. Furthermore, when combined with conventional agents (docetaxel, paclitaxel, cisplatin, and doxorubicin), Rg3 demonstrated synergistic effects in inhibiting cancer cell growth and inducing apoptosis. These effects coincided with a significant reduction in NF-kappaB activity and the enhanced expression of apoptotic genes, while anti-apoptotic and cell proliferation marker genes were significantly suppressed. These findings suggest that ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits NF-kappaB, increasing colon cancer cell susceptibility to chemotherapeutic agents, positioning it as a potential anti-cancer or adjuvant agent.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12272-009-1515-4.
Liu, T. G., Huang, Y., Cui, D. D., Huang, X. B., Mao, S. H., Ji, L. L., Song, H. B., & Yi, C. (2009). Inhibitory effect of ginsenoside Rg3 combined with gemcitabine on angiogenesis and growth of lung cancer in mice. BMC cancer, 9, 250. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-9-250.
Inhibitory effect of ginsenoside Rg3 combined with gemcitabine on angiogenesis and growth of lung cancer in mice
In this study, ginsenoside Rg3, a saponin derived from ginseng known for its anti-angiogenic properties, was combined with low-dose gemcitabine to investigate its impact on angiogenesis and the growth of established Lewis lung carcinoma in mice. Mice treated with the combination therapy exhibited improved quality of life and survival compared to control and gemcitabine-only groups. The combination treatment not only effectively suppressed tumor growth but also increased tumor necrosis. Additionally, it significantly reduced VEGF expression, microvessel density (MVD), and blood flow signals in tumors. These findings suggest that the combination of ginsenoside Rg3 and gemcitabine holds promise as an innovative therapeutic approach for lung cancer, with potential benefits for both tumor inhibition and the well-being of tumor-bearing individuals.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2721848/.
Peng, Z., Wu, W. W., & Yi, P. (2021). The Efficacy of Ginsenoside Rg3 Combined with First-line Chemotherapy in the Treatment of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Frontiers in pharmacology, 11, 630825. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.630825.
The Efficacy of Ginsenoside Rg3 Combined with First-line Chemotherapy in the Treatment of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials
In the context of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), where first-line chemotherapy is the primary treatment option despite its limitations and side effects, the combination of ginsenoside Rg3 with first-line chemotherapy has gained popularity in China to enhance treatment outcomes. A comprehensive meta-analysis was conducted to assess the efficacy and safety of this combined therapy in advanced NSCLC patients. The analysis, which included 22 randomized controlled trials with a total of 2202 patients, revealed that the combination of ginsenoside Rg3 and first-line chemotherapy outperformed chemotherapy alone. It demonstrated improvements in objective response rate, disease control rate, Karnofsky performance status, one-year and two-year survival rates, weight change, and reductions in VEGF levels, while also reducing the incidence of gastrointestinal reactions and bone marrow suppression. These findings suggest that ginsenoside Rg3 can enhance the efficacy of chemotherapy and mitigate its associated toxicity, offering a promising approach to optimizing treatment for advanced NSCLC patients.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8012535/.
Jiang, Z., Yang, Y., Yang, Y., Zhang, Y., Yue, Z., Pan, Z., & Ren, X. (2017). Ginsenoside Rg3 attenuates cisplatin resistance in lung cancer by downregulating PD-L1 and resuming immune. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie, 96, 378–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.09.129.
Ginsenoside Rg3 attenuates cisplatin resistance in lung cancer by downregulating PD-L1 and resuming immune
In the study focusing on non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and chemotherapy resistance, it was found that programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1), a critical immune checkpoint, plays a role in resistance to cisplatin treatment. Ginsenoside Rg3, derived from Panax ginseng, known for its immune-boosting and anti-cancer properties, was investigated for its potential to reduce PD-L1 expression induced by cisplatin resistance and the underlying mechanisms involved. Using human lung cancer cell lines A549 and A549/DDP (cisplatin-resistant), the study revealed that Rg3 could inhibit A549/DDP cell growth, mitigate cisplatin resistance, and reduce PD-L1 expression. Furthermore, Rg3 restored the cytotoxicity of T cells against cancer cells. The study also indicated the involvement of NF-κB p65 and Akt in PD-L1 overexpression, which were suppressed by Rg3. These findings suggest that Rg3 could serve as a novel agent targeting PD-L1 in chemotherapy-resistant NSCLC.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0753332217331384?via%3Dihub.
Tang, Y. C., Zhang, Y., Zhou, J., Zhi, Q., Wu, M. Y., Gong, F. R., Shen, M., Liu, L., Tao, M., Shen, B., Gu, D. M., Yu, J., Xu, M. D., Gao, Y., & Li, W. (2018). Ginsenoside Rg3 targets cancer stem cells and tumor angiogenesis to inhibit colorectal cancer progression in vivo. International journal of oncology, 52(1), 127–138. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2017.4183.
Ginsenoside Rg3 targets cancer stem cells and tumor angiogenesis to inhibit colorectal cancer progression in vivo
Anti-angiogenic therapy has demonstrated success in treating colorectal cancer (CRC). Ginsenoside Rg3, derived from Chinese ginseng, possesses anti-vascularization properties, inhibits tumor growth and metastasis, and sensitizes cancer cells to chemotherapy. This study investigated Rg3’s potential as a CRC treatment. In vitro MTT assays and in vivo orthotopic xenograft models revealed that Rg3 inhibited CRC cell growth and stemness. It also impaired cell migration and downregulated angiogenesis-related genes, reducing vascularization in CRC xenografts. Rg3 enhanced the cytotoxicity of 5-Fluorouracil and oxaliplatin in vivo. Moreover, Rg3 decreased the expression of B7-H1 and B7-H3, which are associated with reduced overall survival in CRC patients. Thus, Rg3 not only curbed CRC cell growth and stemness but also reshaped the tumor microenvironment, making it a promising therapeutic option for CRC treatment.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5743384/.
He, B. C., Gao, J. L., Luo, X., Luo, J., Shen, J., Wang, L., Zhou, Q., Wang, Y. T., Luu, H. H., Haydon, R. C., Wang, C. Z., Du, W., Yuan, C. S., He, T. C., & Zhang, B. Q. (2011). Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits colorectal tumor growth through the down-regulation of Wnt/ß-catenin signaling. International journal of oncology, 38(2), 437–445. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2010.858.
Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits colorectal tumor growth through the down-regulation of Wnt/ß-catenin signaling
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a prevalent and deadly malignancy often initiated by abnormal activation of the Wnt/ß-catenin signaling pathway. Despite advances in early diagnosis and treatment approaches, managing advanced CRC requires effective adjuvant agents. Ginsenoside Rg3, derived from American and Asian ginseng, was investigated for its anticancer potential and mechanism. Rg3 was found to inhibit cell proliferation and viability in vitro by blocking nuclear translocation of ß-catenin, thus inhibiting ß-catenin/Tcf transcriptional activity. In a xenograft tumor model, Rg3 effectively suppressed the growth of human colon cancer-derived tumors, reducing cell proliferation and diminishing ß-catenin nuclear staining. This suggests Rg3’s anticancer activity may involve blocking ß-catenin nuclear translocation, offering potential as an adjuvant agent for CRC management.
You can read the full article at https://www.spandidos-publications.com/ijo/38/2/437.
Park, E. H., Kim, Y. J., Yamabe, N., Park, S. H., Kim, H. K., Jang, H. J., Kim, J. H., Cheon, G. J., Ham, J., & Kang, K. S. (2014). Stereospecific anticancer effects of ginsenoside Rg3 epimers isolated from heat-processed American ginseng on human gastric cancer cell. Journal of ginseng research, 38(1), 22–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2013.11.007.
Stereospecific anticancer effects of ginsenoside Rg3 epimers isolated from heat-processed American ginseng on human gastric cancer cell
In an effort to enhance the pharmaceutical effectiveness of ginseng, research has explored the impact of heat processing on American ginseng (HAG). This study focused on its anticancer potential in human gastric cancer AGS cells, with a particular emphasis on apoptosis as a crucial mechanism. HAG notably reduced cancer cell proliferation while altering the composition of ginsenosides. Specifically, it generated ginsenoside 20(S)-Rg3 primarily from ginsenoside Rb1, and this compound played a pivotal role in inducing apoptosis in AGS cells. This induction occurred through the activation of caspase-3, caspase-8, and caspase-9, as well as the regulation of Bcl-2 and Bax expression. In conclusion, heat processing increased the anticancer activity of American ginseng in AGS cells, with ginsenoside 20(S)-Rg3 being the active component responsible for promoting apoptotic cell death.
You can read the full article at
Qiu, R., Qian, F., Wang, X., Li, H., & Wang, L. (2019). Targeted delivery of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3-based polypeptide nanoparticles to treat colon cancer. Biomedical microdevices, 21(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-019-0374-0.
Targeted delivery of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3-based polypeptide nanoparticles to treat colon cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC) presents a significant challenge due to its high metastasis rate and limitations associated with traditional chemotherapy. To address these issues and improve treatment efficacy, this study developed poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(L-glutamic acid-co-L-phenylalanine) (mPEG-b-P(Glu-co-Phe)) nanoparticles co-loaded with 20(S)-ginsenoside (Rg3) (Rg3-NPs). These nanoparticles possess pH-sensitive properties, enabling them to target cancer cells, extend circulation time, and release Rg3 rapidly within tumor cells. In a subcutaneous colon cancer mouse model, Rg3-NPs demonstrated significant anti-cancer effects, inhibiting tumor proliferation by reducing proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression and inducing tumor apoptosis through increased caspase-3 expression. This study highlights the promising potential of Rg3-NPs for CRC treatment.
You can read the full article at https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10544-019-0374-0.
Li, Y., Wang, Y., Niu, K., Chen, X., Xia, L., Lu, D., Kong, R., Chen, Z., Duan, Y., & Sun, J. (2016). Clinical benefit from EGFR-TKI plus ginsenoside Rg3 in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR active mutation. Oncotarget, 7(43), 70535–70545. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12059.
Clinical benefit from EGFR-TKI plus ginsenoside Rg3 in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR active mutation
The study indicates that adding ginsenoside Rg3 to standard first-line EGFR-TKI treatment in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and EGFR mutation can significantly extend the median progression-free survival (PFS) and increase the objective response rate (ORR), offering a potential strategy to overcome acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI. The combination therapy did not show a significant improvement in overall survival (OS) or increase in side effects, suggesting it is a safe and more effective option for managing EGFR-mutant advanced NSCLC.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5342572/.
Lu, P., Su, W., Miao, Z. H., Niu, H. R., Liu, J., & Hua, Q. L. (2008). Effect and mechanism of ginsenoside Rg3 on postoperative life span of patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Chinese journal of integrative medicine, 14(1), 33–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-007-9002-6.
Effect and mechanism of ginsenoside Rg3 on postoperative life span of patients with non-small cell lung cancer
This study aimed to investigate the impact and mechanism of ginsenoside Rg3 (Shenyi Capsule) on the postoperative survival of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. In a randomized controlled trial involving 133 NSCLC patients, three groups were formed: Shenyi Capsule group, combined therapy group (Shenyi Capsule plus chemotherapy), and chemotherapy group. Survival rates, immune function, and the relationship between vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression and clinical outcomes were assessed. The results showed no significant differences in survival rates among the three groups. However, the Shenyi Capsule and combined therapy groups exhibited improved immune function, while VEGF expression correlated with survival in the chemotherapy group. In conclusion, Shenyi Capsule, especially when combined with chemotherapy, may enhance the postoperative lifespan of NSCLC patients by improving immune function and anti-tumor angiogenesis.
You can read the full article at https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11655-007-9002-6.
Liu, T., Zuo, L., Guo, D., Chai, X., Xu, J., Cui, Z., Wang, Z., & Hou, C. (2019). Ginsenoside Rg3 regulates DNA damage in non-small cell lung cancer cells by activating VRK1/P53BP1 pathway. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie, 120, 109483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109483.
Ginsenoside Rg3 regulates DNA damage in non-small cell lung cancer cells by activating VRK1/P53BP1 pathway
Lung cancer is a prominent cause of cancer-related fatalities, and Ginsenoside Rg3, a primary component of Ginseng, has demonstrated potential in treating non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) by enhancing chemotherapy efficiency and reducing its adverse effects. This study aimed to investigate Rg3’s impact on DNA repair and the VRK1/P53BP1 signaling pathway. Rg3 treatment reduced lung cancer incidence and invasion in a urethane-induced mouse model. Cell survival assays and single-cell gel electrophoresis revealed Rg3’s protective effects against DNA damage and inhibition of tumor cell proliferation. Rg3 also upregulated VRK1 expression, with immunofluorescence assays demonstrating increased P53BP1 and VRK1 protein levels and translocation. This study highlights Rg3’s role in lung cancer by regulating VRK1 signaling and suggests potential therapeutic targets for lung cancer prevention and treatment.
You can read the full article at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0753332219328628?via%3Dihub.
Song, J. H., Eum, D. Y., Park, S. Y., Jin, Y. H., Shim, J. W., Park, S. J., Kim, M. Y., Park, S. J., Heo, K., & Choi, Y. J. (2020). Inhibitory effect of ginsenoside Rg3 on cancer stemness and mesenchymal transition in breast cancer via regulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. PloS one, 15(10), e0240533. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240533.
Inhibitory effect of ginsenoside Rg3 on cancer stemness and mesenchymal transition in breast cancer via regulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells
Ginsenoside Rg3 (Rg3) has been studied in several cancer models and is suggested to act through various pharmacological effects. We investigated the anticancer properties of Rg3 through myeloid-derived suppressor cell (MDSC) modulation in FM3A mouse mammary carcinoma cells. The effects of Rg3 on MDSCs and consequent changes in cancer stem-like cells (CSCs) and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) were evaluated by diverse methods. MDSCs promoted cancer by enhancing breast cancer stemness and promoting EMT. Rg3 at a dose without obvious cytotoxicity downregulated MDSCs and repressed MDSC-induced cancer stemness and EMT. Mechanistic investigations suggested that these inhibitory effects of Rg3 on MDSCs and corresponding cancer progression depend upon suppression of the STAT3-dependent pathway, tumor-derived cytokines, and the NOTCH signaling pathway. In a mouse model, MDSCs accelerated tumor progression, and Rg3 delayed tumor growth, which is consistent with the results of in vitro experiments. These results indicated that Rg3 could effectively inhibit the progression of breast cancer. The anticancer effect of Rg3 might be partially due to its downregulation of MDSCs and consequent repression of cancer stemness and EMT in breast cancer. Hence, we suggest the regulation of MDSCs through Rg3 treatment as an effective therapeutic strategy for breast cancer patients.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7580975/.
Kim, B. M., Kim, D. H., Park, J. H., Na, H. K., & Surh, Y. J. (2013). Ginsenoside Rg3 Induces Apoptosis of Human Breast Cancer (MDA-MB-231) Cells. Journal of cancer prevention, 18(2), 177–185. https://doi.org/10.15430/jcp.2013.18.2.177.
Ginsenoside Rg3 Induces Apoptosis of Human Breast Cancer (MDA-MB-231) Cells
Rg3, a major ginsenoside obtained from heat-processed ginseng, has previously demonstrated anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative properties. In this study, Rg3-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer (MDA-MB-231) cells and its underlying molecular mechanisms were investigated. Treatment with Rg3 resulted in increased apoptotic cell death, depolarization of mitochondrial membrane potential, release of cytochrome c from mitochondria, and the cleavage of caspase-3 and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase. These findings suggest that Rg3 induces apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 cells through the classical mitochondria-dependent caspase activation pathway, highlighting its potential as a breast cancer chemopreventive agent.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4189457/.
Song JH, Eum DY, Park SY, Jin YH, Shim JW, Park SJ, Kim MY, Park SJ, Heo K, Choi YJ. Inhibitory effect of ginsenoside Rg3 on cancer stemness and mesenchymal transition in breast cancer via regulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. PLoS One. 2020 Oct 22;15(10):e0240533. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240533. PMID: 33091036; PMCID: PMC7580975.
Inhibitory effect of ginsenoside Rg3 on cancer stemness and mesenchymal transition in breast cancer via regulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells
Ginsenoside Rg3 (Rg3) has shown promise in cancer research with various pharmacological effects. This study investigated Rg3’s anticancer properties by targeting myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) in FM3A mouse mammary carcinoma cells. MDSCs were found to promote cancer by enhancing breast cancer stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Rg3, at a non-toxic dose, reduced MDSCs and suppressed MDSC-induced cancer stemness and EMT. The underlying mechanisms involve the inhibition of the STAT3 pathway, tumor-derived cytokines, and NOTCH signaling. In a mouse model, MDSCs accelerated tumor progression, while Rg3 delayed tumor growth, consistent with in vitro findings. This suggests that Rg3 effectively inhibits breast cancer progression, partly through MDSC downregulation and subsequent suppression of cancer stemness and EMT, proposing MDSC regulation via Rg3 as a potential therapeutic strategy for breast cancer patients.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7580975/.
Xia, J., Ma, S., Zhu, X., Chen, C., Zhang, R., Cao, Z., Chen, X., Zhang, L., Zhu, Y., Zhang, S., Li, S., Gu, G., Wei, X., Yu, K., & Wang, J. (2022). Versatile ginsenoside Rg3 liposomes inhibit tumor metastasis by capturing circulating tumor cells and destroying metastatic niches. Science advances, 8(6), eabj1262. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abj1262.
Versatile ginsenoside Rg3 liposomes inhibit tumor metastasis by capturing circulating tumor cells and destroying metastatic niches
Overcoming limitations in capturing circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and regulating CTC-supportive metastatic niches (MNs) is crucial for effective treatment of metastatic breast cancers using liposomes. Traditional strategies like ligand modification and immune modulator co-encapsulation are inefficient. This study developed multifunctional Rg3 liposomes loaded with docetaxel (Rg3-Lp/DTX), where Rg3 was incorporated into the lipid bilayer, exposing its glycosyl on the liposome surface. This enhanced CTC capture efficiency through interaction with glucose transporter 1 (Glut1) overexpressed on CTCs. In the lungs with CTCs, Rg3 inhibited MN formation by reversing the immunosuppressive microenvironment. Rg3-Lp/DTX effectively inhibited metastasis by neutralizing CTCs (“seeds”) and inhibiting MNs (“soil”). This strategy holds promise for clinical translation, offering enhanced efficacy and a simplified preparation process for antimetastasis treatment.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8836824/.
Sun, M. Y., Song, Y. N., Zhang, M., Zhang, C. Y., Zhang, L. J., & Zhang, H. (2019). Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits the migration and invasion of liver cancer cells by increasing the protein expression of ARHGAP9. Oncology letters, 17(1), 965–973. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.9701.
Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits the migration and invasion of liver cancer cells by increasing the protein expression of ARHGAP9
Ginsenoside Rg3, a naturally occurring phytochemical, serves an important role in the prevention and treatment of cancer. In the present study, with the aim to reveal the molecular mechanism of Rg3 in liver cancer cell metastasis, the anti-migration and anti-invasion effects of Rg3 on liver cancer cells were investigated. It was demonstrated that Rg3 caused marked inhibition of cell migration and invasion of human liver cancer cells, HepG2 and MHCC-97L, in vitro, and the growth of HepG2 and MHCC-97L tumors in BABL/c nude mice. The protein expression of Rho GTPase activating protein 9 (ARHGAP9) was increased both in HepG2 and MHCC-97L cells. Following ARHGAP9 knockdown, the results of Transwell and tumorigenesis assays revealed that the anti-migration, anti-invasion and anti-tumor growth effects of Rg3 were impaired significantly. The increased expression of ARHGAP9 protein induced by Rg3 was remarkably suppressed. All results suggested that ARHGAP9 protein may be a vital regulator in the anti-metastatic role of Rg3. To the best of our knowledge, the present study is the first to report that Rg3 effectively suppressed the migration and invasion of liver cancer cells by upregulating the protein expression of ARHGAP9, indicating a novel natural therapeutic agent and a therapeutic target for the treatment of liver cancer.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6313058/.
Wu, W., Zhou, Q., Zhao, W., Gong, Y., Su, A., Liu, F., Liu, Y., Li, Z., & Zhu, J. (2018). Ginsenoside Rg3 Inhibition of Thyroid Cancer Metastasis Is Associated with Alternation of Actin Skeleton. Journal of medicinal food, 21(9), 849–857. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2017.4144.
Ginsenoside Rg3 Inhibition of Thyroid Cancer Metastasis Is Associated with Alternation of Actin Skeleton
Ginsenoside Rg3, a bioactive compound derived from Panax ginseng with a traditional Chinese medicine background, exhibits potent anti-tumor activity, particularly in suppressing metastasis. Thyroid cancer is associated with a high risk of metastasis, yet the mechanisms underlying Rg3’s anti-metastatic effects in thyroid cancer remain unexplored. This study demonstrated that Rg3 inhibited the growth and significantly curtailed metastasis of thyroid cancer both in vitro and in vivo. Specifically, Rg3 impeded migration and invasion in various papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) cell lines and reduced pulmonary metastasis in a mouse model using C643 cells. The study revealed that Rg3’s anti-metastatic mechanism in thyroid cancer involved the inhibition of actin cytoskeleton function, suppressing lamellipodia while inducing microspike formation by targeting Rho GTPase. Additionally, Rg3 reduced the expression of key proteins such as Rac-1, Cdc42, matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2), and MMP-9. It also showed promise in inhibiting lymph node metastasis in PTC and angiogenesis in anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC). These findings suggest that Rg3 could be a valuable agent for treating metastatic thyroid cancers.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/10.1089/jmf.2017.4144?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori%3Arid%3Acrossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub++0pubmed.
Kim, H. S., Lee, E. H., Ko, S. R., Choi, K. J., Park, J. H., & Im, D. S. (2004). Effects of ginsenosides Rg3 and Rh2 on the proliferation of prostate cancer cells. Archives of pharmacal research, 27(4), 429–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980085.
Effects of ginsenosides Rg3 and Rh2 on the proliferation of prostate cancer cells
Ginseng has demonstrated anti-cancer effects in various cancer models. This study aimed to identify active constituents of ginseng and their impact on the proliferation of prostate cancer cell lines, specifically LNCaP and PC3. The study assessed cell proliferation through [3H]thymidine incorporation, measured intracellular calcium concentration using a dual-wavelength spectrophotometer system, analyzed effects on mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases via Western blotting, and observed cell attachment and morphological changes under a microscope. Among the 11 tested ginsenosides, Rg3 and Rh2 exhibited inhibitory effects on prostate cancer cell proliferation. The EC50 values for Rg3 and Rh2 on PC3 cells were 8.4 microM and 5.5 microM, respectively, and 14.1 microM and 4.4 microM on LNCaP cells, respectively. Both ginsenosides induced cell detachment and differentially modulated the activities of three modules of MAP kinases in LNCaP and PC3 cells. These findings suggest that the inhibition of prostate cancer cell proliferation and induction of cell detachment by ginsenosides Rg3 and Rh2 may be associated with the modulation of three modules of MAP kinases.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15180309/.
Xu, T. M., Cui, M. H., Xin, Y., Gu, L. P., Jiang, X., Su, M. M., Wang, D. D., & Wang, W. J. (2008). Inhibitory effect of ginsenoside Rg3 on ovarian cancer metastasis. Chinese medical journal, 121(15), 1394–1397.
Inhibitory effect of ginsenoside Rg3 on ovarian cancer metastasis
Ginsenosides are primary components derived from ginseng, with ginsenoside Rg3 being a key constituent known for its ability to inhibit various tumor growth and metastasis processes. This study aimed to explore the impact of ginsenoside Rg3 on human ovarian cancer metastasis and the underlying mechanisms. Experimental models of ovarian cancer lung metastasis using SKOV-3 cells and assays of tumor-induced angiogenesis were employed to assess Rg3’s inhibitory effects. The results demonstrated that Rg3 reduced the number of tumor colonies in the lungs and inhibited vessel formation towards the tumor mass in experimental models. Additionally, Rg3 treatment led to a significant decrease in the invasive capacity of SKOV-3 cells and a reduction in the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9). In conclusion, ginsenoside Rg3 effectively suppresses ovarian cancer metastasis, partly through the inhibition of tumor-induced angiogenesis and the reduction of SKOV-3 cell invasiveness and MMP-9 expression.
You can read the full article at https://journals.lww.com/cmj/fulltext/2008/08010/inhibitory_effect_of_ginsenoside_rg3_on_ovarian.12.aspx.
Available at https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02386.
Available at https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/cpr.12696.
Park, M. W., Ha, J., & Chung, S. H. (2008). 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 enhances glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and activates AMPK. Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin, 31(4), 748–751. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.31.748.
20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 enhances glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and activates AMPK
While Panax ginseng has been traditionally used in Asian countries for its diverse pharmacological benefits, the exact active ingredient remained elusive. Preliminary studies indicated that protopanaxadiol ginsenosides possess insulin secretion-stimulating properties. Specifically, Rg3 demonstrated a concentration-dependent enhancement of insulin secretion in HIT-T15 cells, but this effect was significantly reduced in the presence of diazoxide (a K+ channel opener) or nifedipine (a Ca2+ channel blocker). Oral glucose tolerance tests in ICR mice further revealed that Rg3 effectively suppressed the post-administration increase in blood glucose levels by enhancing insulin secretion at the 30-minute mark. This action was likely associated with ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Moreover, the study compared the effects of different epimers of ginsenoside Rg3, showing that 20(S)-Rg3 significantly enhanced glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in C2C12 myotubes, whereas 20(R)-Rg3 had a lesser effect. These findings suggest that the two epimers of ginsenoside Rg3 exhibit distinct activities, with 20(S)-Rg3 showing greater potential as an anti-diabetic agent due to its stronger effects on insulin secretion and AMPK activation.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/bpb/31/4/31_4_748/_article.
Lee, O. H., Lee, H. H., Kim, J. H., & Lee, B. Y. (2011). Effect of ginsenosides Rg3 and Re on glucose transport in mature 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Phytotherapy research : PTR, 25(5), 768–773. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.3322.
Effect of ginsenosides Rg3 and Re on glucose transport in mature 3T3-L1 adipocytes
Ginsenosides, the active compounds in Panax ginseng, have exhibited various beneficial effects related to hyperglycemia, obesity, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. This study assessed the impact of ginsenosides Rg3 and Re on glucose uptake and the glucose transport system in mature 3T3-L1 cells. The results revealed that both Rg3 and Re, at concentrations of 1-10 µM, significantly increased glucose uptake by approximately 10% and 12%, respectively. Moreover, at 10 µM, these ginsenosides upregulated glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) mRNA expression by approximately 1.73- and 1.43-fold, respectively. Additional experiments demonstrated that Rg3 and Re stimulated insulin receptor substrate (IRS-1) mRNA expression and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-110α protein expression, both involved in the insulin signaling pathway. These findings suggest that Rg3 and Re may enhance glucose uptake through PI3K pathways involving IRS-1, making them potential candidates for effective antidiabetic and antihyperglycemic agents.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ptr.3322.
Kim, K. S., Jung Yang, H., Lee, I. S., Kim, K. H., Park, J., Jeong, H. S., Kim, Y., Seok Ahn, K., Na, Y. C., & Jang, H. J. (2015). The aglycone of ginsenoside Rg3 enables glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion in enteroendocrine cells and alleviates hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetic mice. Scientific reports, 5, 18325. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18325.
The aglycone of ginsenoside Rg3 enables glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion in enteroendocrine cells and alleviates hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetic mice
Ginsenosides can be categorized based on their aglycone backbone. We hypothesized that the sugar components linked to the dammarane structure enable ginsenosides to interact with the sweet taste receptors, triggering the secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in enteroendocrine L cells. Using human NCI-H716 enteroendocrine cells, we demonstrated that 15 ginsenosides stimulate GLP-1 secretion based on the position of their sugar components. By employing pharmacological methods, RNA interference, and Gαgust−/− mice, we clarified that Rg3, a ginsenoside metabolite resulting from steaming, exerts the most potent GLP-1 secretion effects through a sweet taste receptor-mediated signaling pathway. Rg3 also displayed anti-hyperglycemic effects in a type 2 diabetic mouse model by increasing plasma GLP-1 and insulin levels during oral glucose tolerance tests. This study uncovers a novel mechanism in which the sugar moieties of ginsenosides, particularly Rg3, stimulate GLP-1 secretion in enteroendocrine L cells via sweet taste receptor-mediated signaling, thereby offering potential anti-hyperglycemic benefits for type 2 diabetes.
You can read the full article at https://www.nature.com/articles/srep18325.
Wang, H., Wu, W., Wang, G., Xu, W., Zhang, F., Wu, B., & Tian, Y. (2019). Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg3 on lung injury in diabetic rats. Journal of cellular biochemistry, 120(3), 3323–3330. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27601.
Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg3 on lung injury in diabetic rats
Ginsenoside, a known treatment for diabetes, particularly ginsenoside Rg3, the primary active compound in ginseng, has been studied for its impact on lung tissue damage in diabetic rats. The study employed assays and analysis techniques to assess cell proliferation, apoptosis, and lung tissue health in response to Rg3 treatment. Results indicated that Rg3 had no significant effect on BEAS-2B cell proliferation or apoptosis. However, in diabetic rats, Rg3 effectively reduced inflammation, activated the PI3K and MAPK signaling pathways, and prevented lung tissue damage caused by hyperglycemia. These findings suggest that ginsenoside Rg3 holds promise as a potential therapeutic agent for diabetes treatment.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jcb.27601.
Zhou, T., Sun, L., Yang, S., Lv, Y., Cao, Y., Gang, X., & Wang, G. (2020). 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rg3 Protects Kidney from Diabetic Kidney Disease via Renal Inflammation Depression in Diabetic Rats. Journal of diabetes research, 2020, 7152176. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/7152176.
20(S)-Ginsenoside Rg3 Protects Kidney from Diabetic Kidney Disease via Renal Inflammation Depression in Diabetic Rats
20(S)-Ginsenoside Rg3 (20(S)-Rg3) has demonstrated its ability to induce apoptosis and exhibit anticancer and antidiabetic effects. To investigate its protective potential against diabetic kidney disease (DKD), diabetic rat models were created using high-sugar, high-fat diet and streptozotocin injection, and treated with 20(S)-Rg3 for 12 weeks. Three groups were studied: a control group, a diabetic group, and a 20(S)-Rg3 treatment group. Various biochemical markers, glomerular basement membrane, and mesangial matrix changes were assessed. TUNEL staining revealed reduced renal cell apoptosis, and immunohistochemical staining showed decreased expression of fibrosis and inflammation factors in the kidney tissues of the 20(S)-Rg3 treatment group. Furthermore, 20(S)-Rg3 lowered urine protein, fasting blood glucose, creatinine, total cholesterol, and triglyceride levels, pointing to its potential as a novel treatment for DKD by mitigating inflammation and preventing renal damage.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7106937/.
Kim, M., Ahn, B. Y., Lee, J. S., Chung, S. S., Lim, S., Park, S. G., Jung, H. S., Lee, H. K., & Park, K. S. (2009). The ginsenoside Rg3 has a stimulatory effect on insulin signaling in L6 myotubes. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 389(1), 70–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.08.088.
The ginsenoside Rg3 has a stimulatory effect on insulin signaling in L6 myotubes
Ginsenoside Rg3 is recognized for its protective effects against hyperglycemia, obesity, and diabetes in vivo. In this study, the impact of Rg3 on insulin signaling and glucose uptake in cultured L6 myotubes was investigated. Rg3 enhanced glucose uptake under both basal and insulin-stimulated conditions, concurrently stimulating the phosphorylation of IRS-1 and Akt. Notably, Rg3 significantly increased IRS-1 protein levels, while Akt levels remained unaffected. This regulation of IRS-1 expression occurred at the transcriptional level, along with an increase in GLUT4 mRNA levels. Moreover, treatment with ginsam, a compound primarily composed of Rg3, elevated IRS-1 protein levels in OLEFT rats. Importantly, Rg3’s effects on insulin signaling were independent of the AMPK pathway, collectively suggesting that Rg3 enhances insulin signaling and glucose uptake by primarily upregulating IRS-1 and GLUT4 expression.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0006-291X(09)01666-0.
Saba, E., Kim, S. H., Kim, S. D., Park, S. J., Kwak, D., Oh, J. H., Park, C. K., & Rhee, M. H. (2018). Alleviation of diabetic complications by ginsenoside Rg3-enriched red ginseng extract in western diet-fed LDL-/- mice. Journal of ginseng research, 42(3), 352–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2017.04.004.
Alleviation of diabetic complications by ginsenoside Rg3-enriched red ginseng extract in western diet-fed LDL-/- mice
In this study, we elucidated the specific mechanisms through which Rg3-enriched red ginseng extract (Rg3-RGE) effectively reduces glucose, triglyceride, and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels in LDL-/- mice. We observed significant reductions in aspartate aminotransferase/serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase, alanine aminotransferase/serum glutamate-pyruvate transaminase, and steatohepatitis, while Rg3-RGE also demonstrated the inhibition of atheroma formation.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6026365/.
Kim, S. S., Jang, H. J., Oh, M. Y., Eom, D. W., Kang, K. S., Kim, Y. J., Lee, J. H., Ham, J. Y., Choi, S. Y., Wee, Y. M., Kim, Y. H., & Han, D. J. (2014). Ginsenoside Rg3 enhances islet cell function and attenuates apoptosis in mouse islets. Transplantation proceedings, 46(4), 1150–1155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2013.12.028.
Ginsenoside Rg3 enhances islet cell function and attenuates apoptosis in mouse islets
In this study, we investigated the potential of preoperative administration of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 (Rg3), a key component of ginseng, to enhance islet cell function and reduce apoptosis before islet transplantation. Balb/c mice were divided into two groups based on Rg3 administration after islet isolation. Islet viability and function were assessed in vitro, along with responses to a cytokine cocktail. The results showed that Rg3-treated islets exhibited significantly improved glucose-induced insulin secretion, insulin content, and reduced apoptosis when exposed to cytokine-induced damage, compared to untreated islets. These findings suggest that preoperative Rg3 administration has the potential to enhance islet function and mitigate early inflammation post-transplantation, making it a promising approach in islet transplantation therapy.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0041134513014243?via%3Dihub.
Kim YJ, Park SM, Jung HS, Lee EJ, Kim TK, Kim TN, Kwon MJ, Lee SH, Rhee BD, Kim MK, Park JH. Ginsenoside Rg3 prevents INS-1 cell death from intermittent high glucose stress. Islets. 2016 Apr 18;8(3):57-64. doi: 10.1080/19382014.2016.1161874. PMID: 27246809; PMCID: PMC4987017.
Ginsenoside Rg3 prevents INS-1 cell death from intermittent high glucose stress
In this study, we explored the potential of ginsenoside Rg3 to protect pancreatic β cells under intermittent high glucose (IHG) conditions, which can be more detrimental to these cells compared to sustained high glucose. Using INS-1 cells, we found that Rg3 treatment increased cell viability and significantly reduced apoptosis induced by IHG. Rg3 also enhanced the secretion of insulin and promoted cell proliferation. Furthermore, Rg3 activated the ERK and p38 MAPK pathways, which were suppressed by IHG. These findings suggest that ginsenoside Rg3 has a protective effect on INS-1 cells against IHG-induced damage by reducing apoptosis and enhancing proliferation.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4987017/.
Kang, K. S., Yamabe, N., Kim, H. Y., Park, J. H., & Yokozawa, T. (2008). Therapeutic potential of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg(3) against streptozotocin-induced diabetic renal damage in rats. European journal of pharmacology, 591(1-3), 266–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.06.077.
Therapeutic potential of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg(3) against streptozotocin-induced diabetic renal damage in rats
In this study, we investigated the therapeutic potential of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 (20(S)-Rg3) from Panax ginseng in preventing streptozotocin-induced diabetic renal damage. Diabetic rats were orally administered 20(S)-Rg3 at doses of 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg body weight/day for fifteen days. The treatment significantly reduced physiological abnormalities such as increased water intake and urine volume in diabetic rats, and it also lowered elevated serum glucose, glycosylated protein, and thiobarbituric acid-reactive substance levels. Furthermore, the renal dysfunction in diabetic rats was ameliorated in a dose-dependent manner by 20(S)-Rg3 administration. These positive effects on diabetic renal damage were associated with the inhibition of NMDA receptor-mediated nitrosative stress.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0014299908006894?via%3Dihub.
Lee, J. B., Yoon, S. J., Lee, S. H., Lee, M. S., Jung, H., Kim, T. D., Yoon, S. R., Choi, I., Kim, I. S., Chung, S. W., Lee, H. G., Min, J. K., & Park, Y. J. (2017). Ginsenoside Rg3 ameliorated HFD-induced hepatic steatosis through downregulation of STAT5-PPARγ. The Journal of endocrinology, 235(3), 223–235. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-17-0233.
Ginsenoside Rg3 ameliorated HFD-induced hepatic steatosis through downregulation of STAT5-PPARγ
In this study, we investigated the therapeutic potential of ginsenoside Rg3, a major active component of ginseng, under pathological conditions both in vitro and in vivo. We examined its effects on glucose levels, insulin sensitivity, and lipogenesis in high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6 mice, as well as in 3T3-L1 pre-adipocyte cells. Ginsenoside Rg3 reduced the size of epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT), hepatic steatosis, and triglyceride levels in both eWAT and the liver. It also decreased lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 cells. The study revealed that Rg3 regulates PPAR gamma expression through STAT5 both in vitro and in vivo, resulting in the downregulation of lipid metabolism-related genes. These findings suggest that ginsenoside Rg3 has the potential to alleviate obesity-induced insulin resistance and lipotoxicity by acting through the STAT5-PPAR gamma pathway, representing a novel therapeutic approach for managing adipose tissue health in obesity.
You can read the full article at https://joe.bioscientifica.com/view/journals/joe/235/3/JOE-17-0233.xml.
Guo, M., Guo, G., Xiao, J., Sheng, X., Zhang, X., Tie, Y., Cheng, Y. K., & Ji, X. (2018). Ginsenoside Rg3 stereoisomers differentially inhibit vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration in diabetic atherosclerosis. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine, 22(6), 3202–3214. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13601.
Ginsenoside Rg3 stereoisomers differentially inhibit vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration in diabetic atherosclerosis
Ginsenoside 20(R/S)-Rg3, a natural ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ), has shown varying biological effects. This study aimed to understand the stereochemical selectivity of 20(R/S)-Rg3 and its potential differential impact on diabetic atherosclerosis. Molecular modeling was used to examine the binding of 20(R/S)-Rg3 stereoisomers to the PPARγ ligand-binding domain (PPARγ-LBD), revealing that 20(S)-Rg3 had stronger antiproliferative and antimigratory effects due to enhanced PPARγ activation. In a diabetic atherosclerosis mouse model, 20(S)-Rg3 significantly reduced plaque size by inhibiting smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration, leading to more stable plaques. These findings suggest that the (S)-isomer of 20(R/S)-Rg3 holds promise as a potential therapeutic drug for diabetic atherosclerosis.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5980205/.
Ni, J., Liu, Z., Jiang, M., Li, L., Deng, J., Wang, X., Su, J., Zhu, Y., He, F., Mao, J., Gao, X., & Fan, G. (2022). Ginsenoside Rg3 ameliorates myocardial glucose metabolism and insulin resistance via activating the AMPK signaling pathway. Journal of ginseng research, 46(2), 235–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2021.06.001.
Ginsenoside Rg3 ameliorates myocardial glucose metabolism and insulin resistance via activating the AMPK signaling pathway
Ginsenoside Rg3, a prominent compound in ginseng, was investigated for its protective effects on heart function in transverse aortic coarctation (TAC)-induced heart failure mice and the underlying mechanisms. Rg3 treatment improved heart function and preserved mitochondrial function in the TAC-induced heart failure models. Integrative analysis of proteomics and metabolomics data revealed that Rg3 regulated glycolysis and enhanced glucose uptake while improving myocardial insulin resistance. The molecular mechanism involved the activation of AMPK, insulin resistance mitigation, and glucose metabolism regulation. Rg3’s promotion of glucose uptake via AMPK activation was dependent on the insulin signaling pathway. These findings highlight Rg3’s role in modulating glucose metabolism and alleviating insulin resistance through AMPK activation.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9058838/
Liu, T., Peng, Y. F., Jia, C., Yang, B. H., Tao, X., Li, J., & Fang, X. (2015). Ginsenoside Rg3 improves erectile function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. The journal of sexual medicine, 12(3), 611–620. https://doi.org/10.1111/jsm.12779.
Ginsenoside Rg3 improves erectile function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
Ginsenoside Rg3, an active compound from Panax ginseng, was investigated for its protective effects on erectile function in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats. After diabetic induction, rats were treated with daily oral gavage of Rg3 at varying doses for 3 months. Erectile function was evaluated, and penile tissue analysis was performed. In the control group, erectile function was impaired, with notable changes in various molecular markers and oxidative stress levels. Rg3 treatment, especially at 100 mg/kg, significantly improved erectile function, reversed molecular changes, and reduced apoptosis in penile tissues. This suggests that oral Rg3 administration may preserve erectile function, prevent neural degeneration, and provide antioxidant effects in diabetic rats.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://academic.oup.com/jsm/article-abstract/12/3/611/6966903?redirectedFrom=fulltext&login=false.
Success Stories
 before after
before after
At the age of 60, I look and feel better than I ever have in my entire life! Switching my health program and hormone replacement therapy regimen over to Genemedics was one of the best decisions I’ve ever made in my life! Genemedics and Dr George have significantly improved my quality of life and also dramatically improved my overall health. I hav...
Nick Cassavetes ,60 yrs old
Movie Director (“The Notebook”, “John Q”, “Alpha Dog”), Actor and Writer
 Before After
Before After
I am now in my mid-sixties and feel better than I did in my 20’s. Many people have commented that I actually look 20 years younger since I started the program at Genemedics.
Calling Dr. George has proven to be one of the best decisions I have made in my life. Doctors and society convince us that developing various health issues and negative sy...
Pamela Hill ,66 yrs old
Call 800-277-4041 for a Free Consultation
- Usually takes 15-30 minutes
- Completely confidential
- No obligation to purchase anything
- We will discuss your symptoms along with your health and fitness goals
- Free post-consult access for any additional questions you may have
About
Genemedics® Health Institute is a global premier institute dedicated to revolutionizing health and medicine through healthy lifestyle education, guidance and accountability in harmony with functional medicine. Our physician-supervised health programs are personally customized to help you reach your health and fitness goals while looking and feeling better than ever.
Quick Links
Our Services
Our Locations
© Copyright Genemedics Health Institute. All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy.

