GENEMEDICS APP
GENEMEDICS NUTRITION
- 5-amino-1MQ
- Aminophylline
- Aniracetam
- ARA 290
- Argireline + Leuphasyl
- BPC-157
- Bremelanotide
- Cerebrolysin
- CJC-1295
- Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide
- Dihexa
- Elampretide (SS-31)
- Epithalon
- FG Loop Peptide (FGL)
- GHK-Cu
- Ginsenoside Rg3
- Glycyrrhetinic Acid
- Ipamorelin
- Kisspeptin
- KPV
- LL-37
- Melanotan 1
- Melanotan 2
- Mitochondrial ORF of the twelve S c (MOTS-c)
- MK-677 (IBUTAMOREN)
- Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+)
- Nicotinamide Riboside
- NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide)
- Noopept
- Pegylated Mechano Growth Factor
- Selank
- Semax
- Sermorelin
- SRT2104
- Tesamorelin
- Thymosin Alpha 1
- Thymosin Beta 4
- Tiger 17
- Valproic Acid
- Valproic acid + PTD-DBM
- Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide
- Zinc-Thymulin
- Overall Health Benefits of Epithalon
- Key Takeaways
- What is Epithalon?
- How Epithalon Works
- Chemical Structure of Epithalon
- Research on Epithalon
- Associated Side Effects of Epithalon
- More About Epithalamin
- Epithalamin Hormone
- What is Thymalin?
- Epitalon Dosage
- Epitalon Bodybuilding
- Epitalon Nasal Spray
- Epitalon 100mg
- Epitalon Sublingual
- Epithalon Peptide
- Epitalon Cancer
- Epithalon 10mg
- Epithalon 50mg
- Epithalon and Human Somatic Cells
- Epithalon and Pineal Gland
- Epithalon in Neuronal Differentiation Gene Expression
- FAQ
- Reference
Book a Free Consultation
Table of Contents
- Overall Health Benefits of Epithalon
- Key Takeaways
- What is Epithalon?
- How Epithalon Works
- Chemical Structure of Epithalon
- Research on Epithalon
- Associated Side Effects of Epithalon
- More About Epithalamin
- Epithalamin Hormone
- What is Thymalin?
- Epitalon Dosage
- Epitalon Bodybuilding
- Epitalon Nasal Spray
- Epitalon 100mg
- Epitalon Sublingual
- Epithalon Peptide
- Epitalon Cancer
- Epithalon 10mg
- Epithalon 50mg
- Epithalon and Human Somatic Cells
- Epithalon and Pineal Gland
- Epithalon in Neuronal Differentiation Gene Expression
- FAQ
- Reference
Overall Health Benefits of Epithalon
Epithalon benefits include its potential to regulate and extend telomere length, which is crucial for cellular longevity and aging processes. Studies suggest it may also enhance immune function and protect against age-related diseases.
- Reverses signs of aging [1-16]
- Prevents and treats cancer [12 ,17-22]
- Prevents cardiovascular disease [23-26]
- Boosts brain health [9, 27-29]
- Promotes quality sleep [5, 7, 30-32]
- Improves eye health [33-37]
- Boosts immunity [11, 38-41]
- Treats symptoms of diabetes [42-45]
Key Takeaways
- Telomere Regulation: Epithalon is known for its ability to regulate telomere length, which plays a critical role in cellular aging and longevity. It may potentially slow down the aging process at a cellular level.
- Immune Function: Research suggests that Epithalon may enhance immune function by promoting the production of thymic peptides, which are essential for immune system regulation and maintenance.
- Anti-Aging Potential: Epithalon is studied for its anti-aging effects, including its ability to improve skin health, cognitive function, and overall vitality in animal models.
- Safety Profile: Epithalon has shown a favorable safety profile in studies, with minimal reported side effects. However, more research is needed to fully understand its long-term effects in humans.
- Clinical Applications: While primarily investigated in animal studies, Epithalon holds promise for potential therapeutic applications in age-related diseases and as a preventive measure against age-related decline.
What is Epithalon?
Epithalon (Epitalon) is a synthetic peptide that reproduces the effects of epithalamin, a polypeptide found in the pineal gland. Its main role is to increase the natural production of telomeres. This allows DNA replication which is important for the formation and regeneration of cells.
How Epithalon Works
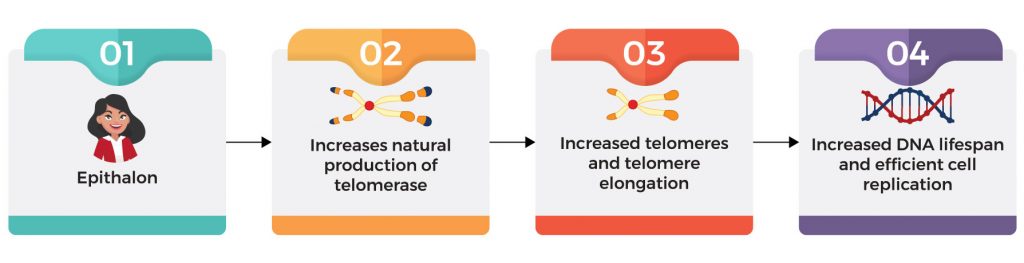
Epithalon increases the body’s natural production of telomerase, an enzyme that helps cells produce telomeres. These act as cap protectors of our DNA that become worn out during DNA replication. The replication process is essential for cell division during the growth or repair of damaged tissues in the body. [1] Similar to other bodily functions, telomeres length shortens as we age. [2] Progressive shortening of telomeres may affect the health and lifespan of an individual. The good news is that we can preserve these telomeres, and there are scientific discoveries that can elongate them. In theory, an elongated telomere can extend the lifespan of a copy of DNA and allows it to be more efficient with cell replication.
Chemical Structure of Epithalon
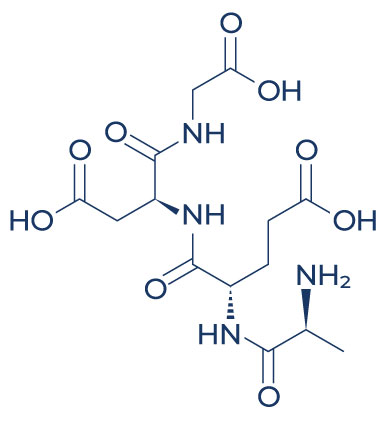
Research on Epithalon
A. Reverses Signs of Aging

Compelling evidence suggests that the administration of epithalon can increase life span and reverse signs of aging:
- It was concluded that the administration of the synthetic peptide epithalon might overcome genetic limitations and normalize body functions. [1]
- Epithalon has been found to fight signs of aging through its immunomodulatory properties, an integral function of the immune system. [2]
- A study was made on rats that showed epithalon administration resulted in increased melatonin production, improved immunological parameters, enhanced antioxidant defenses, and restoration of reproductive function. [3]
- Circadian rhythms of melatonin and cortisol production in old rhesus monkeys were also restored. [4]
- Epithalon was found to stimulate the release of melatonin in older people, which resulted in deeper sleep. [5]
- It also showed to improve complications with Alzheimer’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, jet lag, and nocturnal hypertension. [6]
- In aging monkeys, epithalon stimulated evening melatonin secretion and reestablished the circadian rhythm associated with cortisol release. [7]
- Common fruit flies exposed to epithalon during their developmental stage showed an increased lifespan from 11-16%. [8]
- Epithalon showed a substantial decrease in the extent of memory disorders in old rats. [9]
- There is a study done on chicks that suggest that epithalamin stimulates the growth of brain and spinal nerves. [10]
- Epithalon has been shown to promote an increase in lymphocytes from the thymus of elderly people, thus improving immune function in the specific age group. [11]
- In female mice, epithalon improved biomarkers of aging and life span. [12-13]
- Epithalon was found to have more benefits than melatonin as it also stimulates superoxide dismutase (SOD), ceruplasmin, and other antioxidant enzymes. [14]
- In male rats, epithalamin increased total antioxidant capacity by 36% and superoxide dismutase (a powerful antioxidant) by 19%. [15]
- Because of its ability to stimulate melatonin production and mechanisms related to melatonin, epithalon’s antioxidant benefits were also proven. [16]
B. Prevents and Treats Cancer

One of the diseases caused by oxidative stress or free radical damage is cancer. Studies suggest that epithalon’s ability to increase the body’s antioxidant capacity can also help with slowing cancer growth:
- In female spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR), epithalon injection inhibited the development of leukemia. [12]
- In female transgenic mice, epithalon administration inhibited the development of breast cancer. [17]
- In rats, continued epithalon administration throughout the experiment resulted in a significant inhibitory effect against colon cancer. [18]
- In mice, epithalon slowed and inhibited the spread of tumors. [19]
- When epithalon was given to rats with colon cancer, the peptide increased lymph flow (containing white blood cells) and apoptosis (programmed cell death), while it slowed cancer growth. [20]
- In mice with mammary tumors, epithalon significantly decreased the number of mice with multiple tumors and decreased the maximum size of tumors compared to control mice. [21]
- A study in mice found that treatment with epithalon reduced the number of mice with malignant tumors (cancerous tumors) and prevented cancer from metastasizing (moving to another location in the body) in all of the treated mice. [22]
C. Prevents Cardiovascular Disease
Studies suggest that epithalon can help reduce the risk of heart disease by improving various health parameters:
- A study showed that the ability of epithalon to preserve telomere length can help prevent cardiovascular disease. [23]
- In middle-aged and elderly women, epithalon supplementation greatly reduced the occurrence of ischemic heart disease. [24]
- A study showed that elder women treated with epithalamin had improved lipid metabolism, which eventually led to a reduction in arterial blood pressure. [25]
- Epithalamin was also shown to improve functional stability and quality of cardiovascular system regulation, showing improvement in blood flow of the patients treated. [26]
D. Boosts Brain Health
IMG
Evidence also suggests that epithalon is integral for maintaining normal cognitive function:
- Epithalon showed a substantial decrease in the extent of memory disorders in old rats. [9]
- A study showed that epithalon plays a role in the formation of new neurons in the brain. [27]
- In rats, intranasal administration of epithalon resulted in significant activation of neuronal activities. [28]
- In male rats, intranasal administration of epithalon triggered the neurons to become more active. [29]
E. Promotes Quality Sleep

Studies suggest that the ability of epithalon to regulate the production of the sleep hormone melatonin can help promote quality sleep:
- In older people, epithalon was found to stimulate the release of melatonin, which resulted in a deeper sleep. [5]
- In old female monkeys, epithalon greatly stimulated melatonin synthesis which is important for good sleep. [7]
- In old monkeys, epithalon treatment was found to be effective in treating age-related hormonal imbalance by inducing increased melatonin production. [30]
- In old monkeys and elderly people, epithalon induced safe regulation of blood melatonin levels without any side effects. [31]
- In healthy elderly patients, epithalon treatment initiated the melatonin-producing function of the pineal gland which in turn improved sleep quality. [32]
F. Improves Eye Health

Evidence also found that epithalon can help combat age-related decline in eye function and other eye disorders:
- In rats, epithalon administration resulted in improved retinal functionality and preserved its structure. [33-35]
- A study showed that epithalon stimulated the proliferation of retinal and pigmented epithelial cells. [36]
- In patients with degenerative retinal lesions, epithalon therapy produced beneficial effects on visual function. [37]
G. Boosts Immunity

Studies also show that epithalon has immune-boosting properties:
- In aging mice, it was shown that epithalon could increase T-cell production. [11]
- In chickens, epithalon injections effectively treated humoral immune deficiency. [38-39]
- In adult and old mice, epithalon administration increased the levels of immune system cells such as CD3+, CD4+CD8-, CD4-CD8+, and Mac-1(+)-. [40]
- In old rats, epithalon played a role in regulating immunity by maintaining optimal spleen function. [41]
H. Treats Symptoms of Diabetes

There are also studies supporting the beneficial effects of epithalon on blood sugar and diabetic symptoms:
- In female rhesus monkeys of various ages, epithalon restored the insulin level in response to a glucose load. [42]
- In non-insulin-dependent (Type 2) diabetics, epithalamin treatment improved carbohydrate metabolism and insulin sensitivity. [43]
- Diabetic retinopathy (eye complication of diabetes) was also improved with epithalon administration in diabetic patients. [44]
- In young and old rats, epithalon increased protein and sugar digestion. [45]
Associated Side Effects of Epithalon
Epithalon side effects are very uncommon. There have been some side effects associated with the use of this drug wherein the patient had one of the issues listed below at some point while being on epithalon. However, these side effects weren’t confirmed to be associated with the treatment and could have been a coincidence and not related to the use of epithalon. Despite this, it was listed as a side effect associated with epithalon even though these associated side effects are very uncommon.
Side effects associated with epithalon may include the following:
- Diarrhea
- Difficulty sleeping
- Fatigue
- Flu-like symptoms
- Headache
- Irregular heartbeat
- Joint pain
- Nausea
More About Epithalamin
Epithalamin, commonly known as Epithalon, is a synthetic peptide composed of four amino acids. It gained attention for its role in regulating telomere length, which are protective caps at the ends of chromosomes crucial for cellular stability and lifespan. Research suggests that epithalon peptide induces telomerase, responsible for maintaining telomere length and potentially slowing down cellular aging processes. This mechanism has spurred interest in Epithalon’s potential as an anti-aging agent and its ability to support longevity.
Studies on epithalon peptide-induced telomerase have primarily focused on its effects in animal models, where it has shown promise in extending lifespan, improving immune function, and enhancing overall health. Its ability to modulate the production of thymic peptides, which play a vital role in immune system function, further underscores its potential therapeutic benefits epithalon peptide induces telomerase. However, while early research is promising, more extensive clinical trials are needed to validate these findings and understand their efficacy and safety in humans.
In addition to its anti-aging properties, Epithalon is also being explored for its potential applications in age-related diseases and conditions associated with immune system decline. Its relatively low toxicity profile in studies suggests it may have favorable safety characteristics, but rigorous human trials will be essential to determine its broader medical applications and optimal dosage regimens, particularly concerning mitochondrial function.
Epithalamin Hormone
Epithalamin, also known as Epithalon, is a synthetic peptide designed to mimic the effects of the natural pineal hormone Epithalamin. It was originally isolated from the pineal gland, a small endocrine gland in the brain, and has since been studied for its potential anti-aging properties. Epithalamin is believed to influence the secretion of melatonin and regulate the body’s circadian rhythms, which play a crucial role in sleep-wake cycles and overall health, including preventing spontaneous tumors.
Research on Epithalamin has focused on its ability to regulate telomere length, which are protective caps at the ends of chromosomes that shorten with age and cellular division. By maintaining telomere length, Epithalamin may help delay cellular aging and promote longevity. Studies have also explored its impact on immune function, suggesting it may enhance the body’s immune response and potentially protect against age-related diseases.
While initial studies have shown promising results in animal models, including improved lifespan and enhanced antioxidant activity, more research is needed to determine the full extent of Epithalamin’s benefits and its safety and efficacy in humans. Clinical trials are ongoing to explore its potential therapeutic applications in age-related conditions and to better understand its mechanisms of action at a molecular level.
What is Thymalin?
Thymalin is a polypeptide extract derived from the thymus gland, known for its immunomodulatory effects in the human body. This compound has been extensively studied for its ability to enhance immune function by stimulating the production of T lymphocytes and other immune cells crucial for immune system regulation. Thymalin’s role in supporting thymus gland function is particularly significant as the thymus plays a vital role in T cell maturation and immune response coordination in the human body.
Research on Thymalin has explored its potential therapeutic applications in various conditions where immune function may be compromised, such as autoimmune diseases and infections. Studies suggest that Thymalin may help restore immune balance and improve resistance to infections, though clinical evidence remains limited. Its mechanism of action involves interacting with immune cell receptors to regulate their activity and enhance immune surveillance.
In clinical practice, Thymalin has been used experimentally to address immune deficiencies and support overall immune health. However, more robust clinical trials are needed to establish its efficacy, optimal dosage, and long-term safety profile in treating immune-related disorders effectively, particularly concerning lipid oxidation.
Epitalon Dosage
Determining the appropriate Epitalon dosage is crucial for maximizing its potential benefits while minimizing any potential risks, including lipid oxidation. Typically, Epitalon is administered via subcutaneous injection, with recommended dosages varying based on individual needs and health goals. For general anti-aging purposes and health maintenance, a common dosage regimen involves daily injections over a course of 10-20 days, followed by a pause of 10-20 days before repeating the cycle. This intermittent dosing pattern is believed to help regulate telomere length effectively, potentially reducing lipid oxidation and promoting overall cellular health.
Clinical studies and anecdotal reports suggest that optimal dosages can range from 5 to 10 mg per day, depending on factors such as age, health status, and desired outcomes. It’s essential for individuals considering Epitalon to consult with a healthcare provider experienced in peptide therapies to tailor the dosage to their specific needs and monitor for any potential side effects, particularly those involving T cells. Adherence to recommended dosing schedules and guidance can contribute to maximizing Epitalon’s potential anti-aging benefits while promoting overall health and longevity.
Epitalon Bodybuilding
Pitalon, also known as Epithalon, has gained attention in bodybuilding circles for its potential benefits beyond traditional performance enhancements. While primarily studied for its anti-aging properties and immune system benefits, some bodybuilders speculate that Epithalon could support muscle recovery and overall physical resilience. The peptide’s purported ability to regulate telomere length, essential for cellular aging, has led to speculation about its potential role in promoting longevity research within muscle cells and enhancing overall endurance.
However, concrete evidence supporting Epithalon’s direct benefits for bodybuilding remains limited. Most research focuses on its effects on aging and immune function rather than its impact on muscle growth or performance enhancement specifically. As a result, its use in bodybuilding is often speculative and not supported by robust clinical trials or empirical evidence demonstrating significant positive clinical effect muscle-building effects.
In bodybuilding communities, Epithalon is sometimes considered aspartic acid as part of a broader regimen aimed at promoting overall health and longevity, which could indirectly benefit athletic performance and recovery. Nonetheless, individuals considering Epithalon for bodybuilding purposes should approach its use cautiously and consult healthcare professionals due to the current lack of conclusive evidence regarding its specific effects on muscle development and athletic performance.
Epitalon Nasal Spray
Epitalon nasal spray has emerged as a novel method for delivering Epitalon, also known as Epithalon, a synthetic peptide with potential anti-aging properties. This formulation offers a convenient and efficient way to administer Epitalon, aiming to enhance absorption through the nasal mucosa. By bypassing the digestive system, nasal spray delivery may improve bioavailability and ensure quicker onset of action compared to oral administration, particularly beneficial for immune systems seeking rapid response and absorption efficiency.
Research into Epitalon nasal spray is still evolving, focusing on its efficacy and safety profile in humans. Preliminary studies suggest that nasal administration of Epitalon may offer benefits such as telomere length regulation and potential anti-aging effects in cell culture. This delivery method appeals to individuals seeking non-invasive approaches to promote cellular longevity and mitigate age-related decline, highlighting a possible epigenetic mechanism for enhancing therapeutic outcomes in cell culture.
While promising, the clinical application of Epitalon nasal spray remains in early stages, requiring further research and clinical trials to establish optimal dosing, long-term effects, and broader therapeutic applications. Continued investigation into its mechanisms and outcomes will be crucial in determining its potential as a practical anti-aging intervention, including exploring possible epigenetic mechanisms that may underlie its effects.
Epitalon 100mg
Epitalon 100mg refers to a specific dosage of Epitalon, a synthetic tetrapeptide known for its potential anti-aging effects. This peptide is studied for its ability to regulate telomere length, which are protective caps at the ends of chromosomes that shorten with age and cellular division. By promoting telomere elongation, Epitalon is theorized to support cellular longevity and delay the onset of age-related changes.
Research on Epitalon 100mg primarily focuses on its effects in animal models, where it has shown promising results in extending lifespan, improving immune function, and enhancing overall healthspan. Studies suggest that Epitalon may also contribute to improved sleep quality and cognitive function, which are often affected by aging processes and circadian rhythm disturbances.
While Epitalon 100mg shows potential benefits in preclinical research, its clinical applications in humans, including cancer prevention, are still under investigation. The dosage and frequency of administration may vary depending on specific research protocols and goals, with ongoing studies aiming to elucidate its safety, optimal dosage, and potential therapeutic applications in aging-related conditions, including cancer prevention.
Epitalon Sublingual
Epitalon, when administered sublingually, involves placing the peptide solution under the tongue for absorption directly into the bloodstream. This method bypasses the digestive system, allowing for faster and more efficient delivery of the peptide into the body and enhancing protein synthesis. Sublingual administration is favored by some due to its potential to achieve higher bioavailability and quicker onset of effects compared to oral ingestion.
Studies and user reports suggest that sublingual Epitalon may offer benefits related to anti-aging and overall health. By influencing telomere length and telomerase activity, Epitalon aims to counteract cellular aging processes, potentially promoting longevity and supporting various physiological functions, including protein synthesis. However, the extent of these effects and their long-term implications require further research and clinical validation.
While sublingual administration of peptide bioregulators like Epitalon may enhance its efficacy, determining the optimal dosage and frequency is crucial for maximizing benefits and minimizing potential side effects. As with any peptide therapy, consulting healthcare professionals knowledgeable about peptide administration and personalized health needs is advisable for safe and effective use.
Epithalon Peptide
Epithalon, a synthetic peptide comprising four amino acids, has gained attention among peptide bioregulators for its potential anti-aging properties. It works by stimulating the production of telomerase, an enzyme that can lengthen telomeres—the protective caps at the ends of chromosomes. Telomeres naturally shorten with age, and maintaining their length is associated with cellular longevity and improved healthspan. Epithalon’s ability to regulate telomere dynamics has led to interest in its role in slowing down the aging process and potentially extending lifespan.
Research on Epithalon has primarily focused on its effects in animal models, where it has shown promising results in improving immune function, enhancing antioxidant activity, and protecting against age-related diseases, including skin fibroblast functions. These findings suggest that Epithalon may not only have cosmetic benefits, such as improving skin elasticity and reducing wrinkles but also therapeutic potential in combating age-related declines in overall health, including skin fibroblast functions.
While early studies are encouraging, further research is needed to validate Epithalon’s efficacy and safety in humans, particularly in aging skin fibroblasts. Clinical trials are ongoing to explore its potential benefits in human aging, including its effects on longevity, cognitive function, and disease prevention, especially in aging skin fibroblasts. Understanding Epithalon’s mechanisms and optimizing its applications could pave the way for new approaches in anti-aging medicine and longevity research, focusing on aging skin fibroblasts.
Epitalon Cancer
Epitalon, a synthetic peptide, has drawn interest in cancer research primarily due to its potential role in telomere length regulation. Telomeres, protective caps at the ends of chromosomes, shorten with each cell division and are implicated in cellular aging and cancer progression. Epitalon’s ability to potentially extend telomeres has led to speculation about its impact on cancer cells, as cancer cells often exhibit telomere maintenance mechanisms to sustain their replicative capacity, including stem cells.
Research on Epitalon’s effects on cancer is still in its infancy, with most studies limited to animal models and cell cultures. Some studies have explored its influence on telomerase activity, an enzyme that maintains telomere length and is upregulated in many cancer cells, including stem cells. However, conclusive evidence of Epitalon’s direct impact on cancer initiation, progression, or treatment efficacy remains elusive and requires further rigorous investigation involving stem cells.
While Epitalon shows promise in telomere biology and its potential implications for cancer therapy, caution is warranted. The complex interplay between telomeres, telomerase, and cancer requires a thorough understanding before Epitalon can be considered a viable treatment option for stem cells. Ethical considerations and clinical trials are essential to determine its safety, efficacy, and appropriate use in oncology involving stem cells.
Epithalon 10mg
Epithalon 10mg refers to a synthetic peptide known for its potential anti-aging properties and regulatory effects on telomere length. This dosage represents a typical amount administered in research and clinical studies aimed at exploring its biological effects. Epithalon is believed to work by stimulating the production of telomerase, an enzyme that helps maintain telomeres—the protective caps at the end of chromosomes. By supporting telomere length, Epithalon may slow down cellular aging processes and contribute to overall longevity.
Studies on stem cells Epithalon 10mg have shown promising results in animal models, demonstrating improvements in immune function, skin health, and cognitive abilities. Research suggests that Epithalon’s ability to enhance thymic peptide production may also play a role in boosting immune response and supporting overall vitality. While human trials are limited, ongoing research aims to further validate these findings and explore Epithalon’s potential applications in age-related diseases and longevity interventions.
The administration of Epithalon 10mg typically involves subcutaneous or intramuscular injections, and dosing regimens may vary depending on specific research protocols or clinical recommendations. As with any peptide-based treatment, consulting healthcare professionals knowledgeable in peptide therapy is essential to ensure safe and effective use of Epithalon 10mg for potential anti-aging benefits.
Epithalon 50mg
Epithalon 50mg refers to a specific dosage form of Epithalon, a synthetic peptide studied for its anti-aging properties. This dosage is typically used in research settings to explore its effects on cellular aging, telomere length regulation, and overall health span extension. Epithalon itself is a tetrapeptide composed of four amino acids, known for its ability to stimulate the production of telomerase, an enzyme that protects and extends telomeres—the protective caps at the ends of chromosomes that shorten with age.
Studies on stem cells Epithalon 50mg have shown promising results in animal models, indicating potential benefits in extending lifespan, improving immune function, and enhancing overall vitality. Research focuses on its role in reversing age-related changes at the cellular level, which includes boosting antioxidant defenses and promoting more efficient DNA repair mechanisms. While these findings are encouraging, further clinical trials are necessary to validate its efficacy and safety for human use, particularly regarding long-term effects and optimal dosing strategies.
Epithalon and Human Somatic Cells
Epithalon, also known as Epitalon, is a synthetic peptide known for its potential anti-aging effects and ability to influence telomerase activity in human somatic cells. Telomerase is an enzyme that adds protective caps called telomeres to the ends of chromosomes, which are essential for maintaining genomic stability during cell division. In human somatic cells, telomerase activity typically decreases with age, leading to telomere shortening and cellular aging. Epithalon has been shown to activate telomerase, thereby promoting telomere elongation and enhancing the lifespan and function of somatic cells.
The implications of Epithalon’s effects on human somatic cells are significant for regenerative medicine and aging research. By promoting telomere maintenance, Epithalon may help in reducing the signs of aging and delaying age-related diseases. This peptide’s ability to support cellular health and longevity opens up possibilities for its use in therapies aimed at tissue regeneration and repair. Moreover, its potential to improve overall cellular function makes Epithalon a promising candidate for interventions designed to enhance the quality of life and longevity in humans.
Epithalon and Pineal Gland
Epithalon is a synthetic tetrapeptide that has garnered attention for its potential anti-aging and health-promoting properties. One of its primary mechanisms of action is through its interaction with the pineal gland, a small endocrine gland located in the brain. The pineal gland is responsible for producing melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles and has various roles in maintaining circadian rhythms. Epithalon has been shown to stimulate the production of melatonin, thereby improving sleep quality and regulating biological rhythms, which are crucial for overall health and longevity.
Additionally, Epithalon has been associated with the promotion of telomerase activity, an enzyme that helps maintain the length of telomeres, which are protective caps on the ends of chromosomes. This action is significant because telomere shortening is a key factor in cellular aging. By supporting telomere maintenance, Epithalon may help slow down the aging process and improve cellular health. The pineal gland’s role in regulating aging and biological rhythms makes Epithalon’s interaction with this gland particularly important, offering potential benefits in anti-aging therapies and enhancing overall well-being.
Epithalon in Neuronal Differentiation Gene Expression
Epithalon, also known as Epitalon or Epithalamin, is a synthetic tetrapeptide that has garnered attention for its potential role in modulating gene expression, particularly in neuronal differentiation. This peptide has been found to activate telomerase, an enzyme that elongates telomeres and promotes cellular longevity. In the context of neuronal differentiation, Epithalon can influence the expression of genes responsible for the growth and development of neurons. By affecting these genes, Epithalon supports the maturation of neural stem cells into fully differentiated neurons, which is crucial for maintaining and repairing neural networks in the brain.
Furthermore, Epithalon’s impact on gene expression extends to the regulation of neurotrophic factors, which are vital for neuron survival, growth, and differentiation. Studies have shown that Epithalon can upregulate the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and other growth factors, enhancing the brain’s ability to generate and maintain healthy neurons. This modulation of gene expression not only supports neurogenesis but also protects against neurodegenerative processes, making Epithalon a promising therapeutic agent for conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and other neurological disorders that benefit from enhanced neuronal differentiation and regeneration.
FAQ
What is the function of Epitalon?
Epitalon functions by stimulating the production of telomerase, which in turn helps to maintain and potentially lengthen telomeres—protective caps on the ends of chromosomes. This activity is crucial for cellular longevity and may contribute to anti-aging effects.
What is the effect of Epitalon on telomerase activity, telomere elongation, and proliferative potential in human somatic cells?
Epitalon has been shown in studies to increase telomerase activity in human cells, which supports telomere elongation. This process is associated with enhanced proliferative potential in human cells and may contribute to slowing down cellular aging.
What is the molecular weight of Epitalon?
The molecular weight of epithalon peptide Epitalon is 390.43 g/mol.
What is the function of Epithalamin?
Epithalamin is another name for Epitalon. Its function is primarily focused on regulating telomere length and potentially slowing down the aging process at the cellular level.
What does the Epithalamin hormone do in humans?
Epithalamin (Epitalon) stimulates the pineal gland to produce melatonin, which regulates sleep-wake cycles and has antioxidant properties that may contribute to overall health and longevity. The activity of epithalon peptide in enhancing melatonin production underscores its potential role in supporting circadian rhythms and combating oxidative stress, crucial for maintaining optimal health and longevity.
What is the function of melatonin in the pineal gland?
Melatonin in the pineal gland regulates circadian rhythms, enhances sleep quality, and acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative stress, which are all crucial aspects studied in aging and longevity research.
Is melatonin a peptide?
No, melatonin is not a peptide. It is a hormone derived from serotonin and synthesized in the pineal gland. This hormone peptide promotes overcoming sleep disorders and regulates the body’s circadian rhythms, including the sleep-wake cycle.
What are the primary benefits of using Epithalon for anti-aging?
The primary benefits of Epithalon include potential longevity by maintaining telomere length, improving immune function, and supporting overall vitality peptide promotes overcoming.
How does Epithalon improve overall health?
Epithalon may improve overall health by enhancing immune response, promoting better sleep quality, and potentially reducing oxidative stress associated with aging, including the mitigation of reactive oxygen species.
Are there any potential risks associated with long-term use of Epithalon?
Long-term risks of Epithalon are not well-documented, but concerns may include unknown effects on hormone levels and cellular processes, particularly regarding the management of reactive oxygen species.
What specific effects does Epithalon have on the immune system?
Epithalon is believed to enhance immune function by supporting peptide regulation of thymus function and promoting the production of immune cells.
How quickly can one expect to see results after starting Epithalon?
Results from Epithalon may vary, but some users report improvements in energy levels and sleep quality within weeks to months of consistent use, as it stimulates gene expression, potentially lengthening telomeres and contributing to overall cellular health.
Is Epithalon effective in improving cognitive function?
While primarily studied for its effects on aging and immune function, Epithalon may have indirect benefits on cognitive function through its overall support of cellular health, including potential interactions with stem cell therapy.
Can Epithalon help with weight management?
There is no conclusive evidence that Epithalon directly affects weight management in vivo experiments. Its primary focus is on anti-aging and immune enhancement, rather than on influencing weight management through stem cell therapy in vivo experiments.
What are the guidelines for dosing and administration of Epithalon?
Dosing guidelines for Epithalon are not standardized. It is typically administered via injections or nasal sprays, and dosages can vary based on individual needs and practitioner recommendations, promoting the generation of new cells and normalizing T cell function.
How does Epithalon influence sleep quality and circadian rhythms?
Epithalon may influence sleep quality and circadian rhythms by supporting melatonin production, which regulates these biological processes, thus acting as a potent antioxidant and normalizing T cell function, promoting the generation of new cells and supporting overall immune health.
Is Epithalon therapy suitable for everyone?
Epithalon therapy is not universally recommended and should be approached with caution, particularly by consulting healthcare professionals due to its experimental nature and potential long-term effects involving mesenchymal stem cells.
What clinical trials have been conducted on Epithalon?
Clinical trials on Epithalon are limited, and most research has been conducted in animal models, including studies where female rats exposed to Epithalon showed promising results. More studies are needed to validate its efficacy and safety in humans, especially involving mesenchymal stem cells and female rats exposed to Epithalon.
How does Epithalon compare with other anti-aging treatments?
Epithalon’s focus on telomere regulation sets it apart from traditional anti-aging treatments, which often target skin health or hormone replacement. Its potential to influence telomere length may have implications for cellular rejuvenation and the longevity of human stem cells. This unique mechanism of action, where peptide induces telomerase activity, underscores its relevance in research aimed at extending cellular lifespan and enhancing the vitality of human stem cells in various therapeutic contexts.
Can Epithalon reverse the effects of aging?
While it may slow down cellular aging processes, Epithalon’s ability to reverse aging effects in humans remains speculative and requires further research. Research suggests that peptide induces telomerase activity, which could potentially contribute to its anti-aging effects.
What mechanisms does Epithalon use to enhance skin health?
Epithalon may indirectly enhance skin health through its antioxidant properties and support of overall cellular function, but direct effects on skin are not well-documented.
Are there any drug interactions with Epithalon that users should be aware of?
Specific drug interactions with Epithalon are not well-established, but caution should be exercised when combining it with other medications without professional advice, especially in molecular biology and human somatic cell contexts.
Is Epithalon legally available for use in all countries?
The legal status of Epithalon varies by country. In many places, it is primarily available for research purposes and may require special permits or prescriptions. Availability as oral supplements is limited due to regulatory restrictions in several regions.
How should Epithalon be stored to maintain its efficacy?
Epithalon should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from light and moisture, to maintain its stability and effectiveness, especially for research involving human somatic cell studies. When considering its application in clinical trials, proper storage is crucial to ensure the integrity of oral supplements and their potential benefits for participants.
What age group benefits most from using Epithalon?
Epithalon’s potential benefits may be more relevant for older adults experiencing an age-related decline in immune function, overall vitality, and neuronal differentiation gene expression. Research into its applications in regenerative medicine continues to explore these promising avenues, aiming to harness its effects for rejuvenation and longevity in clinical settings.
Are there any immediate side effects after administering Epithalon?
Immediate side effects of Epithalon are typically mild and may include injection site reactions or mild discomfort, while long-term effects and their potential impact on neuronal differentiation gene expression and division limit are less understood.
What research is currently underway regarding new applications of Epithalon?
Current research on Epithalon explores its potential applications in treating age-related diseases, enhancing immune response in human somatic cells, and understanding its broader effects on longevity and health span, including its impact on telomere length and division limit.
Reference
Vladimir Kh Khavinson. Peptides and Ageing. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 2002;23 Suppl 3:11-144.
Peptides and Ageing
In Vladimir Kh. Khavinson’s article titled “Peptides and Ageing,” published in Neuro Endocrinol Lett in 2002, the author delves into the connection between peptides and the aging process. The article explores how peptides, small protein fragments, may impact various aspects of aging, including cellular repair, tissue regeneration, and hormonal regulation. Khavinson likely discusses the potential therapeutic applications of peptides in addressing age-related health concerns and promoting longevity.
M Karasek. Melatonin, human aging, and age-related diseases. Exp Gerontol Nov-Dec 2004;39(11-12):1723-9. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2004.04.012.
Melatonin, human aging, and age-related diseases
In this article by M. Karasek, titled “Melatonin, Human Aging, and Age-Related Diseases,” the author explores the role of melatonin in the aging process and its potential relevance to age-related diseases. Melatonin is a hormone that regulates the sleep-wake cycle and has antioxidant properties. The article likely discusses how melatonin levels change with age, how it affects circadian rhythms, and how it may impact various age-related conditions. It may also touch upon the potential therapeutic applications of melatonin in mitigating age-related diseases and promoting healthy aging.
Full article on https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0531556504002876
V M Dilman, V N Anisimov, M N Ostroumova, V K Khavinson, V G Morozov. Increase in lifespan of rats following polypeptide pineal extract treatment. Exp Pathol (Jena) 1979;17(9):539-45. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4908(79)80076-9.
Increase in lifespan of rats following polypeptide pineal extract treatment
In this 1979 study by V. M. Dilman, V. N. Anisimov, M. N. Ostroumova, V. K. Khavinson, and V. G. Morozov, titled “Increase in Lifespan of Rats Following Polypeptide Pineal Extract Treatment,” the authors investigate the effects of polypeptide pineal extract on the lifespan of rats. The pineal gland produces melatonin, a hormone known for its role in regulating sleep-wake cycles and its antioxidant properties. The study likely explores how this extract, possibly containing melatonin or related peptides, impacts the aging process in rats, particularly in terms of longevity. The authors may discuss the potential mechanisms behind the observed effects and their implications for understanding age-related changes.
Full article on https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0014490879800769
I F Labunets, G M Butenko, L V Magdich, O V Korkushko, V Kh Khavinson, V B Shatilo. Effect of epithalamin on circadian relationship between the endocrine function of the thymus and melatonin-producing function of the pineal gland in elderly people. Bull Exp Biol Med 2004 May;137(5):507-9. doi: 10.1023/b:bebm.0000038165.09563.b5.
Effect of epithalamin on circadian relationship between the endocrine function of the thymus and melatonin-producing function of the pineal gland in elderly people
In this 2004 study by I. F. Labunets, G. M. Butenko, L. V. Magdich, O. V. Korkushko, V. Kh. Khavinson, and V. B. Shatilo, titled “Effect of Epithalamin on Circadian Relationship Between the Endocrine Function of the Thymus and Melatonin-Producing Function of the Pineal Gland in Elderly People,” the authors investigate the impact of Epithalamin, a peptide preparation, on the circadian rhythms of the thymus and pineal gland functions in elderly individuals. The study likely explores how Epithalamin affects the interaction between these endocrine functions and their potential relevance to the aging process. The authors may discuss the implications of their findings for understanding age-related changes and the potential therapeutic applications of Epithalamin in improving the health of elderly individuals.
Full article on https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/B:BEBM.0000038165.09563.b5
S V Trofimova, N S Linkova, A A Klimenko, T V Kvetnaia, V Kh Khavinson. Pineamin increased pineal melatonin synthesis in elderly people. Adv Gerontol 2017;30(3):422-426.
Pineamin increased pineal melatonin synthesis in elderly people
In this 2017 study by S. V. Trofimova, N. S. Linkova, A. A. Klimenko, T. V. Kvetnaia, and V. Kh. Khavinson, the authors investigate the effects of Pineamin on pineal melatonin synthesis in elderly individuals. Pineamin is likely a substance or preparation that is studied for its potential impact on melatonin production in the pineal gland, which plays a crucial role in regulating sleep-wake cycles and circadian rhythms. The study likely explores how Pineamin supplementation affects melatonin levels in elderly people and its potential implications for improving sleep patterns and overall health in this age group.
Full article on https://europepmc.org/article/med/28849889
Available from https://nccih.nih.gov/health/melatonin#hed3
V Khavinson,, N Goncharova, B Lapin. Synthetic tetrapeptide epitalon restores disturbed neuroendocrine regulation in senescent monkeys. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 2001 Aug;22(4):251-4.
Synthetic tetrapeptide epitalon restores disturbed neuroendocrine regulation in senescent monkeys
In this 2001 study by V. Khavinson, N. Goncharova, and B. Lapin, titled “Synthetic Tetrapeptide Epitalon Restores Disturbed Neuroendocrine Regulation in Senescent Monkeys,” the authors investigate the effects of the synthetic tetrapeptide Epitalon on the neuroendocrine regulation in aging monkeys. Epitalon is likely a synthetic peptide that has been studied for its potential to restore normal neuroendocrine function in aging individuals. The study probably explores how Epitalon supplementation affects neuroendocrine pathways in senescent monkeys and its potential implications for improving age-related neuroendocrine dysregulation.
Full article on https://khavinson.info/downloads/2001-Khavinson_Goncharova.pdf
V K Khavinson, D M Izmaylov, L K Obukhova, V V Effect of epitalon on the lifespan increase in Drosophila melanogaster. Mech Ageing Dev 2000 Dec 1;120(1-3):141-9.
Effect of epitalon on the lifespan increase in Drosophila melanogaster
In this 2000 study by V. K. Khavinson, D. M. Izmaylov, L. K. Obukhova, and V. V., the authors investigate the impact of Epitalon on the lifespan of Drosophila melanogaster, a common model organism in aging research. Epitalon is likely a substance or preparation that has been studied for its potential to extend the lifespan of these fruit flies. The study probably explores the mechanisms through which Epitalon affects the aging process and its potential implications for longevity.
Full article on https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0047637400002177
I A Vinogradova. Comparative study of the effects of melatonin and epitalon on the protracted memory under the shuttle labyrinth test conditions in rats in the course of aging. Eksp Klin Farmakol Nov-Dec 2006;69(6):13-6.
Comparative study of the effects of melatonin and epitalon on the protracted memory under the shuttle labyrinth test conditions in rats in the course of aging
In this 2006 study by I. A. Vinogradova, the author conducts a comparative investigation to assess the effects of melatonin and Epitalon on protracted memory using the shuttle labyrinth test in aging rats. The study likely examines how both melatonin and Epitalon influence memory function as rats age and may explore their potential as interventions to improve cognitive performance in aging animals. The research may provide insights into the cognitive benefits of these substances and their relevance to aging-related memory decline.
Full article on https://europepmc.org/article/med/17209456
N I Chalisova, V K Khavinson. Studies of cytokines in nerve tissue cultures. NeurosciBehavPhysiol May-Jun 2000;30(3):261-5. doi: 10.1007/BF02471779.
Studies of cytokines in nerve tissue cultures
In this 2000 study by N. I. Chalisova and V. K. Khavinson, titled “Studies of Cytokines in Nerve Tissue Cultures,” the authors investigate the presence and behavior of cytokines in nerve tissue cultures. Cytokines are signaling molecules that play essential roles in regulating the immune system and inflammatory responses. The study likely explores the interaction between cytokines and nerve tissue in a cultured environment, shedding light on the potential role of cytokines in neural physiology or neuroinflammation.
Full article on https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF02471779
N S Lin’kova, B I Kuznik, V Kh Khavinson. Peptide Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly and interferon gamma: their role in immune response during aging. Adv Gerontol 2012;25(3):478-82.
Peptide Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly and interferon gamma: their role in immune response during aging
In this 2012 study by N. S. Lin’kova, B. I. Kuznik, and V. Kh. Khavinson, the authors explore the roles of the peptide Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly and interferon gamma in the immune response during the aging process. The study likely investigates how these substances influence the immune system as individuals age, potentially shedding light on their roles in immunosenescence (age-related changes in the immune system). The research may provide insights into mechanisms that impact immune function in older individuals and offer potential avenues for addressing age-related immune challenges.
Full article on https://europepmc.org/article/med/23289226
Anisimov VN, Khavinson VKh, Popovich IG, Zabezhinski MA, Alimova IN, Rosenfeld SV, Zavarzina NY, Semenchenko AV, Yashin AI. Effect of Epitalon on biomarkers of aging, life span and spontaneous tumor incidence in female Swiss-derived SHR mice. Biogerontology. 2003;4(4):193-202. doi: 10.1023/a:1025114230714. PMID: 14501183.
Effect of Epitalon on biomarkers of aging, life span and spontaneous tumor incidence in female Swiss-derived SHR mice
In this 2003 study by Anisimov VN, Khavinson VKh, Popovich IG, Zabezhinski MA, Alimova IN, Rosenfeld SV, Zavarzina NY, Semenchenko AV, and Yashin AI, the authors investigate the effects of Epitalon on various biomarkers of aging, lifespan, and spontaneous tumor incidence in female Swiss-derived SHR mice. Epitalon is likely a substance or preparation that is studied for its potential impact on aging-related markers, longevity, and the development of spontaneous tumors in these mice. The research may provide insights into the potential anti-aging and anti-cancer properties of Epitalon.
Full article on https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/A:1025114230714
Anisimov VN, Khavinson VKh, Alimova IN, Semchenko AV, Yashin AI. Epithalon decelerates aging and suppresses development of breast adenocarcinomas in transgenic her-2/neu mice. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2002 Aug;134(2):187-90. doi: 10.1023/a:1021104819170. PMID: 12459848.
Epithalon decelerates aging and suppresses development of breast adenocarcinomas in transgenic her-2/neu mice
In this 2002 study by Anisimov VN, Khavinson VKh, Alimova IN, Semchenko AV, and Yashin AI, the authors investigate the effects of Epithalon on aging and the development of breast adenocarcinomas in transgenic HER-2/Neu mice. Epithalon is likely a substance or preparation studied for its potential to slow down the aging process and inhibit the formation of breast adenocarcinomas in these genetically modified mice. The study may provide insights into the anti-aging and anti-cancer properties of Epithalon.
Full article on https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/A:1021104819170
Syed Saqib Ali, Haseeb Ahsan, Mohammad Khalid Zia, Tooba Siddiqui, Fahim Halim Khan. Understanding oxidants and antioxidants: Classical team with new players. J Food Biochem2020 Mar;44(3):e13145. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13145. Epub 2020 Jan 20.
Understanding oxidants and antioxidants: Classical team with new players
In this 2020 article by Syed Saqib Ali, Haseeb Ahsan, Mohammad Khalid Zia, Tooba Siddiqui, and Fahim Halim Khan, titled “Understanding Oxidants and Antioxidants: Classical Team with New Players,” the authors explore the concept of oxidants and antioxidants in the context of oxidative stress and health. The article likely discusses the roles of traditional antioxidants as well as newly identified molecules in combating oxidative stress and their implications for overall well-being. It may offer insights into the evolving understanding of the balance between oxidants and antioxidants in the human body.
Full article on https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jfbc.13145
L S Kozina, A V Arutjunyan, V KhKhavinson. Antioxidant properties of geroprotective peptides of the pineal gland. Arch GerontolGeriatr. 2007;44 Suppl 1:213-6. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2007.01.029.
Antioxidant properties of geroprotective peptides of the pineal gland
In this 2007 study by L. S. Kozina, A. V. Arutjunyan, and V. Kh. Khavinson, titled “Antioxidant Properties of Geroprotective Peptides of the Pineal Gland,” the authors investigate the antioxidant properties of geroprotective peptides derived from the pineal gland. These peptides are likely studied for their potential to combat oxidative stress, which is associated with aging and various age-related diseases. The research may provide insights into the role of these pineal gland peptides in protecting cells and tissues from oxidative damage and their potential as geroprotective agents.
Full article on https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167494307000301
V N Anisimov, A V Arutjunyan, V K Khavinson. Effects of pineal peptide preparation Epithalamin on free-radical processes in humans and animals. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 2001;22(1):9-18.
Effects of pineal peptide preparation Epithalamin on free-radical processes in humans and animals
In this 2001 study by V. N. Anisimov, A. V. Arutjunyan, and V. K. Khavinson, the authors investigate the effects of the pineal peptide preparation Epithalamin on free-radical processes in both humans and animals. The study likely explores how Epithalamin influences oxidative stress and free-radical activity, which are implicated in the aging process and various age-related conditions. The research may provide insights into the potential antioxidant properties of Epithalamin and its impact on overall health and aging-related processes.
Full article on https://khavinson.info/downloads/2001-Anisimov_Arutjunyan.pdf
Anisimov VN, Khavinson VK, Provinciali M, Alimova IN, Baturin DA, Popovich IG, Zabezhinski MA, Imyanitov EN, Mancini R, Franceschi C. Inhibitory effect of the peptide epitalon on the development of spontaneous mammary tumors in HER-2/neu transgenic mice. Int J Cancer. 2002 Sep 1;101(1):7-10. doi: 10.1002/ijc.10570. PMID: 12209581.
Inhibitory effect of the peptide epitalon on the development of spontaneous mammary tumors in HER‐2/neu transgenic mice
In this 2002 study by Anisimov VN, Khavinson VK, Provinciali M, Alimova IN, Baturin DA, Popovich IG, Zabezhinski MA, Imyanitov EN, Mancini R, and Franceschi C, the authors investigate the inhibitory effect of the peptide Epitalon on the development of spontaneous mammary tumors in HER-2/neu transgenic mice. Epitalon is likely a peptide that has been studied for its potential to suppress the growth of mammary tumors in genetically modified mice. The research may provide insights into the anti-cancer properties of Epitalon and its potential as a therapeutic agent for breast cancer prevention or treatment.
Full article on https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/ijc.10570
Kossoy G, Zandbank J, Tendler E, Anisimov V, Khavinson V, Popovich I, Zabezhinski M, Zusman I, Ben-Hur H. Epitalon and colon carcinogenesis in rats: proliferative activity and apoptosis in colon tumors and mucosa. Int J Mol Med. 2003 Oct;12(4):473-7. PMID: 12964022.
Epitalon and colon carcinogenesis in rats: proliferative activity and apoptosis in colon tumors and mucosa
In this 2003 study by Kossoy G, Zandbank J, Tendler E, Anisimov V, Khavinson V, Popovich I, Zabezhinski M, Zusman I, and Ben-Hur H, the authors investigate the effects of Epitalon on colon carcinogenesis in rats. The study likely assesses the impact of Epitalon on proliferative activity and apoptosis (cell death) in both colon tumors and the surrounding mucosa. The research may provide insights into the potential anti-cancer properties of Epitalon and its effects on the development and progression of colon tumors.
Full article on https://www.spandidos-publications.com/ijmm/12/4/473
Kossoy G, Anisimov VN, Ben-Hur H, Kossoy N, Zusman I. Effect of the synthetic pineal peptide epitalon on spontaneous carcinogenesis in female C3H/He mice. In Vivo. 2006 Mar-Apr;20(2):253-7. PMID: 16634527.
Effect of the synthetic pineal peptide epitalon on spontaneous carcinogenesis in female C3H/He mice
In this 2006 study by Kossoy G, Anisimov VN, Ben-Hur H, Kossoy N, and Zusman I, the authors investigate the effect of the synthetic pineal peptide Epitalon on spontaneous carcinogenesis in female C3H/He mice. The study likely assesses whether Epitalon has any impact on the development of spontaneous tumors in these mice. The research may provide insights into the potential anti-cancer properties of Epitalon and its role in preventing or inhibiting the formation of tumors.
Full article on https://iv.iiarjournals.org/content/20/2/253.short
E EVishnevskaia, I A Kosenko. Long-term results of comprehensive treatment for cervical cancer with poor prognosis. VoprOnkol1999;45(4):420-3.
Long-term results of comprehensive treatment for cervical cancer with poor prognosis.
In this 1999 study by E. E. Vishnevskaia and I. A. Kosenko, the authors present the long-term results of comprehensive treatment for cervical cancer cases with poor prognosis. The study likely explores the outcomes and effectiveness of various treatment approaches for cervical cancer patients who faced a challenging prognosis. It may provide insights into the strategies employed to improve the prognosis and long-term survival of these patients.
Vladimir N Anisimov. The role of pineal gland in breast cancer development. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol2003 Jun;46(3):221-34. doi: 10.1016/s1040-8428(03)00021-0.
The role of pineal gland in breast cancer development
In this 2003 article by Vladimir N. Anisimov, the author explores the role of the pineal gland in breast cancer development. The study likely investigates the potential influence of the pineal gland, which produces the hormone melatonin, on the development of breast cancer. It may discuss the mechanisms through which melatonin and the pineal gland impact breast cancer risk, progression, or prognosis. The research could provide insights into the relationship between the pineal gland, melatonin production, and breast cancer, offering valuable information for understanding and potentially managing this disease.
Full article on https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1040842803000210
Khavinson VKh, Morozov VG. Geroprotektornaia éffektivnost’ timalina i épitalamina [Geroprotective effect of thymalin and epithalamin]. Adv Gerontol. 2002;10:74-84. Russian. PMID: 12577695.
Zhan Y, Hägg S. Telomere length and cardiovascular disease risk. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2019 May;34(3):270-274. doi: 10.1097/HCO.0000000000000613. PMID: 30747731
Telomere length and cardiovascular disease risk
In this 2019 article by Zhan Y and Hägg S, the authors discuss the relationship between telomere length and the risk of cardiovascular disease. The study likely explores the potential link between telomere length, a marker of cellular aging, and the development of cardiovascular diseases. It may provide insights into how telomere length can be a predictive factor for cardiovascular disease risk and offer valuable information for understanding the underlying mechanisms involved in this relationship.
Full article on https://journals.lww.com/co-cardiology/FullText/2019/05000/Telomere_length_and_cardiovascular_disease_risk.6.aspx
G A Merkur’eva, G A Ryzhak. Effect of the pineal gland peptide preparation on the diurnal profile of arterial pressure in middle-aged and elderly women with ischemic heart disease and arterial hypertension. Adv Gerontol2008;21(1):132-42.
Effect of the pineal gland peptide preparation on the diurnal profile of arterial pressure in middle-aged and elderly women with ischemic heart disease and arterial hypertension
In this 2008 study by G. A. Merkur’eva and G. A. Ryzhak, the authors investigate the effect of a pineal gland peptide preparation on the diurnal profile of arterial pressure in middle-aged and elderly women who have ischemic heart disease and arterial hypertension. The study likely explores how this peptide preparation influences blood pressure fluctuations throughout the day and night in individuals with these cardiovascular conditions. The research may provide insights into the potential therapeutic applications of the pineal gland peptide in managing blood pressure in this specific patient population.
Full article on https://europepmc.org/article/med/18546838
V A Cherkashin, G F Semin, A AVeretenko. Optimization of cardiovascular function by peptide bio-regulators. Klin Med Mosk2002;80(5):30-4.
Optimization of cardiovascular function by peptide bio-regulators
In this 2002 article by V. A. Cherkashin, G. F. Semin, and A. A. Veretenko, the authors discuss the optimization of cardiovascular function through the use of peptide bio-regulators. The study likely explores the potential benefits of these bio-regulators in improving cardiovascular health. It may discuss how peptide-based approaches can be used to optimize the functioning of the cardiovascular system. The research may provide insights into novel therapeutic strategies for cardiovascular conditions. For more detailed information, you can access the full article through scientific journal databases or academic sources.
Full article on https://europepmc.org/article/med/12087883
O V Korkushko, V KhKhavinson, V B Shatilo, I A Antonyuk-Shcheglova. Geroprotective effect of epithalamine (pineal gland peptide preparation) in elderly subjects with accelerated aging. Bull Exp Biol Med 2006 Sep;142(3):356-9. doi: 10.1007/s10517-006-0365-z.
Geroprotective effect of epithalamine (pineal gland peptide preparation) in elderly subjects with accelerated aging
In this 2006 study by O. V. Korkushko, V. Kh. Khavinson, V. B. Shatilo, and I. A. Antonyuk-Shcheglova, the authors investigate the geroprotective effect of Epithalamine, a pineal gland peptide preparation, in elderly subjects with accelerated aging. The study likely explores how Epithalamine may have a protective effect against age-related processes in individuals experiencing accelerated aging. The research may provide insights into the potential benefits of Epithalamine in improving the health and well-being of elderly individuals with advanced age-related changes.
Full article on https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10517-006-0365-z
Khavinson V, Diomede F, Mironova E, et al. AEDG Peptide (Epitalon) Stimulates Gene Expression and Protein Synthesis during Neurogenesis: Possible Epigenetic Mechanism. Molecules. 2020;25(3):609. Published 2020 Jan 30. doi:10.3390/molecules25030609.
AEDG Peptide (Epitalon) Stimulates Gene Expression and Protein Synthesis during Neurogenesis: Possible Epigenetic Mechanism
In this 2020 study by Khavinson V, Diomede F, Mironova E, et al., the authors investigate the effects of the AEDG peptide, also known as Epitalon, on gene expression and protein synthesis during neurogenesis. The study likely explores how Epitalon influences the processes involved in the formation of new neurons and neural tissue. It may discuss the potential epigenetic mechanisms through which Epitalon exerts its effects. This research could provide insights into the role of Epitalon in promoting neurogenesis and its potential implications for neurological health.
Full article on https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/25/3/609
Sibarov DA, Vol’nova AB, Frolov DS, Nozdrachev AD. Effects of intranasal administration of epitalon on neuron activity in the rat neocortex. Neurosci Behav Physiol. 2007 Nov;37(9):889-93. doi: 10.1007/s11055-007-0095-3. PMID: 17955380.
Effects of intranasal administration of epitalon on neuron activity in the rat neocortex
In this 2007 study by Sibarov DA, Vol’nova AB, Frolov DS, and Nozdrachev AD, the authors investigate the effects of intranasal administration of Epitalon on neuron activity in the rat neocortex. The study likely explores how Epitalon, when administered intranasally, influences the activity of neurons in the neocortex of rats. The research may provide insights into the potential neurological effects of Epitalon and its impact on neural function.
Full article on https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11055-007-0095-3
Sibarov DA, Vol’nova AB, Frolov DS, Nosdrachev AD. [Intranasal epitalon infusion modulates neuronal activity in the rat neocortex]. Ross Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova. 2006 Aug;92(8):949-56. Russian. PMID: 17217245.
Intranasal epitalon infusion modulates neuronal activity in the rat neocortex
In this 2006 study conducted by Sibarov DA, Vol’nova AB, Frolov DS, and Nosdrachev AD, the authors investigate the impact of intranasal administration of Epitalon on neuronal activity in the rat neocortex. The study likely examines how Epitalon, when administered through the nasal route, influences the activity of neurons in the neocortex of rats. This research may provide insights into the potential neurological effects of Epitalon and its influence on neural function.
Full article on https://europepmc.org/article/med/17217245
Goncharova ND, Vengerin AA, Shmaliĭ AV, Khavinson VKh. Peptidnaia korrektsiia vozrastnykh narusheniĭ funktsii épifiza u obez’ian [Peptide correction of age-related pineal disturbances in monkeys]. Adv Gerontol. 2003;12:121-7. Russian. PMID: 14743609.
Peptide correction of age-related pineal disturbances in monkeys
In this study, conducted in 2003 by Goncharova ND, Vengerin AA, Shmaliĭ AV, and Khavinson VKh, the authors explore the use of peptide correction to address age-related disturbances in pineal gland function in monkeys. The research likely investigates how specific peptides are employed to correct disruptions in the pineal gland’s activity due to aging in primates. This study may offer insights into the potential therapeutic applications of peptides for addressing age-related changes in pineal gland function in primates, which could have implications for understanding aging-related processes.
Full article on https://europepmc.org/article/med/14743609
Korkushko OV, Lapin BA, Goncharova ND, Khavinson VKh, Shatilo VB, Vengerin AA, Antoniuk-Shcheglova IA, Magdich LV. [Normalizing effect of the pineal gland peptides on the daily melatonin rhythm in old monkeys and elderly people]. Adv Gerontol. 2007;20(1):74-85. Russian. PMID: 17969590.
Normalizing effect of the pineal gland peptides on the daily melatonin rhythm in old monkeys and elderly people
In this study, published in 2007 and authored by Korkushko OV, Lapin BA, Goncharova ND, Khavinson VKh, Shatilo VB, Vengerin AA, Antoniuk-Shcheglova IA, and Magdich LV, the authors investigate the normalizing effects of pineal gland peptides on the daily melatonin rhythm in old monkeys and elderly individuals. The research likely explores how these peptides can restore or regulate the daily fluctuations in melatonin production, which may be disrupted in aging individuals. This study may provide insights into the potential benefits of pineal gland peptides in addressing age-related changes in melatonin rhythms and their associated effects on health and well-being.
Full article on https://europepmc.org/article/med/17969590
Korkushko OV, Khavinson VKh, Shatilo VB, Magdich LV. Effect of peptide preparation epithalamin on circadian rhythm of epiphyseal melatonin-producing function in elderly people. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2004 Apr;137(4):389-91. doi: 10.1023/b:bebm.0000035139.31138.bf. PMID: 15452611.
Effect of peptide preparation epithalamin on circadian rhythm of epiphyseal melatonin-producing function in elderly people
In this 2004 study authored by Korkushko OV, Khavinson VKh, Shatilo VB, and Magdich LV, the authors investigate the effect of the peptide preparation Epithalamin on the circadian rhythm of melatonin production in the pineal gland (epiphyseal melatonin-producing function) in elderly individuals. The research likely explores how Epithalamin influences the daily fluctuations in melatonin production, which plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes. The study may provide insights into the potential benefits of Epithalamin in regulating melatonin rhythms in elderly individuals, which could have implications for aging-related health and sleep patterns.
Full article on https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/B:BEBM.0000035139.31138.bf
Khavinson V, Razumovsky M, Trofimova S, Grigorian R, Razumovskaya A. Pineal-regulating tetrapeptide epitalon improves eye retina condition in retinitis pigmentosa. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2002 Aug;23(4):365-8. PMID: 12195242.
Pineal-regulating tetrapeptide epitalon improves eye retina condition in retinitis pigmentosa
In this study published in 2002 by Khavinson V, Razumovsky M, Trofimova S, Grigorian R, and Razumovskaya A, the authors investigate the impact of the pineal-regulating tetrapeptide Epitalon on the condition of the eye retina in individuals with retinitis pigmentosa. The research likely explores how Epitalon influences the health and function of the retina, which is affected in this eye disorder. The study may provide insights into the potential therapeutic use of Epitalon in improving eye health and addressing the effects of retinitis pigmentosa.
Full article on https://khavinson.info/downloads/2002-Khavinson_Razumovsky-Pineal.pdf
Khavinson VKh, Razumovsky MI, Trofimova SV, Razumovskaya AM. Retinoprotective effect of Epithalon in campbell rats of various ages. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2003 May;135(5):495-8. doi: 10.1023/a:1024931812822. PMID: 12910293.
Retinoprotective effect of epithalon in Campbell rats of various ages
In this 2003 study by Khavinson VKh, Razumovsky MI, Trofimova SV, and Razumovskaya AM, the authors investigate the retinoprotective effect of Epithalon in Campbell rats of different ages. The study likely examines how Epithalon influences and protects the retina in rats of varying age groups. The research may provide insights into the potential benefits of Epithalon in preserving retinal health and protecting against age-related changes in the eye. This information could have implications for understanding retinal health and potential interventions for retinoprotection.
Full article on https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/A:1024931812822
Khavinson VKh, Razumovskii MI, Trofimova SV, Grigor’yan RA, Chaban TV, Oleinik TL, Razumovskaya AM. Effect of epithalon on age-specific changes in the retina in rats with hereditary pigmentary dystrophy. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2002 Jan;133(1):87-9. doi: 10.1023/a:1015125031829. PMID: 12170316.
Effect of epithalon on age-specific changes in the retina in rats with hereditary pigmentary dystrophy.
The study investigated the impact of Epithalon, a peptide bioregulator, on hereditary pigmentary retinal degeneration in Campbell rats. Beginning from birth, the administration of Epithalon preserved the morphological structure of the retina, enhanced its bioelectrical activity, and improved its functional performance.
Full article on https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12170316/
Khavinson VKh, Zemchikhina VN, Trofimova SV, Malinin VV. Effects of peptides on proliferative activity of retinal and pigmented epithelial cells. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2003 Jun;135(6):597-9. doi: 10.1023/a:1025497806636. PMID: 12937684.
Effects of peptides on proliferative activity of retinal and pigmented epithelial cells
The study conducted by Khavinson et al. in 2003 focused on assessing the impact of two peptides, Retinalamin (derived from the retina) and Epithalon (a synthetic peptide), on the growth of retinal and pigmented epithelial cells. The research demonstrated that both peptides, when applied in specific concentrations, could selectively stimulate the proliferation of these cell types in vitro, suggesting potential therapeutic applications for retinal and eye-related conditions.
Full article on https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12937684/
-
Kuznik BI, Pateiuk AV, Baranchugova LM, Rusaeva NS. [Effects of epithalon and cortagene on immunity and hemostasis in neonatallyhypophysectomized chicken and old birds]. Adv Gerontol. 2008;21(3):372-81. Russian. PMID: 19432169.
Effects of epithalon and cortagene on immunity and hemostasis in neonatallyhypophysectomized chicken and old birds
The study by Kuznik BI et al. examined the effects of Epithalon and Cortagene on immunity and hemostasis in neonatally hypophysectomized chickens and older birds. This research, published in “Advances in Gerontology,” investigates how these compounds influence the immune system and blood clotting processes in birds with removed pituitary glands at a young age and in aged birds, providing insights into potential applications for improving health and longevity.
Full article on https://europepmc.org/article/med/19432169
Kuznik BI, Pateiuk AV, KhavinsonVKh, Malinin VV. Vliianieépitalonanaimmunitetigemostaz u gipofizéktomocheskikhtsypliatistarykhkur [Effect of epitalon on the immunity and hemostasis in hypophysectomized chicken and old hens]. Adv Gerontol. 2004;13:90-3. Russian. PMID: 15490730.
Effect of epitalon on the immunity and hemostasis in hypophysectomized chicken and old hens
The study by Kuznik BI et al. explored the impact of Epitalon on immunity and hemostasis in both hypophysectomized chickens and older hens. Published in “Advances in Gerontology” in 2004, this research aimed to understand how Epitalon could influence immune response and blood clotting processes in animals with surgical removal of the pituitary gland and in aging poultry, highlighting the potential benefits of this peptide in managing health issues related to aging and hormonal deficits.
Full article on https://europepmc.org/article/med/15490730
Labunets IF, Butenko GM, KhavinsonVKh, Magdich LV, Dragunova VA, Pishel’ IN, Azarskova MV. Reguliruiushcheevliianiepeptidovépifizanarazvitie T-limfotsitov u mysheĭlinii CBA pristarenii: rol’ mikrookruzheniiaorganovimmunnoĭsistemyineĭroéndokrinnykhfaktorov [Regulating effect of pineal gland peptides on development of T-lymphocytes in CBA aging mice: role of microenvironment of immune system organs and neuroendocrine factors]. Adv Gerontol. 2003;12:111-20. Russian. PMID: 14743608.
Regulating effect of pineal gland peptides on development of T-lymphocytes in CBA aging mice: role of microenvironment of immune system organs and neuroendocrine factors
This study investigates the influence of pineal gland peptides on T-lymphocyte development in aging CBA mice, focusing on the immune system’s microenvironment and neuroendocrine factors. It suggests that these peptides could play a crucial role in modulating immune responses and potentially counteracting age-related declines in immune function, through their regulatory effects on both the immune system’s microenvironment and the neuroendocrine system. This research highlights the potential therapeutic uses of pineal gland peptides in enhancing immune function in the elderly.
Full article on https://europepmc.org/article/med/14743608
Khavinson VK, Konovalov SS, Yuzhakov VV, Popuchiev VV, Kvetnoi IM. Modulating effects of epithalamin and epithalon on the functional morphology of the spleen in old pinealectomized rats. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2001 Nov;132(5):1116-20. doi: 10.1023/a:1017989113287. PMID: 11865335.
Modulating effects of epithalamin and epithalon on the functional morphology of the spleen in old pinealectomized rats
The study by Khavinson VK et al. investigated the effects of epithalamin and epithalon on the functional morphology of the spleen in aged pinealectomized rats. It aimed to explore how these pineal gland peptides could modulate spleen function, potentially offering insights into their role in aging and immune system regulation.
Full article on https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/A:1017989113287
N D Goncharova, AAVengerin, V KhKhavinson, B A Lapin. Peptide correction of age-related hormonal dysfunction of the pancreas in monkeys. Bull Exp Biol Med 2004 Jul;138(1):80-3. doi: 10.1023/b:bebm.0000046946.25425.f5.
Peptide correction of age-related hormonal dysfunction of the pancreas in monkeys
The study by Goncharova et al. focused on the peptide correction of age-related hormonal dysfunction of the pancreas in monkeys. It aimed to explore the potential of specific peptides in addressing and potentially reversing age-associated decline in pancreatic function, a crucial aspect of endocrine health and metabolism. The research, published in the “Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine” in July 2004, offers valuable insights into the therapeutic possibilities for aging-related endocrine issues.
Full article on https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/B:BEBM.0000046946.25425.f5
S B Shustov, V KhKhavinson, T S Shutak, B V Romashevskiĭ. Epithalamin effects on carbohydrate metabolism and cardiovascular system in patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Klin Med Mosk1998;76(9):45-8.
Epithalamin effects on carbohydrate metabolism and cardiovascular system in patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus
The study by Shustov et al. investigated the impact of Epithalamin on carbohydrate metabolism and the cardiovascular system in patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). Published in “Klinicheskaya Meditsina” in 1998, it aimed to explore how this peptide could potentially improve metabolic control and cardiovascular health in NIDDM patients, suggesting a novel therapeutic approach for managing diabetes-related complications.
Full article on https://europepmc.org/article/med/9821374
Vladimir KhKhavinson, Vyacheslav G Morozov. Peptides of pineal gland and thymus prolong human life. NeuroEndocrinolLett Jun-Aug 2003;24(3-4):233-40.
Peptides of pineal gland and thymus prolong human life
The study by Khavinson and Morozov in 2003 discusses the effects of peptides derived from the pineal gland and thymus on extending human life. The research highlights the potential of these peptides to influence longevity by modulating various biological processes and systems that contribute to aging. This groundbreaking work provides insight into how specific peptides could play a role in promoting a longer, healthier life, presenting a significant advancement in the field of gerontology and bioregulation.
Full article on http://www.antiagingatlanta.com/epthalamin%20thymalin%20Khavinson.pdf
V KhKhavinson, V VMalinin, N M Timofeeva, V VEgorova, AANikitina. Effects of epithalon on activities gastrointestinal enzymes in young and old rats. Bull Exp Biol Med 2002 Mar;133(3):290-2. doi: 10.1023/a:1015807305791.
Effects of epithalon on activities gastrointestinal enzymes in young and old rats
The study by Khavinson et al. in 2002 investigated the impact of Epithalon on the activity of gastrointestinal enzymes in both young and old rats. This research aimed to understand how Epithalon affects digestive processes across different age groups, potentially offering insights into its role in aging and digestive health. The findings suggest that Epithalon could have significant effects on gastrointestinal enzyme activity, which might contribute to its reported benefits in aging and longevity.
Full article on https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/A:1015807305791
Other Peptides
Success Stories
 before after
before after
At the age of 60, I look and feel better than I ever have in my entire life! Switching my health program and hormone replacement therapy regimen over to Genemedics was one of the best decisions I’ve ever made in my life! Genemedics and Dr George have significantly improved my quality of life and also dramatically improved my overall health. I hav...
Nick Cassavetes ,60 yrs old
Movie Director (“The Notebook”, “John Q”, “Alpha Dog”), Actor and Writer
 Before After
Before After
I am now in my mid-sixties and feel better than I did in my 20’s. Many people have commented that I actually look 20 years younger since I started the program at Genemedics.
Calling Dr. George has proven to be one of the best decisions I have made in my life. Doctors and society convince us that developing various health issues and negative sy...
Pamela Hill ,66 yrs old
Call 800-277-4041 for a Free Consultation
- Usually takes 15-30 minutes
- Completely confidential
- No obligation to purchase anything
- We will discuss your symptoms along with your health and fitness goals
- Free post-consult access for any additional questions you may have
About
Genemedics® Health Institute is a global premier institute dedicated to revolutionizing health and medicine through healthy lifestyle education, guidance and accountability in harmony with functional medicine. Our physician-supervised health programs are personally customized to help you reach your health and fitness goals while looking and feeling better than ever.
Quick Links
Our Services
Our Locations
© Copyright Genemedics Health Institute. All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy.

